Manufacturing has continuously evolved. Many of the industry’s changes were incremental and, at times, reluctant.
Today, digital factories disrupt manufacturing in ways no one could have imagined. At the heart of this disruption are advanced machine data platforms that make IIoT a reality on the shop floor.
Below, we’ll discuss how digital factories work, how they’re transforming manufacturing, and how you can start your digital transformation.
What is a Digital Factory?
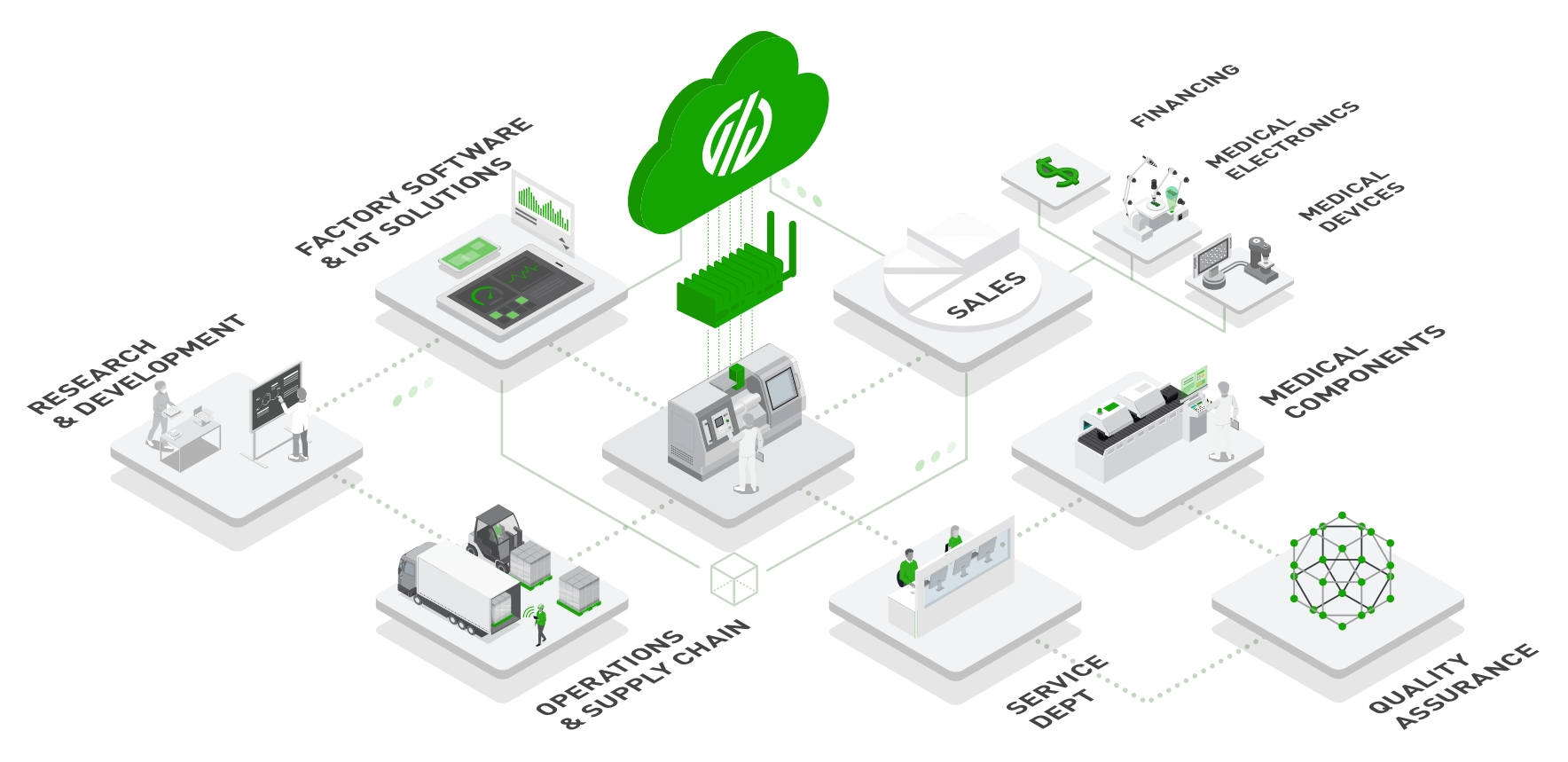
A digital factory -also called a smart factory - uses technology to automatically share information digitally across the operation, including data from materials, people, and machines. Digital manufacturing relies on an integrated system consisting of simulation technologies, connected equipment, and collaboration tools.
There is no single technology that turns an analog factory into a smart factory. However, there are many common technologies and traits that digital factories share, and manufacturers that blend multiple technologies are the ones most likely to be considered “digital factories.”
