The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to drive innovations in how data is collected, processed, and analyzed. Edge devices are a vital part of the continued expansion of IoT and play an increasingly important role in its success.
What is an Edge Device?
Edge devices are pieces of equipment that serve to transmit data between the local network and the cloud. They are able to translate between the protocols, or languages, used by local devices into the protocols used by the cloud where the data will be further processed. Local devices use protocols like Bluetooth, wi-fi, Zigbee, and NFC while the cloud uses protocols like AMQP, MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP. In order for IoT data to move between the cloud and local devices, an edge device—like a smart gateway—translates, sorts, and securely transfers information between the two sources.
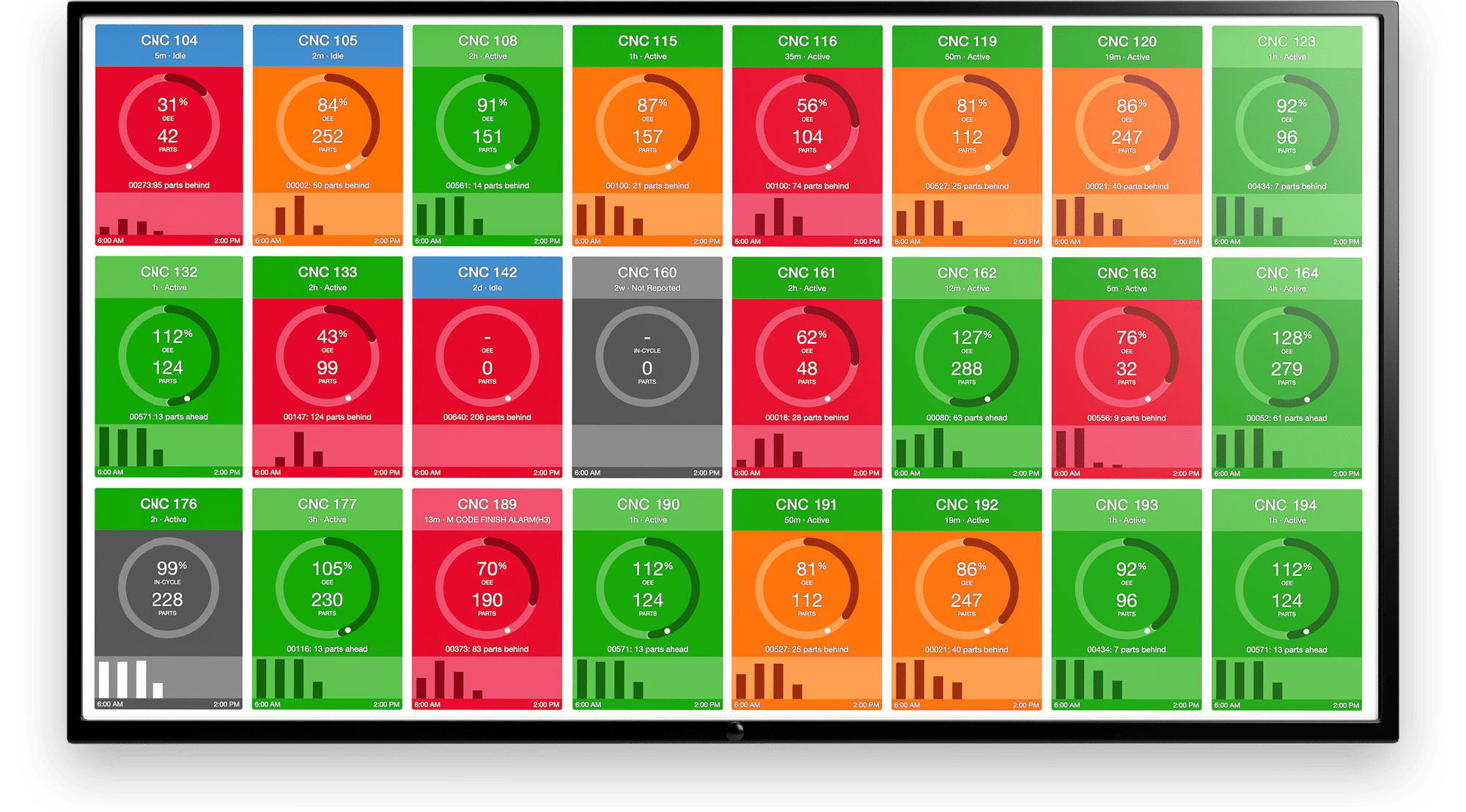
Without an edge device, these types of data would be incompatible and unable to reach cloud services for deep analysis. The MachineMetrics Edge is one security-conscious example of this technology. It can be configured as an Edge Pro to support up to 50 machines over a network, or installed near, and powered by, a single machine as an Edge.

