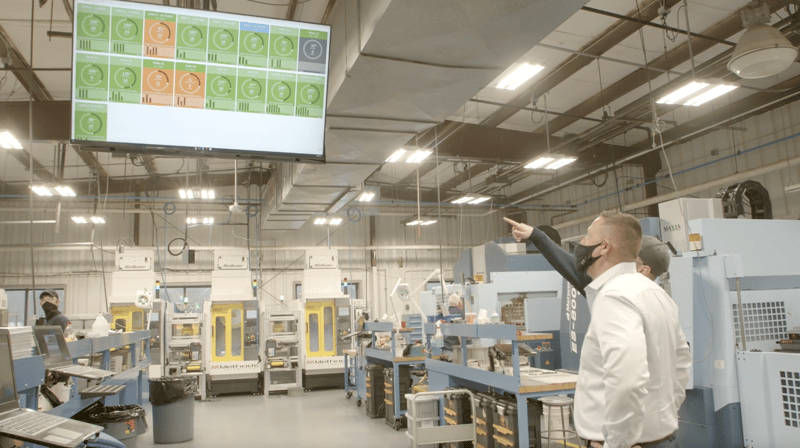
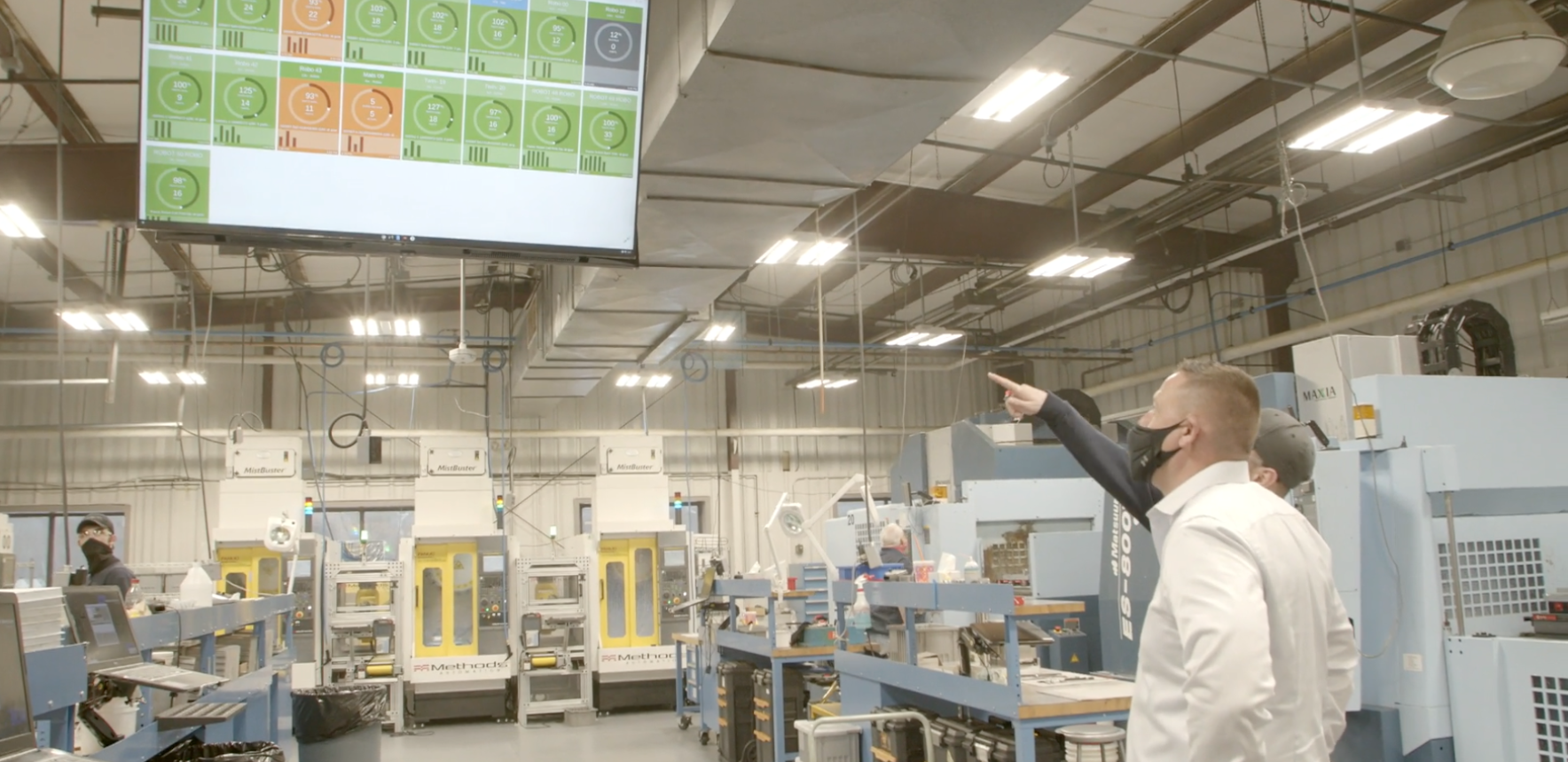
With the arrival of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), a digital transformation is currently underway. The manufacturing industry is beginning to use manufacturing analytics data driven by real-time production data to make better, faster decisions and enable automation across the organization.
Equipment connected through sensors and edge devices feeds massive volumes of data to cloud-based analytics platforms that can analyze and understand data faster than human perception. This data analytics for manufacturing can then be used to drive real-time decision-making and significant process improvement throughout the company.
This article will explain analytics in manufacturing and list use cases for consideration. It will also explain the benefits and goals of data analytics applied in any shop floor or factory.
What is Analytics in Manufacturing?
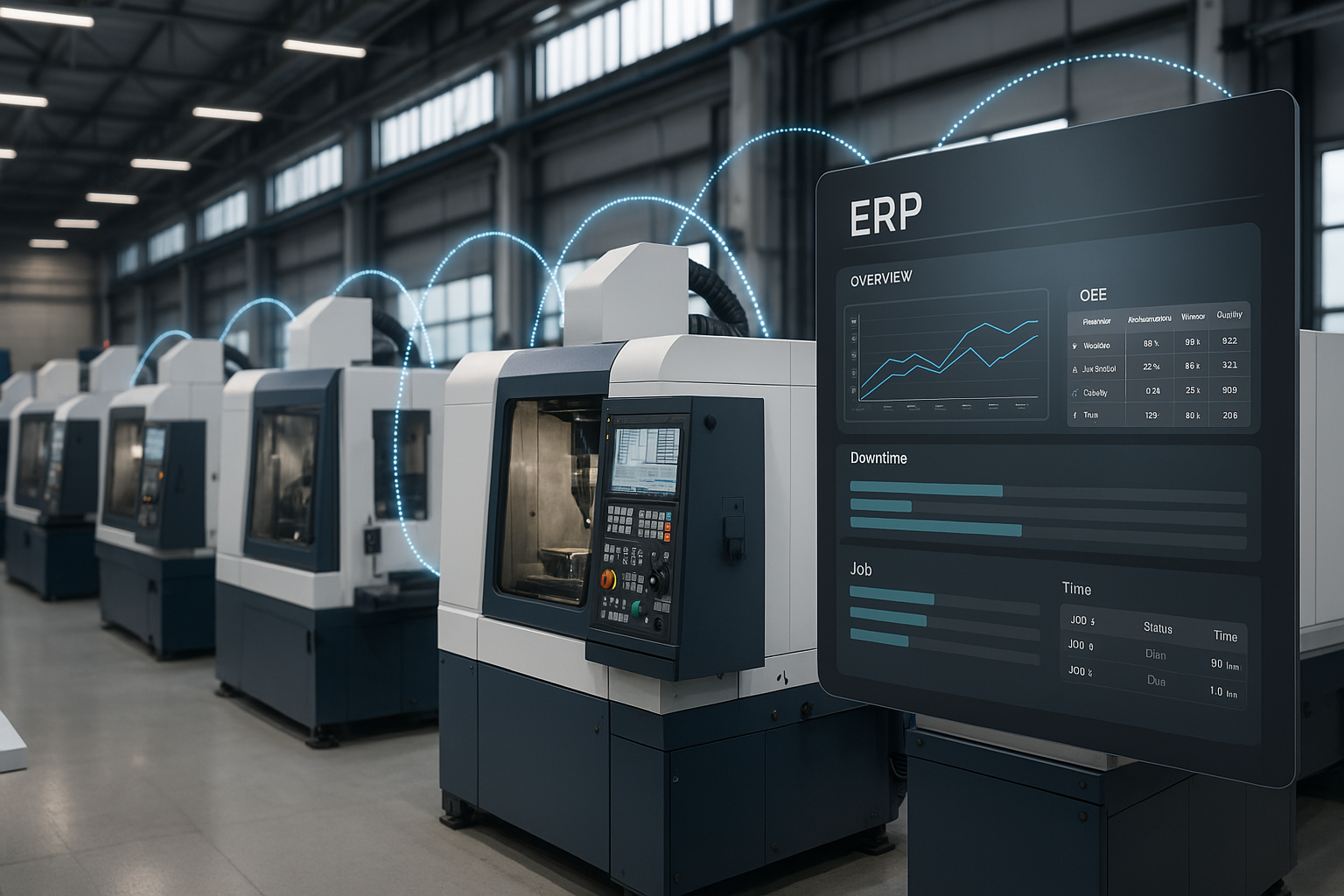
Data analytics in manufacturing industry uses machine, operational, and system data to manage and optimize production, including key functions such as maintenance, quality, and planning. With accurate and real-time data, manufacturers can make better, faster decisions.
Manufacturers have used data to improve efficiency and advance their market share for many years. But the most significant change today is how data is collected. Many companies still use fragmented, traditional methods for data capture, with staff manually checking and recording factors, filling forms, and