Lights out manufacturing is a technique that uses fully-automated technology to run a production factory with little or no human intervention. This requires the support of multiple technologies such as machine learning and high-frequency data collection.
It has been the dream of many manufacturers to use a set-it-and-forget-it mindset for production. Simply show up to work, set the machines in motion, flip off the lights, and head out the door. No workers. No humans in the building at all. Just machines doing what they do best—accurate, repeated tasks at speeds far faster than their homo sapien counterparts.
This would drastically reduce workplace accidents, the cost to keep the facility well heated or cooled, and the cost of the labor itself. Manufacturers would encounter fewer quality issues too, because—unlike humans—the machines can replicate their behaviors exactly, day-in and day-out.
These 24-hour production facilities sound like pure fantasy, but they are a reality today in manufacturing facilities spanning the globe. There is no question. Although most facilities are at the early stages of automating production activities, automation solutions are being increasingly adopted across the industry.
What Is Lights Out Manufacturing?
Lights out manufacturing (also known as a “dark factory”) is a production method that requires little to no human interaction—essentially running on its own, even in a dark and otherwise empty factory.
In order to achieve this, you need to be able to automate every single step of the manufacturing process. Companies that utilize this strategy do so with a tech stack that usually includes machine vision, additive manufacturing equipment (3D printing), industrial IoT, edge computing, cloud data, machine learning, and robotics.
One example of a company using this technique to great effect is FANUC, which utilizes a lights-out factory to produce robots and manufacturing systems without any human assistance.
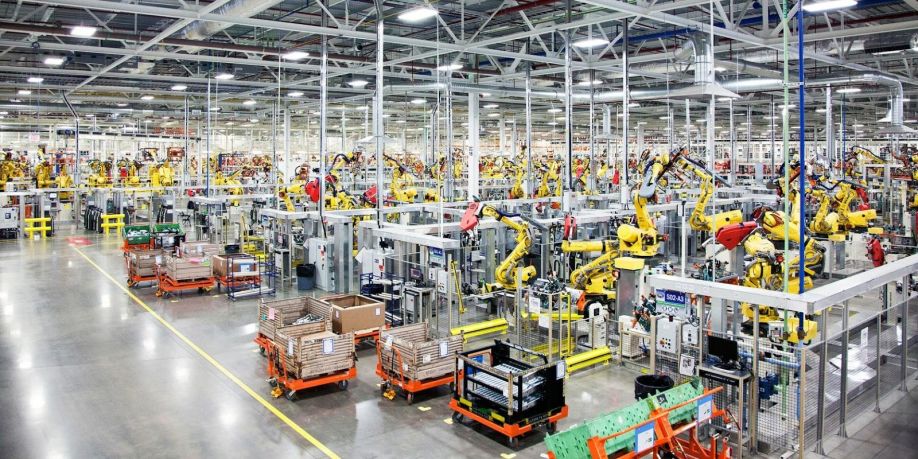

Fanuc has successfully launched a lights out factory, allowing their robots to build robots without much human intervention. [Source]
