Industrial IoT Gateways
Industrial IoT gateways play a key role in an IoT infrastructure. At the edge, IIoT gateways collect, process, and transfer machine asset data, ensuring complete shop floor connectivity.
In the past, manufacturers have managed OT devices with SCADA systems and other locally-based solutions. Industrial gateways ensure OT device data is propagated in the cloud for use in production monitoring, condition monitoring, and shop floor visibility.
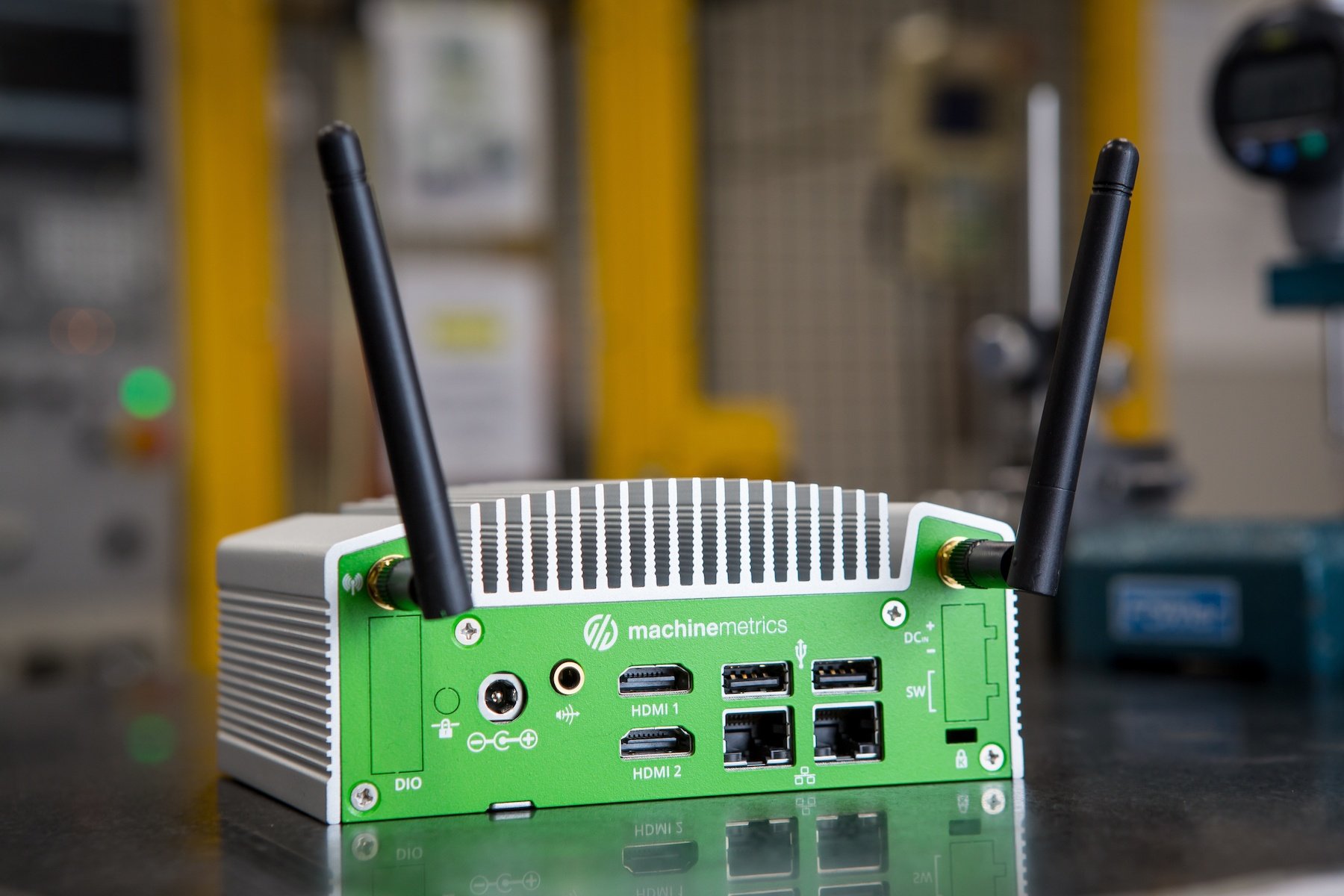

Industrial IoT Gateways: Unlocking Machine Data at the Edge
What is an Industrial IoT Gateway?