writing down operation and maintenance histories for the machines on the floor. Unfortunately, these methods are highly inaccurate due to human errors. They are also time-consuming, open to bias, and do not generate the quality of analysis required for accurate decision-making.
However, with digital transformation underway across manufacturing, connected devices can reduce labor associated with manual data collection and documentation. And because this manufacturing analytics software uses advanced analytics and algorithms, the insights gained are real-time and much more actionable.
Automated machine data collection drives the next generation of manufacturing data analysis, unlocking a myriad of advanced use cases ranging from simple monitoring and diagnosis to predictive maintenance and process automation.
In manufacturing data analytics, data capture that records events can be leveraged to increase equipment utilization, reduce cost, drive process improvement, reduce human-based errors, and do so at a depth that reveals accurate machine conditions and trends in production.

Use Cases
Data analytics for manufacturing with real-time production data is changing the manufacturing industry dramatically. Let's consider several use cases that real-time machine connectivity has made possible in manufacturing:
Fault Prediction and Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance programs have been around manufacturing for decades. The idea is that unplanned breakdowns are less likely to occur through use-based or time-based programs. By applying analytics, real-time data can be leveraged to do more than prevent breakdowns.
It can predict with high accuracy the likelihood of a breakdown and the moment it will occur. This reduces costs by allowing technicians to perform repairs at the machine's optimal time and stage parts. This reduces overall downtime and increases productivity.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
Demand forecasting is critical for modern manufacturers; having complete supply chain control allows better inventory control.
However, demand planning can be complex. With the addition of data science methods, end-to-end supply chain control can be used in conjunction with real-time shop floor data better to manage purchasing, inventory control, and transportation. Highly accurate demand plans can be generated to identify trends that would go unnoticed.
With a better understanding of how long it takes to make parts, how long job runs will take, and the expected costs and profit of a given job, manufacturers can better estimate their need for material to improve planning.
Price Optimization
Cycle times play a significant role in pricing. Knowing precise times for part creation and the associated costs allows for accurate cost models and optimized pricing strategies. Setting them too low reduces profitability, while setting them too high may impact demand.
An advanced analytics platform for manufacturing can bring this data forward to ensure prices are set appropriately. MachineMetrics can help manufacturers optimize their job standards to ensure accurate cycle times.