The MachineMetrics Edge device.
Types of Edge Devices
There are many different types of edge devices. These devices use IoT or industrial IoT to transmit data to the cloud or perform functions directly at the edge. Edge devices also transmit data across the internet.
There are two types of edge devices – traditional and intelligent edge. Traditional edge devices transfer data over a secure network with little or no processing capability. Intelligent edge devices are smart devices that can perform edge computing tasks near the data source for industrial automation.
Traditional Edge Devices
Traditional edge devices include:
- Edge Routers: Edge routers connect multiple packet transmission networks. They manage data traffic to an IP address so multiple devices can operate using a single internet connection. For a Local Area Network (LAN), a router is responsible for several devices within a specific geography.
- WAN Devices: Wide Area Network (WAN) devices extend over large areas and can even be global. WAN devices allow organizations to work seamlessly across the enterprise regardless of location.
- Routing Switches: Routing switches are used in situations like industrial IoT. They can perform many of the same functions as a router but also allow connections across different devices.
- Firewalls: Firewalls monitor all network traffic for security. They contain rules-based functionality and can be configured to block data traffic deemed harmful by the rule set.
- Multiplexers: Multiplexers merge data from multiple data sources over a single signal. They’re integrated access devices (IAD) that help automation systems and advanced IoT networks perform efficiently.
Intelligent Edge Devices
Intelligent edge devices are used in advanced IoT and industrial IoT to connect the entire system's onboard processing or analytics capabilities. This functionality enables smart factories and IIoT platforms to facilitate advanced automation and analytics.
Intelligent edge devices include:
- Sensors: Sensors measure a condition or event, trigger action, and route data to the next destination. Sensor types are almost limitless and include GPS, motion, optical, temperature, humidity, vibration, and more.
- Actuators: Actuators act as the physical connectivity bridge between electronic devices like sensors and the physical movement required on a machine. Actuators take the sensor signals and instructions from intelligent edge devices and trigger actions using electric, air, or hydraulic power.
- IoT Gateways: IoT gateways connect multiple sensors and other devices to cloud computing platforms for analytics, computing, processing, and storage.
- M2M Devices: M2M devices connect equipment or machines to transfer data and facilitate automation.
Together, traditional and intelligent edge devices can be used in a platform to connect assets and machinery.
How Does an Edge Device Work?
An edge device works by being near the source of the data it manages. Devices like embedded or added sensors act as the device layer, acquiring data and sending it to the edge computing device or a cloud computing platform.
If the data is informational or transactional, the device may send it directly to the cloud for storage. Or, based on parameters, it may send it to an edge device for processing and instructions and then forward the instructions to an actuator to trigger a response. Devices in M2M systems can be linked to perform tasks sent from an edge computing device or an edge network.
In large connected systems, data flow may be controlled by a router. Using extended access to devices within a system, a combination of sensors, actuators, routers, switches, and edge computing devices can be controlled and accessed locally or over WAN to provide visibility and the capability to act over long distances.
The Benefits of Edge Devices
There are many benefits to using edge devices and edge computing:
Improved Performance
In an extensive centralized system, data flow may be constrained by too much traffic across a narrow bandwidth. The vast volume of data in systems like an advanced machine data platform can overwhelm resources.
Edge computing and edge computing infrastructure create a local edge layer where a great deal of functionality for automation and response can be conducted near the source, reducing latency and bandwidth constraints. Built-in processors and onboard analytics do much of the work that would’ve been sent to the cloud.
