What is Machine Condition Monitoring?
Machine condition monitoring is the ability to assess the health of a machine over a period of time. This can include things like its efficiency, since losses in efficiency may indicate an underlying issue. It also includes wear and tear on parts, performance indicators such as output of defective parts, usage statistics, and maintenance statistics.
Currently, a majority of the manufacturing industry operates with primitive maintenance strategies, often maintaining their equipment based on a reactive or calendar-based approach. The reasoning for this is that most manufacturers do not have the machine condition data to inform them of the operational health of their equipment.
As a result, their choices are to either maintain equipment on a schedule, or simply wait until it fails, neither being an efficient solution. This leads to a staggering amount of waste in the form of unnecessary maintenance expenses or large amounts of machine downtime.
Within this article, we will be exploring how condition monitoring solves this problem, providing manufacturers with the necessary, real-time machine condition data to make proactive decisions based on the current health of their equipment, even enabling them to introduce automation to the shop floor.
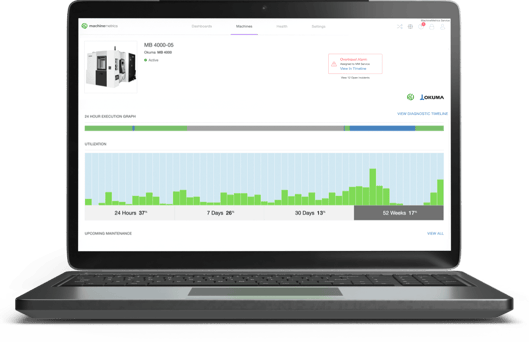
With condition monitoring, you have instant access to machine health and diagnostics for a real-time look at machine performance.