Warranty Analysis
For many manufacturers, warranty support can be a drain. Often, warranties consist of a "one-size-fits-all" approach that’s more general. This allows uncertainty and unexpected problems into the equation.
By applying data science and capturing information from active warranties in the field, products can be improved or changed to reduce failure and cost. It can also lead to more informed iterations for new lines of products to proactively avoid field complaints.
Robotization
By including this data within a powerful cloud-based analytics platform, quality can be controlled at the micro-level. Robotics evolution will also lead to improved machine construction from OEM machine builders.
By including this data within a powerful cloud-based manufacturing analytics platform, quality can be controlled at the micro-level. Robotics evolution will also lead to improved machine construction from OEM machine builders.
Product Development
One costly process in manufacturing is product development. To stay competitive, companies must pay for R&D to create new product lines, improve existing models, and develop new value-added services.
Previously, this was done through excessive iterative modeling to arrive at the best product. But now, data science and advanced manufacturing data analysis allow much of this process to be simulated. Using "digital twins" and other modeling methods, real-world conditions can be generated virtually to predict performance and reduce R&D costs.
Computer Vision Applications
Automated quality control has come a long way. It’s evolved from trip sensors, drop wires, and other mechanical devices to a highly sophisticated collection of advanced optical devices. By tying these devices into data collection, sensors can add data to the stream through optics, temperature, and advanced vision applications such as thermal and infrared detection to accurately control stops. This also allows for higher speeds, lower labor, and the holy grail of any factory – "lights out" manufacturing.
Managing Supply Chain Risk
Like the data coming from production machines, data can also be captured from materials in transit and transmitted directly from vendor equipment to the analytics software platform to help provide end-to-end visibility in the supply chain.
Companies can use manufacturing data analysis to manage their supply chains in a "control tower" format, directing and redirecting resources to speed up or slow down. They can also order backup supplies and buffer stocks when new demand is sensed and trigger secondary vendors when disruption occurs.
Benefits of Analytics in Manufacturing
Contextual awareness is critical for advanced manufacturing systems. Analytics provides that awareness in real time. This makes companies more competitive as cost, quality, product development, and customer satisfaction are optimized. Manufacturing analytics software empowers companies to improve productivity and profitability by leveraging the massive data stream their production equipment generates. With intuitive visualization tools, dashboards, machine learning algorithms, and advanced analytics, actionable insights are available to managers and decision-makers across the company.

We believe the benefits of analytics in manufacturing fall into three distinct categories:
Reduced Costs
The cost can be significantly reduced because processes can be optimized with the insights revealed in analytics. And the growth of robotics, as well as autonomous or semi-autonomous machine decision-making, reduces labor. The same is true of predictive and prescriptive maintenance programs proven to reduce cost and increase productivity by lowering downtime and managing parts inventories better.
Increased Revenue
Data analytics in manufacturing offers real-time insights for production, inventory management, and demand and supply planning, manufacturers can respond quickly to changes in demand. Suppose the data tells them that they’re nearing max capacity. In that case, they can add overtime, add capacity, alter processes, or adjust other aspects of production to respond and maintain delivery times.
Miscellaneous Benefits
With the increased capabilities of manufacturing analytics, there are also miscellaneous benefits. These include reduced energy consumption, safer environmental protocols, reduced compliance errors, and increased customer satisfaction.
Goals of Manufacturing Analytics
Traditional data collection within manufacturing was fragmented and error-prone. It was also challenging to translate data into meaningful action and decision-making. Either the information was delayed, incomplete, or it contained unintentional human bias (such as rounding part counts or downtimes). Analytics in manufacturing seeks to reduce siloed data, analyze it in real-time, and use it to enable better, faster decisions across the enterprise, or even automate those decisions altogether.
By detecting issues before they occur, production processes can be optimized, and overall equipment utilization can be significantly improved. It also helps streamline supply chains and create transparency within them. Because analytics uses advanced machine learning algorithms, it can help identify opportunities and optimize processes.