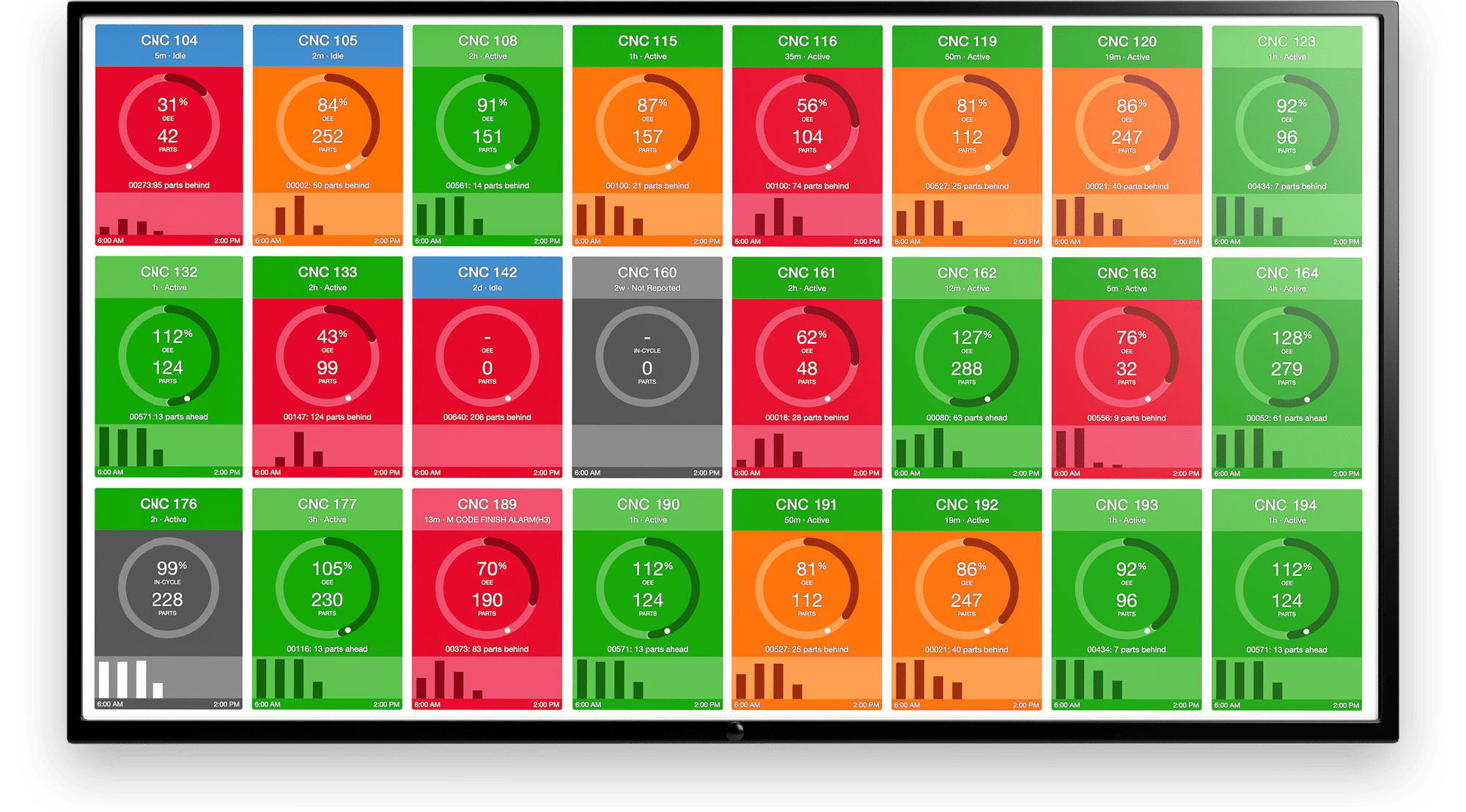
We understand that manufacturers are at the early stages of introducing automation within their operations. At the core of enabling automation is accurate production data that can drive decision-making for humans and machines. With data straight from the control of equipment, manufacturers can begin introducing automation based on the performance and health of their machines.
This can be as simple as showing real-time OEE data on dashboards above the shop floor or as sophisticated as collecting high-frequency data to enable predictive maintenance.
Want to See the Platform in Action?
The Benefits of a Lights Out Production
Full automation can be of exceptional benefit, especially in hostile manufacturing environments such as those containing oils and lubricants, caustic chemicals, fumes, etc. After all, robots can be made of far more durable components than that of their human counterparts.
While most manufacturers are not, at present, aiming for end-to-end automation, most do currently or intend to use many of the processes underpinning full automation, and to great benefit. The core benefits of lights out manufacturing are reducing costs and driving greater efficiency, but also include:
- Reduce accidents and increase worker safety
- Improve operational efficiency
- Reduce scrap and rework via greater production consistency
- Drive more advanced maintenance strategies
The Challenges of Lights-Out Manufacturing
It would not be appropriate to only address the benefits of a fully autonomous factory. Below we outline the challenges that a manufacturer may address when rolling out a dark factory.
Technical Challenges
Turning on the light is as simple as flicking a switch. Unfortunately, setting up completely automated processes can be a highly technical challenge that may require a significant investment. However, solutions like MachineMetrics allow manufacturers to easily and quickly collect and use machine data to automate processes, with ROI occurring in as few as 5 days.