Difference Between Condition Monitoring and Machine Monitoring
Whereas condition monitoring provides diagnostics and helps determine the health of a machine based on various measured conditions, machine monitoring provides a simple machine status: Is the machine being productive or not?
Machine monitoring is certainly helpful for manufacturers as it provides machine uptime data so that operators and maintenance teams can react quickly to downtime events. However, this is inadequate for two primary reasons.
First off, it fails to provide the deeper machine analytics of condition monitoring in order to diagnose problems and adjust processes to optimize asset performance. Furthermore, simple machine downtime tracking forces manufacturers to engage in either costly preventative maintenance measures that are unnecessary, or rely on reactive maintenance, unable to truly understand the nature of the problem, but simply fixing it until it is bound to happen again.
Interestingly, over-maintenance (often a result of a calendar-based strategy) can be just as wasteful as unplanned downtime, as it is not only expensive but also time-consuming.
On the other hand, condition monitoring allows manufacturers to harness real-time conditions from their assets to monitor and optimize the maintenance and performance of their machines to ensure that they are not over-maintaining or suffering from unplanned downtime.
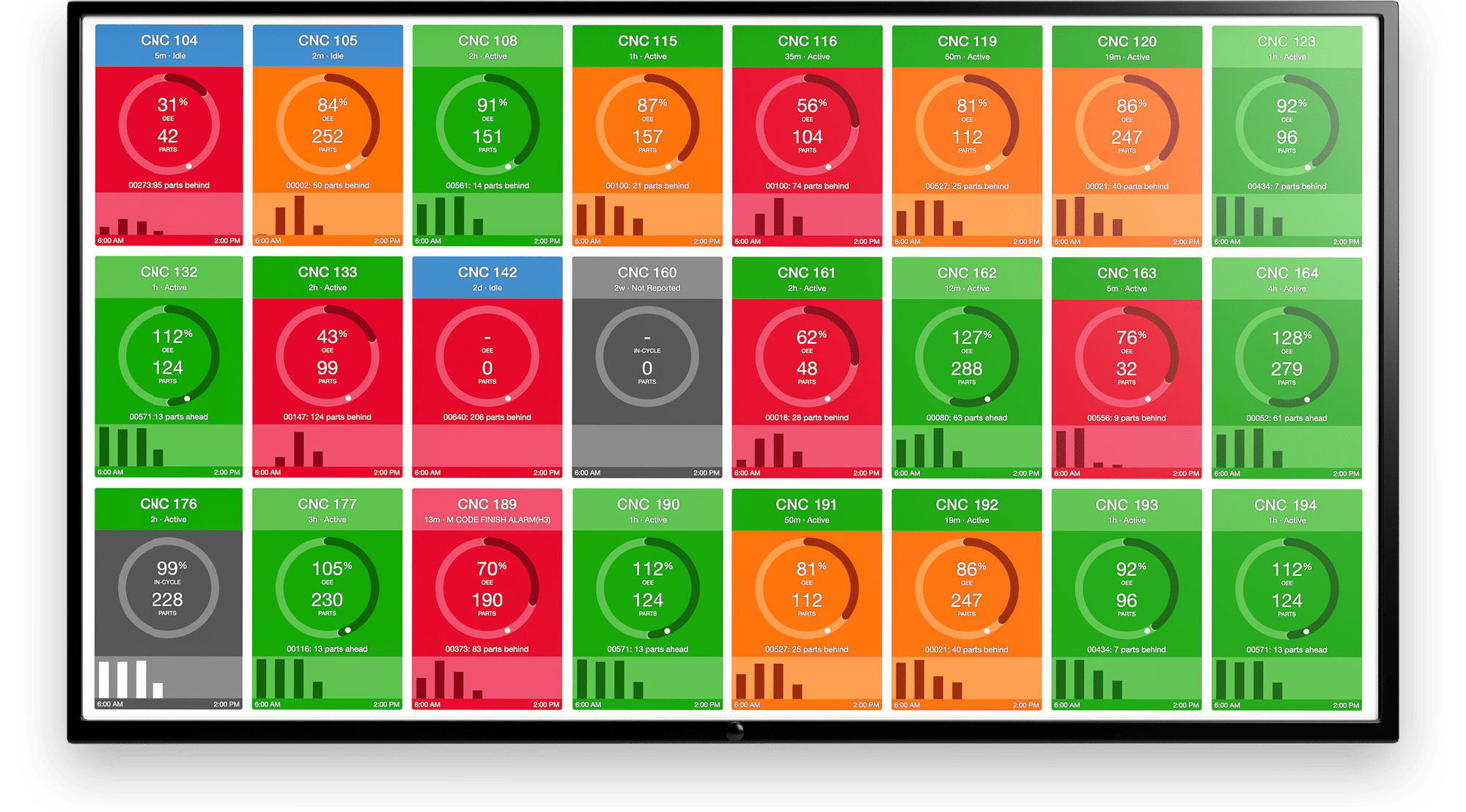
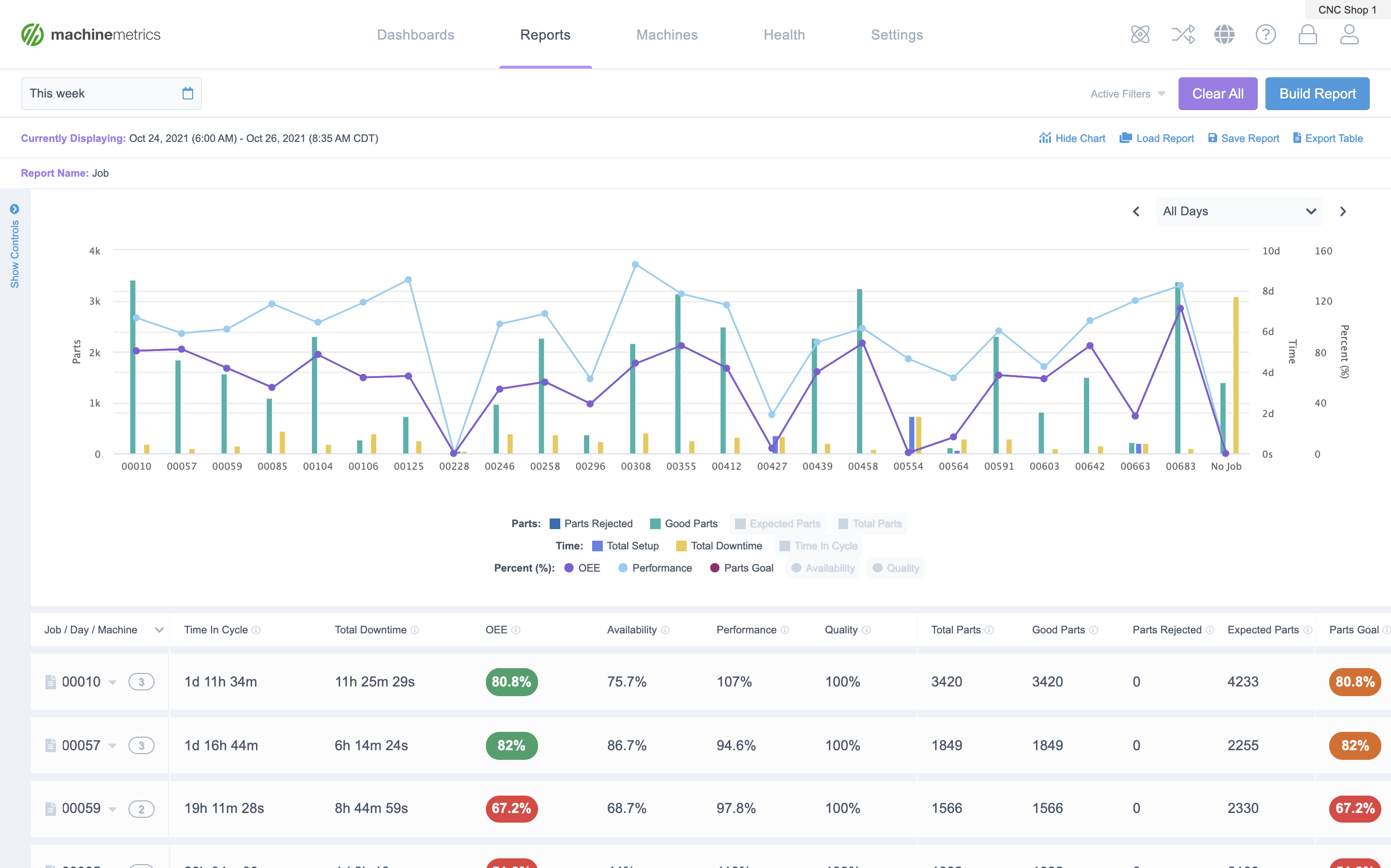
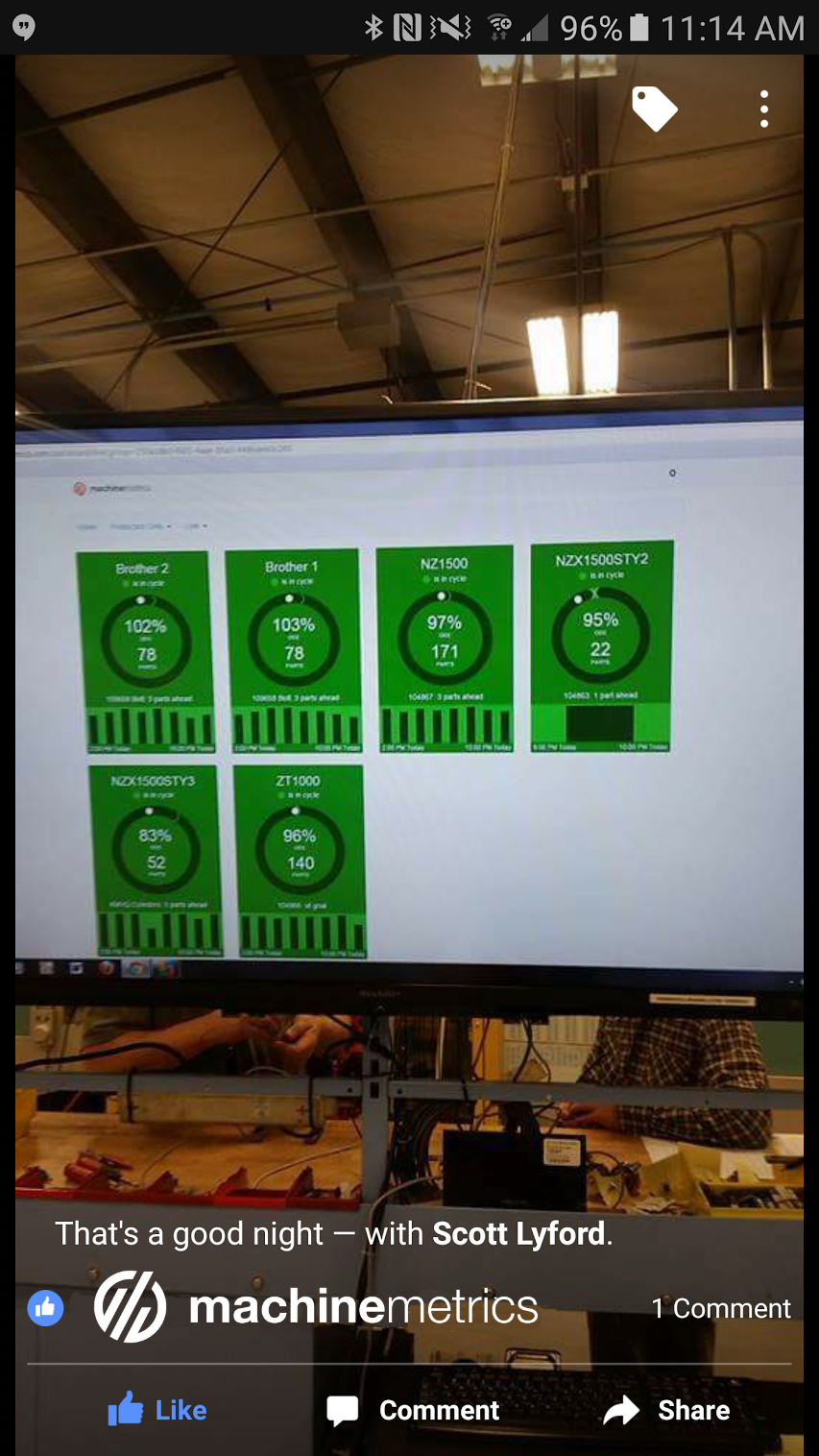
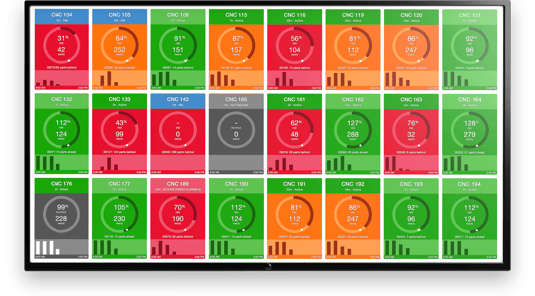 An example of the MachineMetrics current shift dashboard displaying machine performance data in real-time.
An example of the MachineMetrics current shift dashboard displaying machine performance data in real-time.
Why is Condition Monitoring Important?
Condition monitoring is important to lean manufacturing facilities because it reduces downtime, boosts production efficiency, and helps with cost prediction, spare parts supplies, maintenance needs and timing, as well as more accurate production predictions.
In summary, machine condition monitoring helps manufacturers squeeze more out of their existing equipment, without spending time and budget on unnecessary maintenance. They are able to do this because they have deeper, accurate insight into the performance of their equipment, which can be used for improved decision-making.
This enables higher-performing operators, managers, and maintenance teams, as well as drives a variety of notable KPIs, including machine uptime, utilization, and, of course, OEE. In a sense, condition monitoring is a more mature form of machine monitoring, leveraging helpful machine data to take advantage of the happy medium between calendar-based maintenance and reactive maintenance.