Digital factories are the result of a digital transformation strategy to enable the use of data from people, equipment, and systems to identify and prioritize continuous improvement initiatives. Technology you might find in a smart factory includes:
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
This consists of small sensors and other hardware that are connected and communicate with one another. They might be used for asset management, energy reduction through smart HVAC and lighting, machine data collection, and more.
Big Data
When IIoT devices collect data, it must go somewhere. Big data simply refers to these massive stores of information that manufacturers can pull from as well as ways to sort and manage this information for use with other tools and analytics software. Interested in learning more about this concept? Read our complete article on “Industrial DataOps."
Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning
Machine learning and predictive analytics are critical for a smart factory. Data can be combined and used to fuel machine learning models that offer decision-making insights from sets of information too complex for humans to derive value from. They can be used to forecast demand, perform predictive and prescriptive maintenance on machines, spot openings and opportunities in the market, and more.

Automation
In a smart factory, connected machines provide the opportunity for humans to step outside of the loop, and allow automation to step in. In many cases, machines are better able to handle tasks faster and more accurately than their human counterparts. Industrial automation frees these humans to focus on other complex cognitive tasks that are better suited for human minds than machine minds (at least for today.)
Some digital factories take automation to the next level using lights-out manufacturing techniques, removing humans from the manufacturing process entirely. This type of smart factory means the ability to start the factory, turn the lights out, and walk out with the understanding that the factory will continue to produce, even 24 hours a day, without human intervention.
Cloud and Edge Computing Technology
Cloud technology empowers digital factories with the ability to store and analyze vast swaths of data using secure equipment they share with others, accessed through the web. Cloud technology affords manufacturers faster and more powerful machines and greater storage capacities (with greater protections) than what is usually feasible to purchase and maintain in-house.