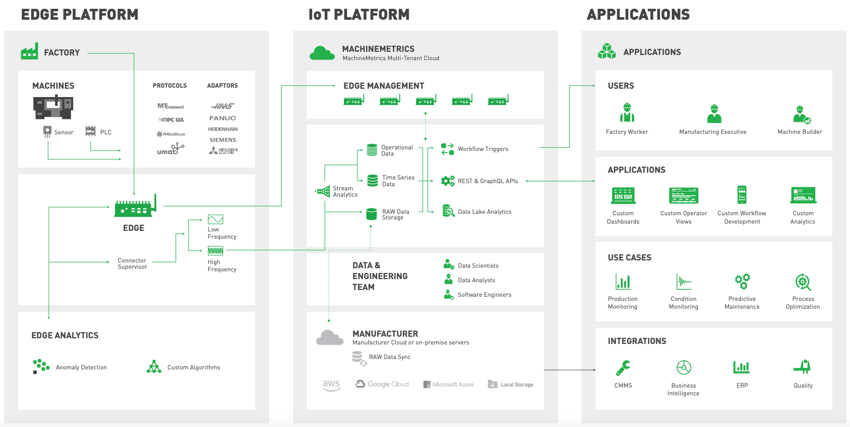
Industrial IoT Gateways bridge the gap between edge and cloud by collecting, processing, and standardizing data from sensors, I/O devices, and PLCs before sending it to the cloud.
Although IoT gateway devices are simply ruggedized computers, the software that lives on the devices is incredibly important. While edge devices have the ability to connect to a variety of manufacturing equipment, systems, and devices, it is necessary to transform the data into a standard model so that it can be ingested and used by other cloud-based systems. Effective IoT gateway software has the ability to connect and standardize data across all manufacturing equipment, from modern machine controls to legacy assets.
This capability transforms disparate data streams into a common model that end users can take action on immediately, whether it be in real-time production reports or in enabling automated notifications to support condition-based maintenance.
And as for why they are called IIoT Gateways, these computers act as a gate in the flow of information from the edge (devices and the local network) to the cloud.
What is the Main Function of IIoT Gateway Devices?
Industrial IoT Gateways enable a variety of functions to support greater efficiency in production environments by enabling connectivity among equipment, devices, and systems.
1. Connectivity, Data Collection, and Communication
At their core, Industrial IoT Gateways ensure connectivity among industry networks and legacy devices. With IoT Gateways, manufacturers can collect data to monitor performance across all equipment, including both modern machines and legacy assets. This data is also standardized into a common model for consumption in cloud-based systems as well as actionability at the edge. This enables interoperability among systems, machines, and devices to unlock efficient communication and automation.
Although the cloud is a valuable resource for storing and analyzing data, it requires network connectivity, increases latency over local computing, and requires reliance upon 3rd party security. With IIoT gateways, edge computing can be introduced to solve these problems, enabling unprecedented flexibility, reliability, and speed in a cost-controlled, security-conscious way.
2. Real-Time Processing and Decision Making
Real-time data collection and processing at the edge enabled autonomous and low-latency decision-making to happen. For example, a model can be built to predict the failure of equipment and this model can be deployed at the edge. When a given anomaly occurs, the edge device can immediately take action to prevent the impending failure from occurring.
This local data analysis functionality also reduces strain on the cloud. As data is processed at the edge, irrelevant information can be discarded to ensure only necessary information is sent to the cloud. This also acts as a fail-safe in the case of a lost connection between edge and cloud. In the case that it should happen, data can buffer at the edge to ensure that no information is lost until the cloud is available. This reliability is incredibly important for data-conscious end users
3. Condition Monitoring
Monitoring individual machines and entire plants manually is a major challenge for maintenance teams. In order to track equipment condition data, manufacturers can deploy IIoT gateways and additional devices (such as industrial sensors) to monitor the health of their assets and enable maintenance teams to make better decisions. This allows teams to move from calendar-based or reactive maintenance strategies to condition-based or even predictive maintenance.
4. Production Monitoring
Driving deeper operational visibility is a key component of making better, faster decisions to enable greater operational efficiency. With real-time, accurate data from equipment, manufacturers have immediate insight into production performance. This real-time visibility ensures problems can be tackled as soon as they appear. IIoT-enabled production monitoring also drives deeper insights to unlock hidden capacity, reduce waste, and optimize processes.

What is IoT Gateway Software?
IoT Gateway Software is deployed on gateways to ensure that data from the edge is standardized into a common model before being sent to the cloud. Effective software will have the ability to connect to and collect data from a multitude of devices.
This automated communication and data collection is capable due to the support of standard industrial communication protocols as well as machine control connectors. MachineMetrics offers Plug-and-Play universal data collection for PLC’s supporting open protocols including MTConnect, OPC-UA, and Modbus, as well as proprietary connectors to Fanuc, Mitsubishi, Citizen, Haas, Heidenhain, Siemens Sinumerik.
Depending on the software provider, additional capabilities may be available. For example, edge management allows users to monitor and control multiple edge devices. Further, IoT gateway software may provide the ability to deploy applications at the edge, such as predictive models.
How Do I Ensure Connectivity to All Equipment?
This is where a connectivity solution like MachineMetrics comes into play. MachineMetrics is an Industrial Data Platform that enables connectivity to any make and model of equipment, including legacy machines.
MachineMetrics is the leading platform to collect, monitor, analyze, and drive action with manufacturing equipment data. Our platform easily captures data from your manufacturing equipment and provides a complete toolkit to drive actionable insights for frontline workers and other factory floor systems that improve the efficiency and quality of production.
Whether the equipment is MTConnect native or not, you can easily connect and collect data across all your devices for complete operational visibility.
Want to see the platform in action? Book a Demo Today.