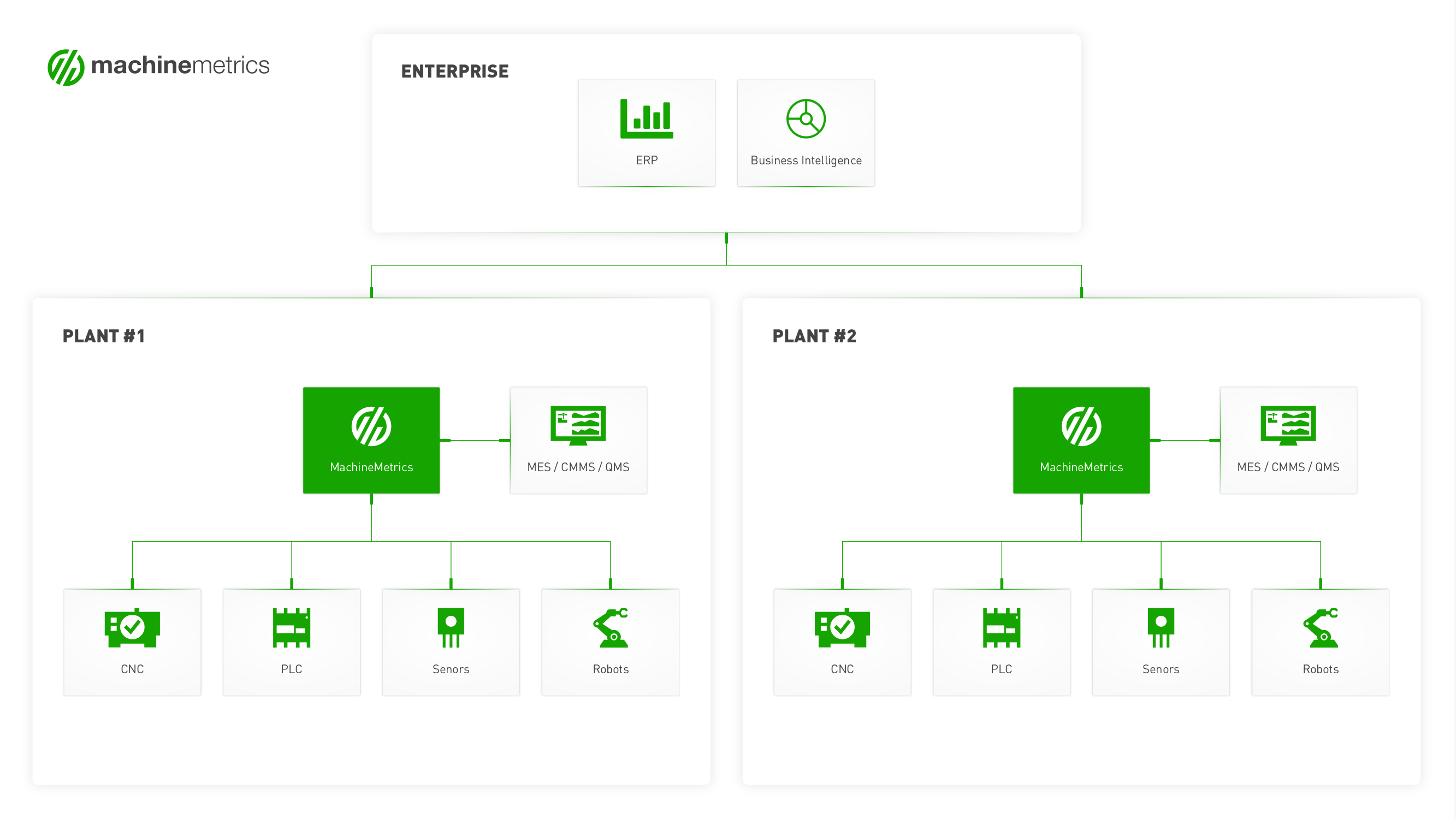
Plug-and-play Machine Connectivity
While most manufacturers may begin with simply monitoring equipment uptimes, eventually competition will force them to progress to monitoring machine conditions to understand the health of their equipment and optimize its performance.
Benefits of Condition Monitoring
The benefits of condition monitoring are plentiful. One major boon of condition monitoring is increasing the longevity of equipment. If a specific parameter is continuously out of expected ranges, especially factors that could severely damage a machine or its components, then underlying issues can be assessed and repaired before a downtime event or long-term, costly damage occurs.
Condition monitoring is also beneficial to overall production efficiency because it can help leaders make important decisions such as whether or not to continue production using partially damaged equipment and for how long without incurring additional costs or reducing product quality. In this way, it limits downtime as well as part costs, because machines can be used to their maximum efficiency. This is especially important for 24/7 facilities, and manufacturers running a lights out factory.