As seen in the use cases above, product usage can be included in the new development of products. Alongside digital twin technology and incoming warranty information, it can drive new, better products with reduced failure rates and lower production costs. These same use case examples can drive increased throughput by detecting and alerting staff quickly to problems at the machine level. This reduces downtime and scrap rates.
Selecting the Right Solution
Manufacturing is undergoing considerable changes due to the development of technologies that can collect production data and leverage it to make better daily decisions.
However, when making a decision on the right solution to enable analytics on the shop floor, manufacturers should consider a few key-value props. Here are some questions to ask when considering analytics software:
-
Can the solution collect production data in real time?
-
What is the source of the production data? Equipment, people, or systems? All the above?
-
Is the data standardized into a model that can be easily propagated in out-of-the-box reports and consumed by other production management systems (MES, ERP, CMMS)?
-
How quickly can the software get you to value? What problems will it solve?
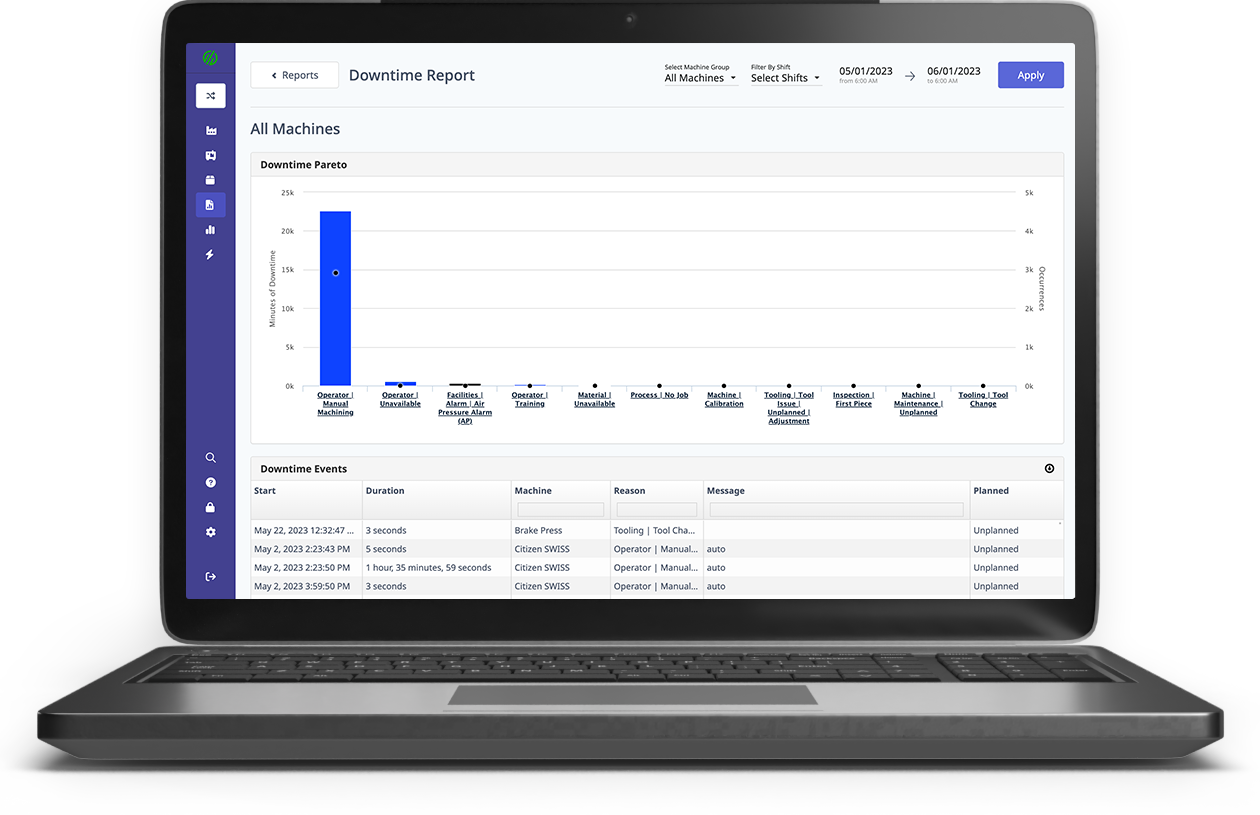
We would like to introduce you to MachineMetrics Manufacturing Analytics Software. Our platform enables the real-time, autonomous collection of machine data for accurate production reporting. Stakeholders at various levels of the operation can easily consume out-of-the-box reports and visualizations to reduce downtimes, identify production bottlenecks, increase capacity, track their most important KPIs, and enable complete visibility and control of the shop floor.