Complex Production
Simple, repeatable tasks are the best fit for automation. More complex tasks, as well as small-scale production runs and operations, may prove more difficult to roll out automation or experience enough value.
Safety and Failure Prevention
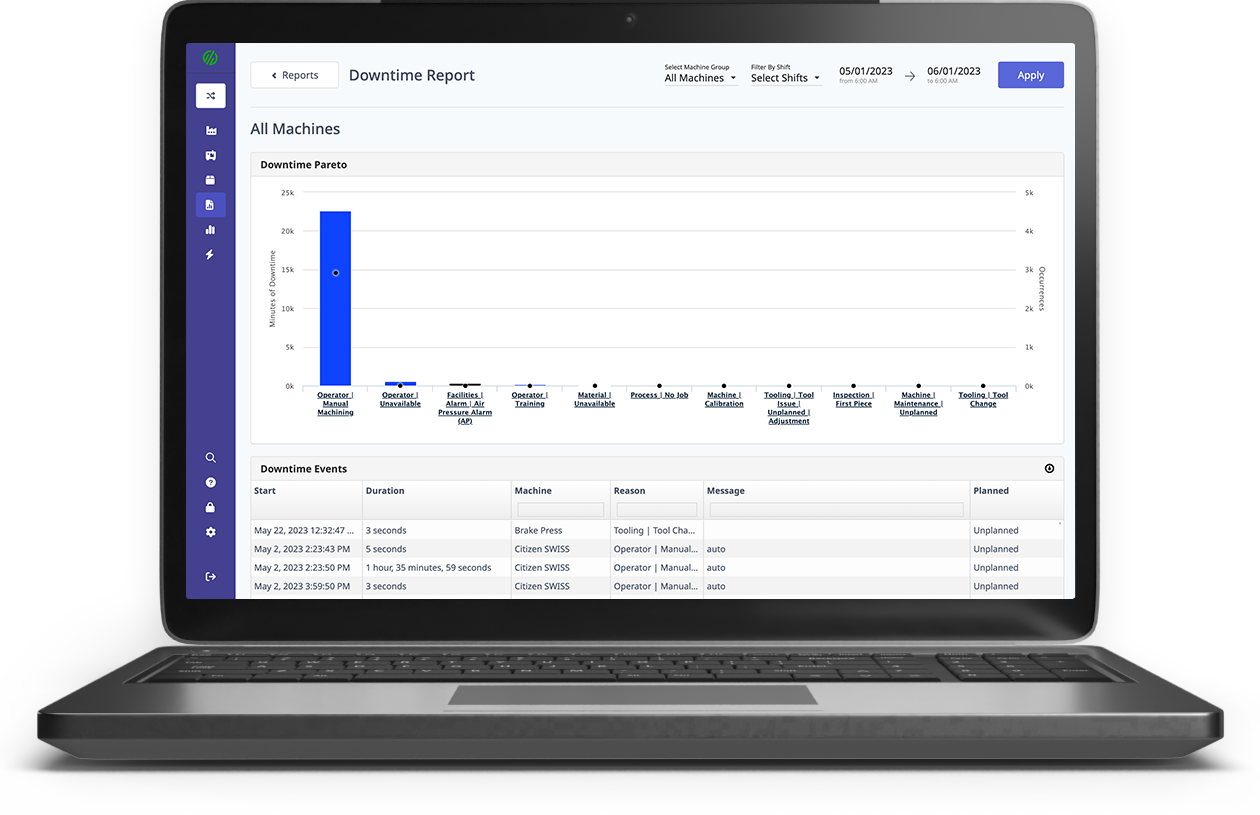
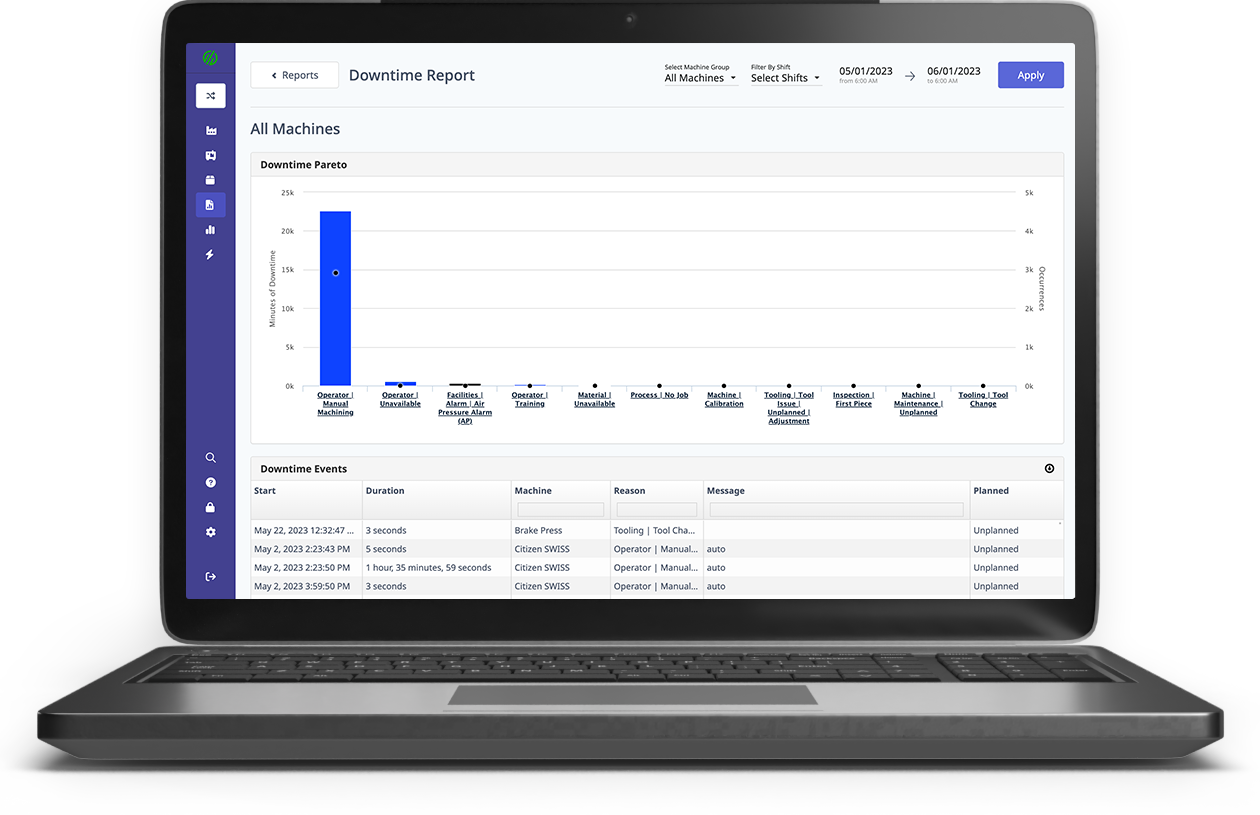
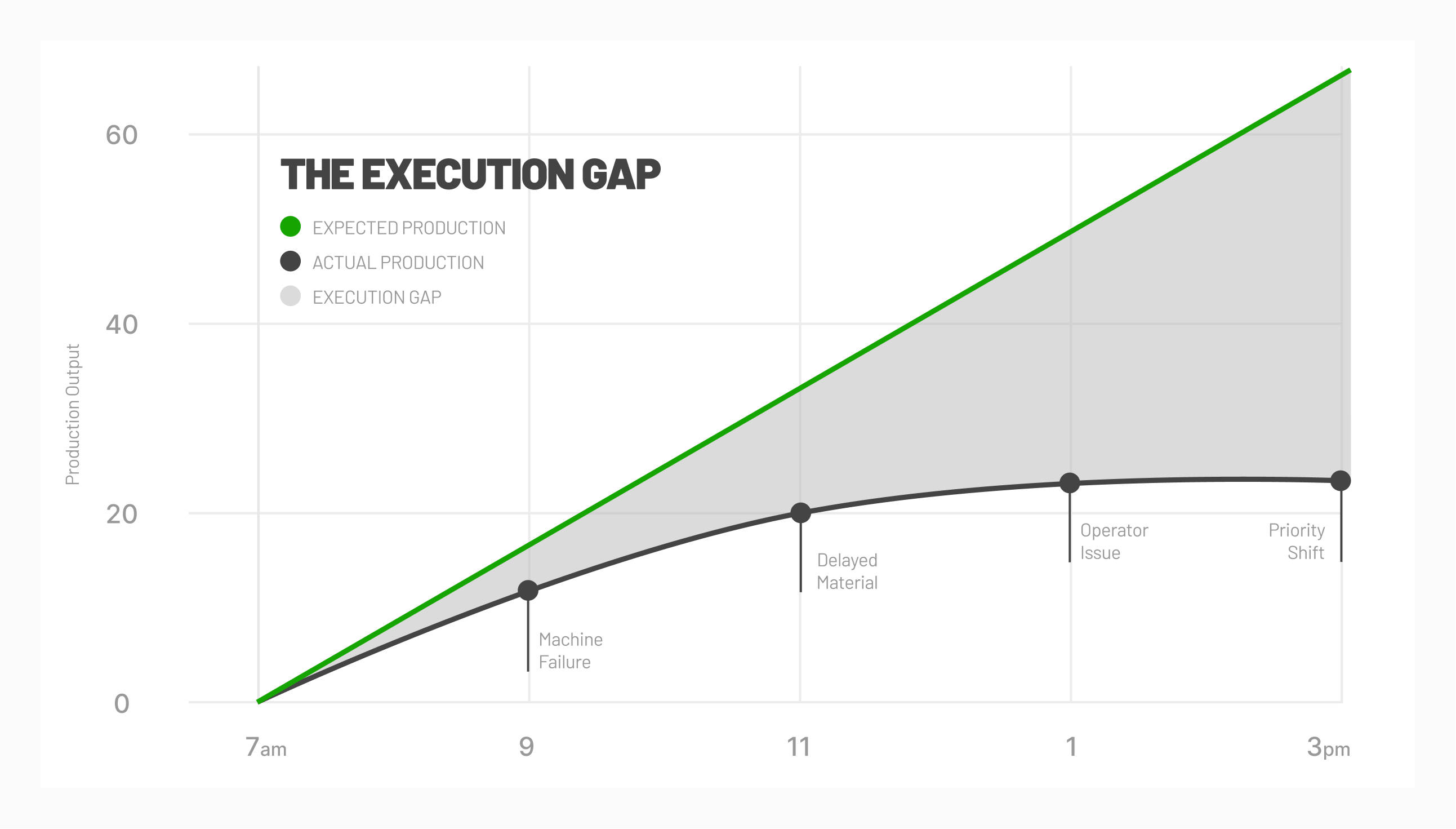
There’s a catch with having no humans monitoring production. If something does go wrong, there may be no one to catch it, which could result in thousands of dollars worth of scrap parts, or significant damage to machines. Luckily, remote monitoring and automated machine failure detection can work to avoid these issues.

What About Maintenance in a Lights Out Factory?
Lights out manufacturers must also be prepared for eventualities like maintenance. While machines may be less prone to errors than human operators, they do not change the laws of chaos. Machinery