Machine condition monitoring supports a variety of goals for manufacturers, including:
- Reducing and eliminating unplanned machine downtime
- Optimizing machine health and performance
- Improving quality and reducing scrap parts
- Driving a higher performing maintenance program based on accurate machine data
- Enabling automation based on real-time machine condition data
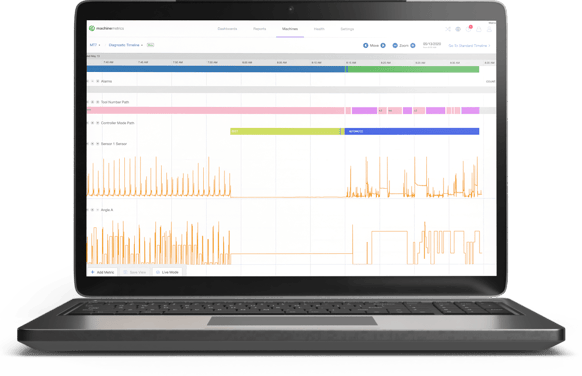
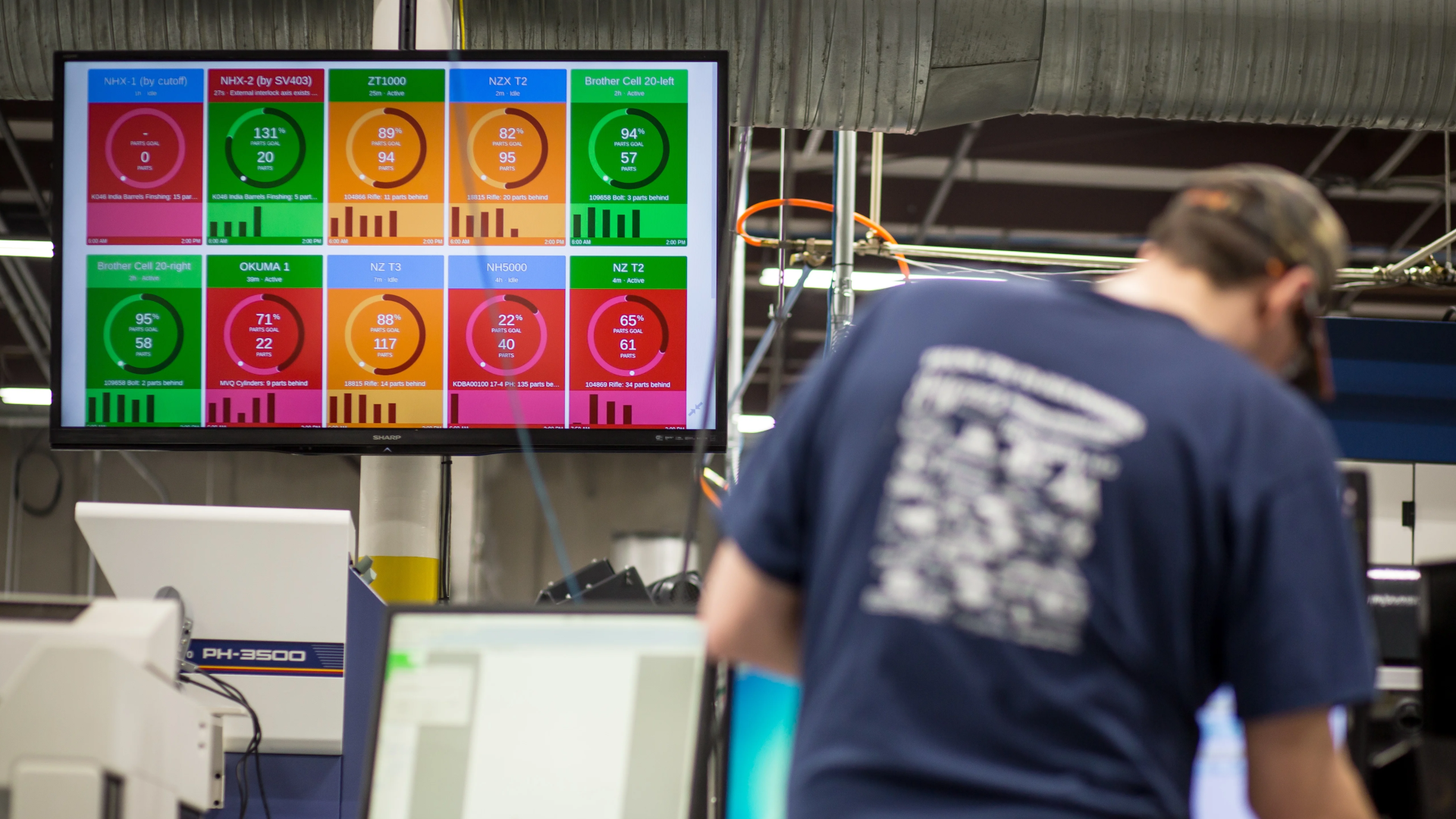
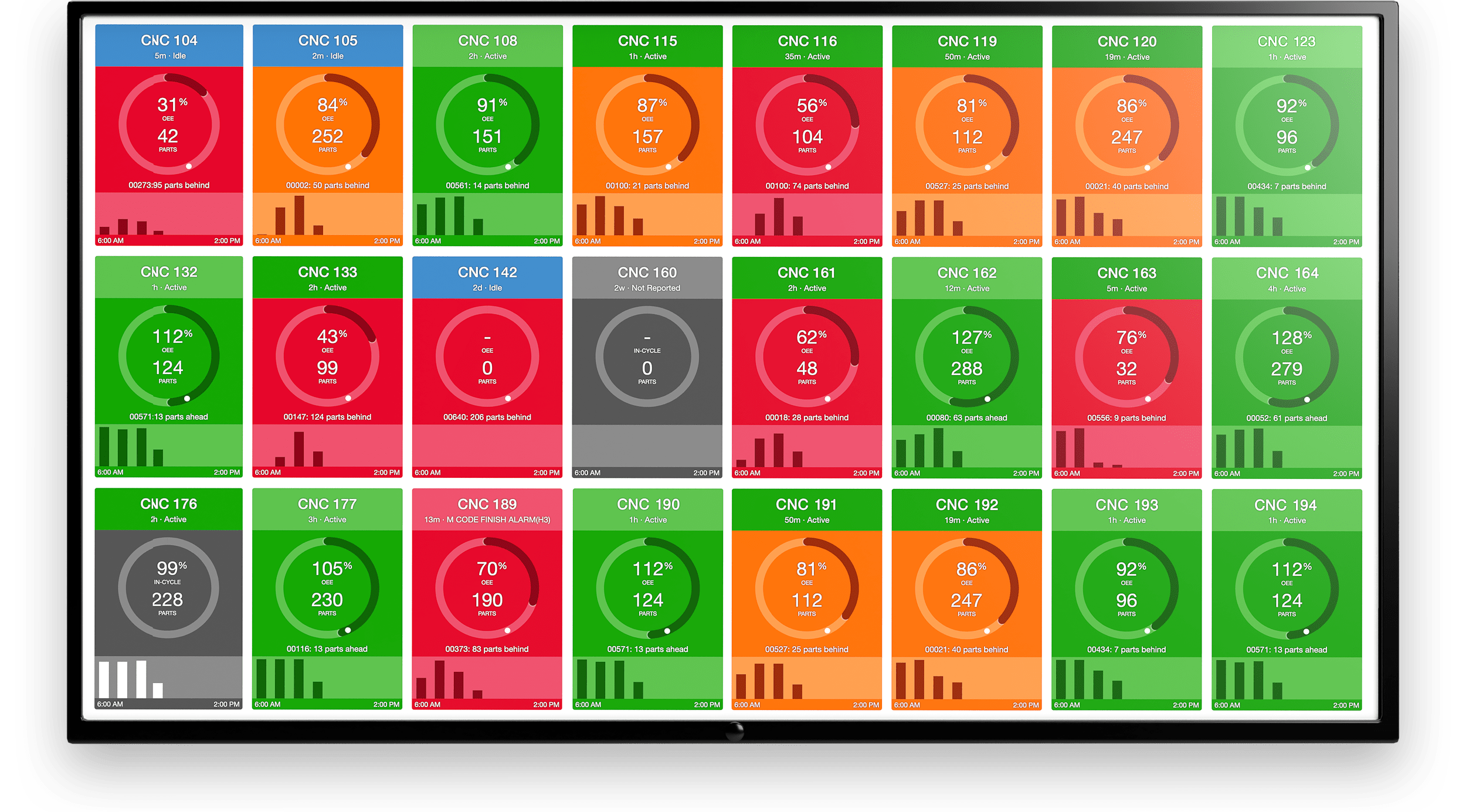
A machine condition monitoring dashboard for reporting machine uptime, health of equipment, and providing notifications for maintenance activity.
What Conditions Can You Monitor On A Machine?
There are nearly an unlimited number of conditions that can be monitored on a machine. The MachineMetrics Edge device connects directly to the PLC of a machine, giving you access to a wide variety of machine data. Furthermore, you can add external sensors or connect older equipment with digital and analog IO to ensure all equipment is being monitored.
This machine condition data can then be analyzed to better understand machine health and take action to maintain equipment when there is a given variable indicating impending machine failure. Below are some of the conditions and components that can be monitored to identify trends, predict failures, and roll out condition-based maintenance activities:
- Vibration Monitoring: Vibration patterns can indicate many different things. Monitoring vibration patterns can offer insight into part durability and changes to this pattern can indicate a failing tool, often 15 minutes or more than when a human operator can begin to see a problem.