Want to See the Platform in Action?
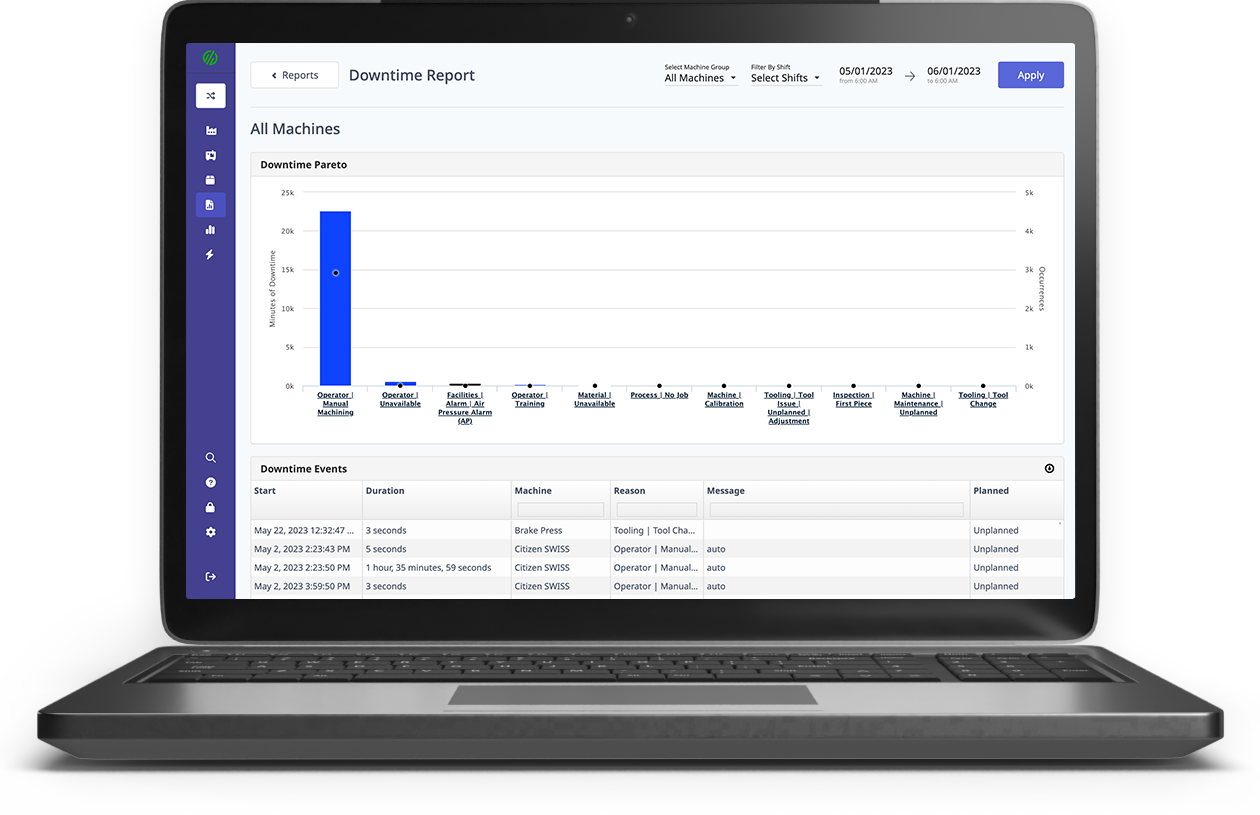
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)









Comments