wears down. Tools will break. However, automation can notably reduce the impact of such instances by narrowing downtime and, sometimes, even dynamically planning for repairs.
Utilizing a high-frequency data adapter, manufacturers can monitor equipment remotely for any abnormalities. With the addition of machine learning technology to seek patterns surrounding breakdowns, this type of system can be used for both predictive and prescriptive maintenance, the two most advanced manufacturing maintenance techniques available today.
MachineMetrics offers a high-frequency data adapter that utilizes the computer systems of manufacturing equipment to capture machine data at a rate of 1000 data points/second—no warranty-voiding actions or sensors required. In addition to accurately predicting when maintenance is near, sometimes forty minutes before a human operator would realize it, machines can be stopped remotely before any damage occurs.
Basically anything a machine can do can be managed remotely by a human or via a tech-based decision tree that results in full automation based on the real-time circumstances of the machine itself, the facility’s production goals, quality assurance, and more. Beyond automatically stopping a machine for repairs prior to causing any further wear or damage to surrounding machinery, this system can offer prescriptive maintenance as well, providing if-then scenario predictions for different actions regarding the machine.
Our tools provide manufacturers with the resources for machine diagnostics, tooling optimization so manufacturers have less breakage and ideal throughput, quality optimization based on tool chatter detection, and, of course, predictive maintenance. They even withstand hostile manufacturing environments, unlike aftermarket sensor solutions.
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



.gif)






Comments