- Bearing Wear: Ball bearing wear can cause damage to manufacturing equipment, and usually occurs during startup and slowdown times because the fluid pressure in the machine is not high enough to maintain proper lubrication. Too-low lubricant levels can also cause bearing wear, as can using the wrong type of lubricant for the job. By monitoring the condition of bearings using an edge device, costly maintenance and downtime can be prevented, and machine costs can be drastically reduced as critical failures become less and less frequent.
- Load: As a machine tool performs work on material, it will naturally become dull, forcing the machine to increase the load to ensure the proper cut, similar to how you may apply more pressure to an unsharpened pencil when writing. What this may tell operators is that as load increases, tool life may be ending.
- Torque: Identify anomalies in the rotational force of the machine, developing a better understanding of how it changes during job runs and any correlation with scrap parts, machine failures, and broken tools.
- Acceleration: Axis do not immediately start at a given speed, but accelerating and decelerate based on the program.
- Spindle Speed: Analyze RPMs (revolutions per minute) of your spindles, noting how the spindle speed can increase wear on the tool, encourage chatter, or lead to tool breakages.
- Temperature: Temperature is an apparent indicator of many potential problems within a machine. Monitoring machine temperature can alert production employees of an impending machine failure or even health risks such as major machine breaks or even fires in some more hostile manufacturing environments.
- Tool Failure: With a condition monitoring solution deployed, you can not only identify when a tool breaks, but even predict when a tool failure is impending, so you can deploy preventive maintenance to fix the problem before it ever happens.