Advanced capabilities allow network entry across traditional cables, cellular, or wireless access points at the network edge.
Empowering AI and ML
Edge computing creates a decentralized edge network so that advanced cloud-based artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) platforms can focus on the volume of data requiring the most complex analysis and insight.
Edge computing extends the reach of AI and ML to the edge near the data source, making the entire system more efficient.
Better Regulatory and Compliance Performance
Many industries, such as medical, pharmaceutical, defense, and aerospace, have tight regulation and compliance requirements. Edge computing facilitates the quick and efficient update and analysis of data at the edge so users have the most relevant insights.
This functionality may be as simple as sensors that perform precise measurements for pharmaceuticals. They can also be tied to expiry parameters and fully traceable supply chains. Or, they can be tasked to identify quality and strength requirements for military and aerospace parts.
Greater Interoperability
Many providers offer plug-and-play devices that enable interoperable legacy equipment and software. It’s possible to create a system where analog and digital assets communicate in a single platform with cloud-based analytics and advanced edge networks.
Edge Device Use Cases
There are endless possibilities for edge computing with the IoT technology stack:
Smart Factories
Smart factories use advanced cloud-based machine data platforms with edge networks, edge computing, and edge devices to drive advanced automation and improve business practices.
Predictive Maintenance
Edge computing is capable of machine condition monitoring, vibration analysis, and real-time equipment analysis. These insights allow managers to design and deploy predictive maintenance that reduces cost, improves equipment utilization, and increases efficiency.
New Business Opportunities and Innovation
Since processes are linked and analyzed in real time, IoT devices can extend their reach to the end user. This visibility allows companies to use advanced technologies like digital twins to create new products and designs or improve existing products to meet customer expectations.
Why Are Edge Devices Essential for IIoT?
Edge devices are critical for modern industrial IoT implementations, especially for tasks that require real-time data analysis. IoT Edge devices offer a reliable, low-latency solution for local data analysis. In a manufacturing environment, edge devices have the following benefits:
- Enable condition-based monitoring to monitor the condition of shop-floor machines, even if they are legacy devices
- Prevent critical failures by monitoring and analyzing data to detect anomalies sooner.
- Improved equipment uptime, lower spare parts inventory, and lower maintenance costs because upcoming issues can be predicted and maintenance technicians are equipped with necessary data about the machine’s state to rectify the issue on the first visit
- Capture new business opportunities through added efficiency and self-monitoring analysis.
Because edge devices translate and transmit local data and cloud data through their associated protocols, IIoT systems utilizing edge devices reap the benefits of real-time local analysis as well as robust cloud-based analysis and storage. Cloud computing benefits manufacturers in the following ways:
- Low maintenance system because the cloud provider is off-site and generally not the responsibility of the manufacturer
- Scalability beyond what is feasible from a standalone local network due to data storage constraints, computing constraints, etc.
- Cost reductions for similar storage and computing capacities
- Data accessibility from anywhere as well as redundancy in case of disaster
However, cloud computing requires network connectivity, increases latency over local computing, and requires reliance upon 3rd party security. Edge computing, on the other hand, provides low-latency, reliable computing that can be deployed in areas with no network connections or in extreme security conditions where 3rd-party security is disallowed. However, data can become incomplete due to the higher cost of storage, and local computing has higher overall maintenance than cloud computing because it must be managed in-house.
With edge computing, IIoT systems get the best of both worlds. Bridging the gap with IoT edge devices offers manufacturers unprecedented flexibility, reliability, and speed in a cost-controlled, security-conscious way.
Edge computing devices are a crucial component in creating a digital twin of a manufacturing facility. Other reasons edge devices and IIoT gateways are critical for modern IIoT infrastructure include:
- Data Management: Edge devices are able to decide which data to keep and which to discard in order to prevent unwieldy datasets full of information that is likely to never be utilized
- Offline Capabilities: Edge devices can hold information until a system is able to gain access to a network connection, preventing data loss and allowing for deeper analysis
- Complex Event Processing: The cloud can be used for computational-heavy work to develop and recognize patterns that can then be pushed to edge devices to be acted upon locally when those patterns arise.
- Applications: Some IoT devices now utilize applications that operate on edge devices. One example of this is a monitoring and alerts system that takes advantage of the low-latency nature of edge computing.
- AI and ML: Artificial intelligence and machine learning using edge devices can enable real-time, autonomous decision-making processes for manufacturers as well as immediate BI insights.
Learn more about edge devices and edge analytics free edge eBook, which explores the important role of the edge in enabling manufacturing analytics. Or learn more about the MachineMetrics Edge Platform built for manufacturers.

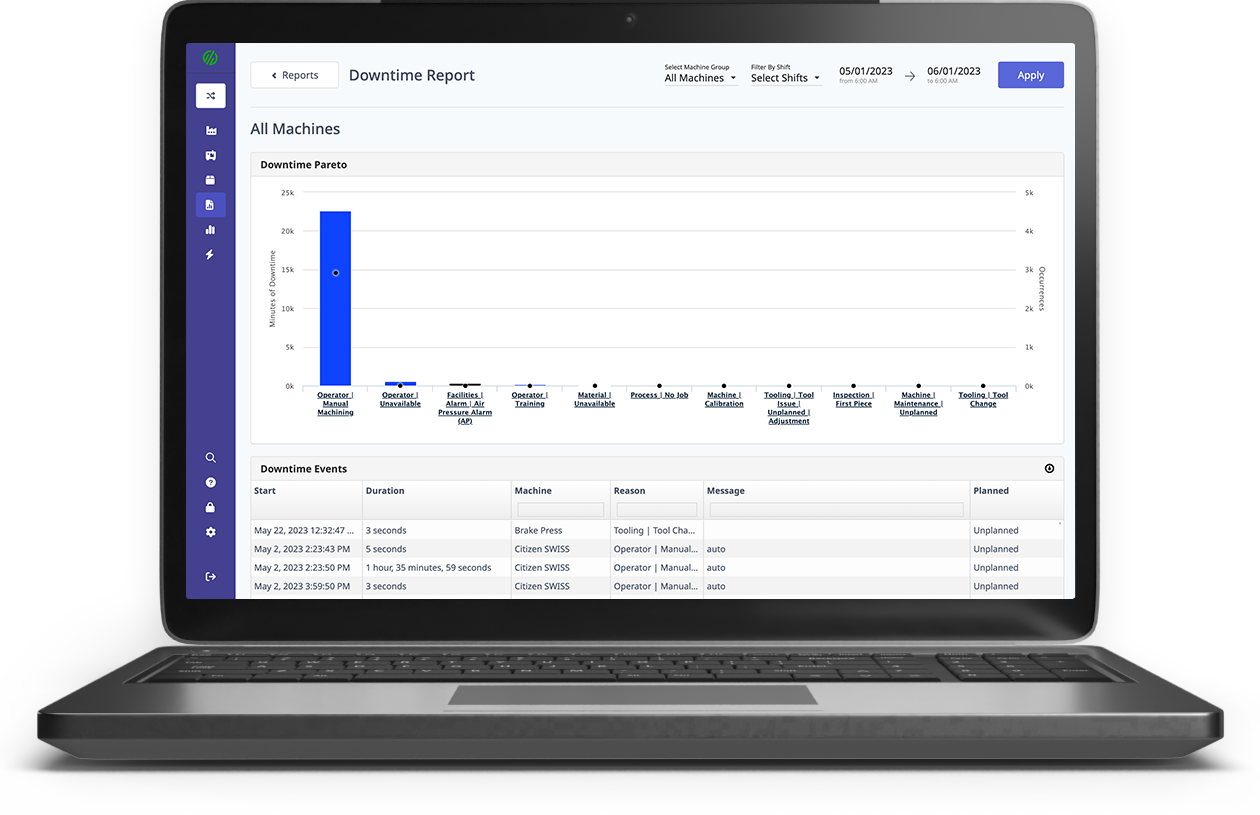
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



.gif)






Comments