[Case Study: How BC Machining predicts and prevents machine tool failures, generating $72,000 in annual savings per machine]
Machine Condition Monitoring Techniques
There are three main types of machine monitoring techniques, including:
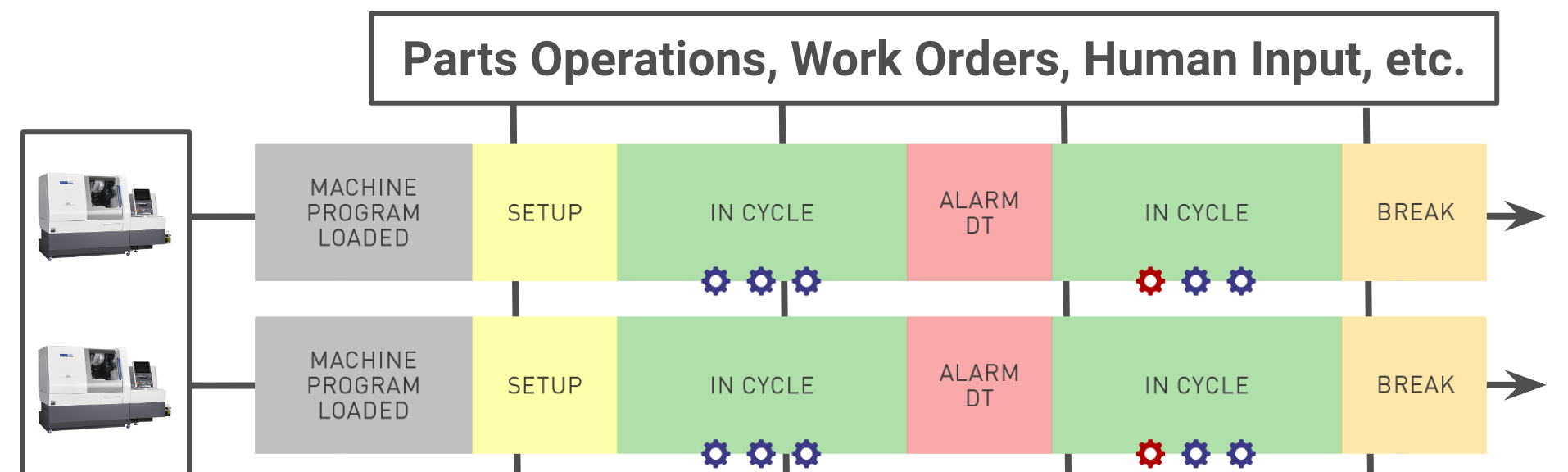
- Manual condition monitoring which involves manually inspecting equipment for wear and tear, documenting equipment failures, temperature, and other relevant data. This analog technique requires someone to be on-site to gather the information and expects a degree of accuracy which humans are not generally designed for. This is why we recommend digital manufacturing dashboards to ensure visibility of machine data across the shop floor.
- Machine control and sensor-based monitoring involves extracting data directly from the machine control, using digital and analog I/O, or putting sensors on machines in order to collect and assess data. In manufacturing environments, basic sensors often experience issues such as being knocked over or otherwise rendered imprecise due to being bumped, chemical or heat conditions, etc. However, solutions like the MachineMetrics High-Frequency Data Adapter are less a sensor in the traditional sense in that it plugs directly into the PLC and is immune to bumps, tilts, flying metal shavings, and other hazardous conditions. It also collects data at 1000x the speed of most sensors on the market.
- Leveraging IoT takes machine condition monitoring to the next level because it allows for remote machine monitoring and can utilize cloud-based software to aggregate data, run analytics, create reports, and more. IoT also opens the possibility of condition-based maintenance, often in real-time.
Maximize tool life and eliminate scrap
Enabling Condition-Based Maintenance
Condition-based monitoring drives a condition-based maintenance routine wherein maintenance is completed when machines are in indicating that there is a high chance of machine failure.
With a condition monitoring solution enabled, manufacturers can quickly pivot from a calendar-based or reactive maintenance strategies to a usage-based or condition-based approach. This gives them the opportunity to support equipment maintenance tasks at the right time, rather than over-maintaining equipment, or waiting for a machine to go down.
Alarms, Notifications, and Automation
MachineMetrics IoT-enabled condition monitoring system provides the infrastructure to integrate with other systems to enable notifications and other automated activities. In this way, the real-time machine condition data can inform and empower your team to make better, faster decisions based on accurate data.
Let's run through a few examples:
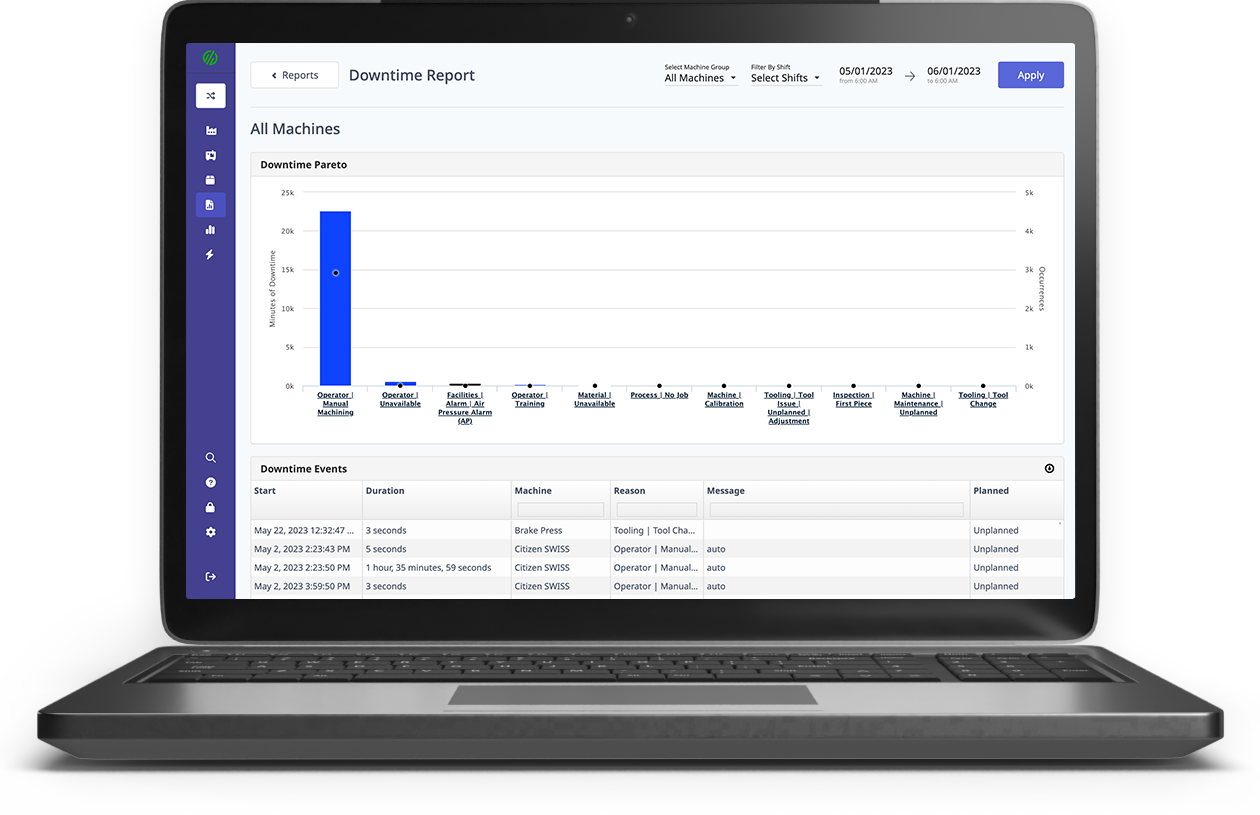
- Integration with CMMS: Your maintenance team and operators are responsible for ensuring your equipment is running optimally, but your maintenance system does not collect accurate machine data. With MachineMetrics, downtime events, setup stages, anomalies, general usage, or alarms can automatically be sent to a CMMS or other system.
- Automating Maintenance: In tracking machine conditions, an alarm can enable a workflow that notifies the correct person of the problem immediately. Not only is this useful to ensure the problem is resolved as fast as possible, but, depending on the machine data, condition thresholds may enable operators and maintenance teams to fix the problem before it becomes a problem. For example, perhaps a "low fluid" alarm triggers a notification for an operator to top off fluids before the machine fails. This moves us closer to predictive maintenance.
Condition-based maintenance is certainly beneficial to a manufacturer’s bottom line as compared to a reactive maintenance strategy that resolves machine issues only after they break. However, moving toward a predictive maintenance strategy is even more efficient and lucrative for data-savvy manufacturers.
With predictive maintenance, condition monitoring can be used as a data source alongside others for analysis to answer the question, “When will the machine break?” As long as a model is accurately trained, this type of insight can reduce downtime and costs even further than a condition-based maintenance routine.
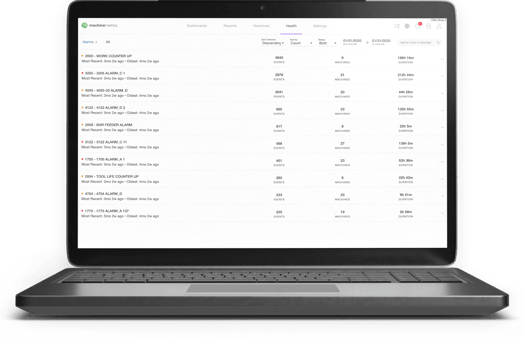 Machine down or imminent failure detected? Automatically notify the right person at the right time to resolve the issue as fast as possible, or before the problem even happens.
Machine down or imminent failure detected? Automatically notify the right person at the right time to resolve the issue as fast as possible, or before the problem even happens.
Machine Condition Monitoring Solutions
MachineMetrics Industrial IoT platform offers a system for machine condition monitoring so manufacturers can leverage the real-time data streaming from their machines to monitor performance, deploy maintenance, and more.
We offer a plug-and-play solution for connecting to machines via the PLC and collecting and transforming data into consumable machine data and insights in a matter of minutes. With this in hand, you can easily view and manage the health of your equipment, as well as notify the right person at the right time to take action when it is needed. On top of the contextual data provided by operators, you’ll have instant visibility not only into individual machine performance and health, but the status of the operation as a whole.
This supports a variety of goals for manufacturers. A simple deployment of condition monitoring provides insight into machine health via diagnostics and alarms, and more advanced use cases via cycle analysis, as well as automated workflows.
Explore MachineMetrics condition monitoring solution or learn how AccuRounds drove a 20% increase in OEE after deploying MachineMetrics.
Ready to connect your shop floor?
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)








Comments