Edge computing takes data coming from the smart factory floor and processes it close by, removing the wait time it can take to upload to the cloud, analyze, and redistribute info to the factory floor. Edge computing enables real-time analytics and ultra-fast decision-making using data, and is perfect for safety mechanisms, predictive maintenance, and similarly time-sensitive computing tasks.
What else do digital factories have in common?
- No Paper: Because processes are digitized, there is no need for paper in a digital factory. Everything is stored on the cloud or locally, in digital format.
- Connected Stack: As mentioned, it’s less about having one technology or another, and more about having a system of integrated technologies. This can include PLC info from the floor, merged with ERP data, merged with MES and SCADA data, etc. This exchange of information between machines allows for quick, data-driven, machine-led decision making at all levels of the manufacturing process.
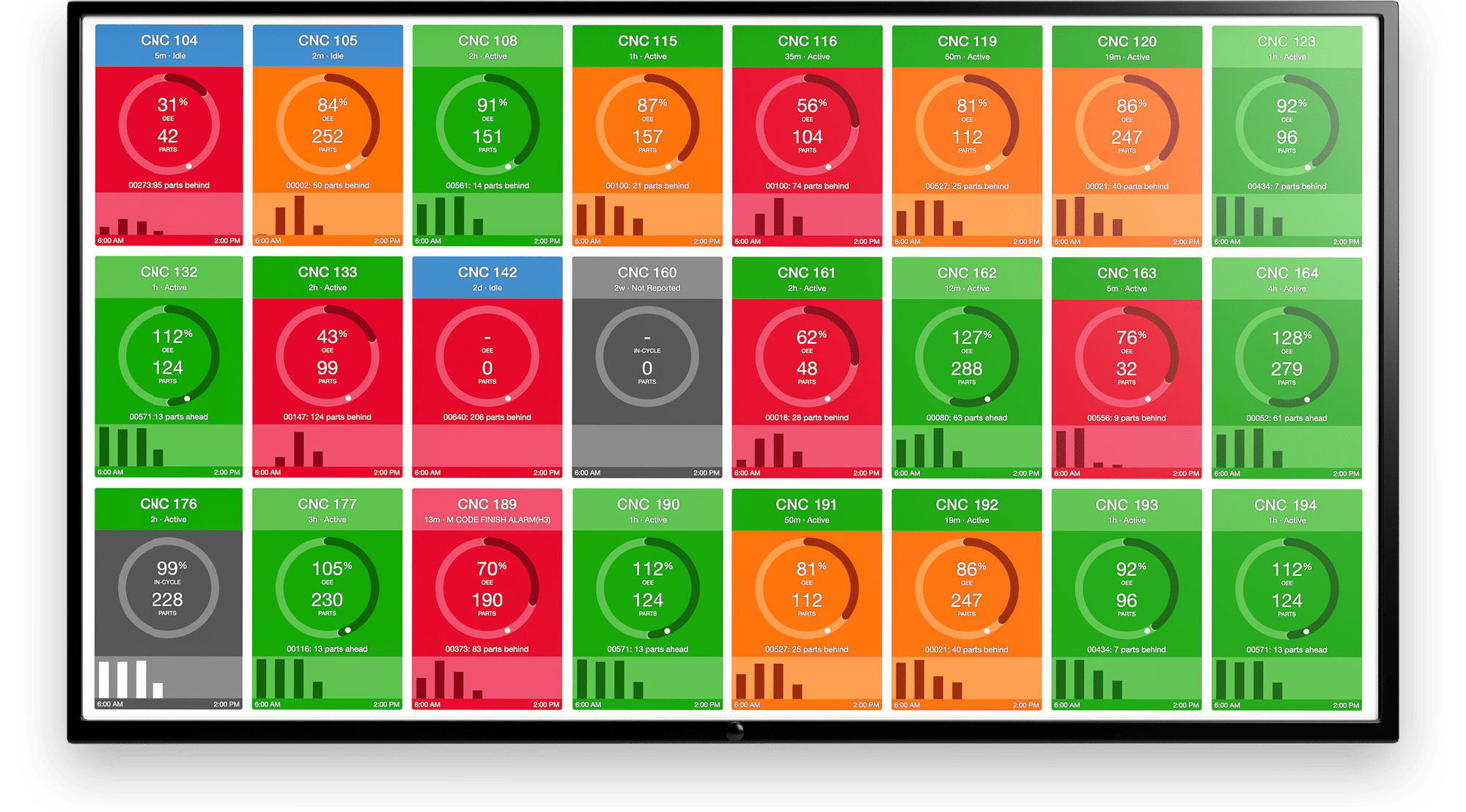
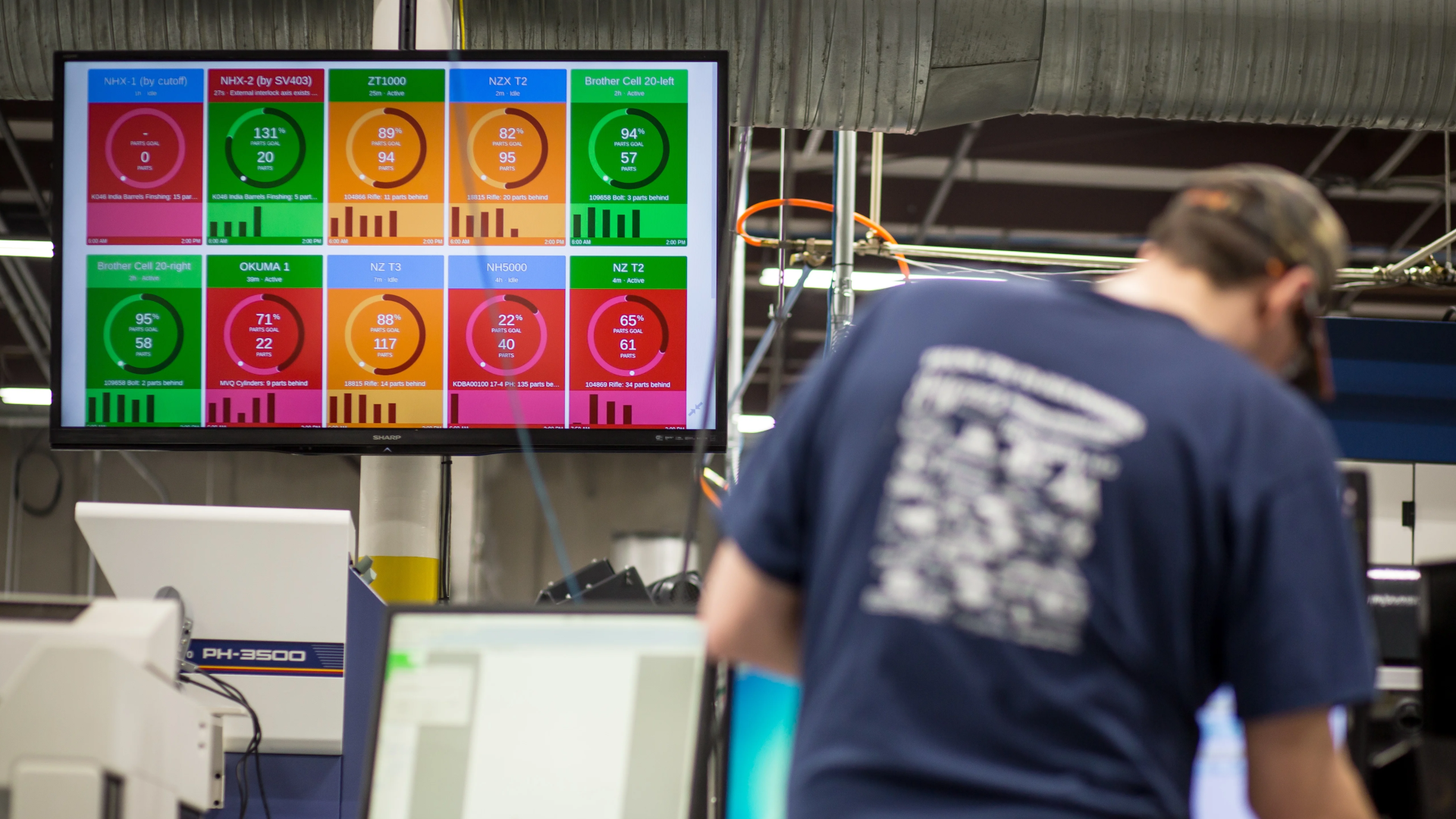
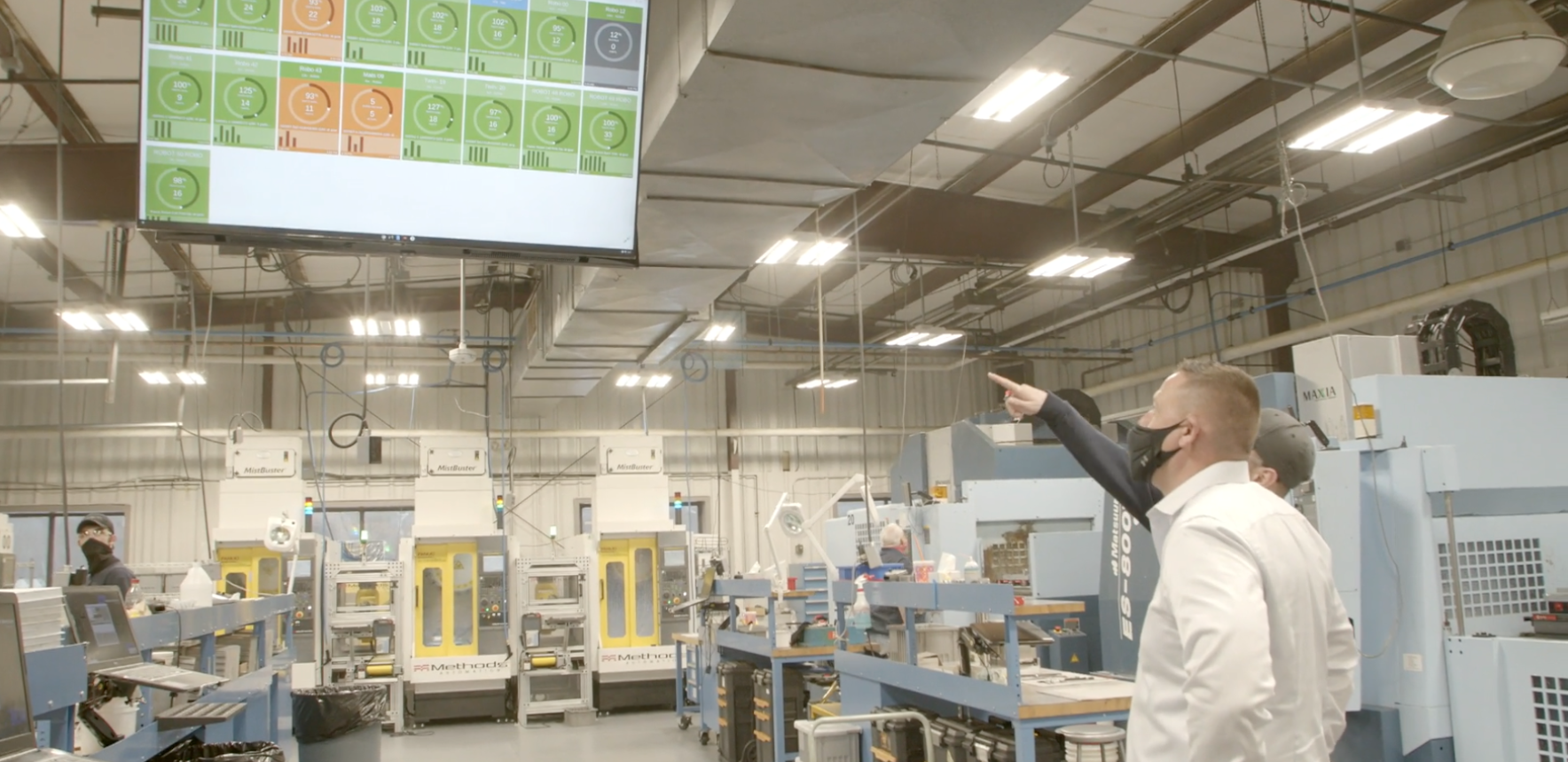
- Real-Time Metrics: To operate with the type of efficiency expected from a digital factory, manufacturers must have access to real-time metrics that let them adjust on the fly to ensure production goals and other company initiatives are continuing to be met—no surprises.
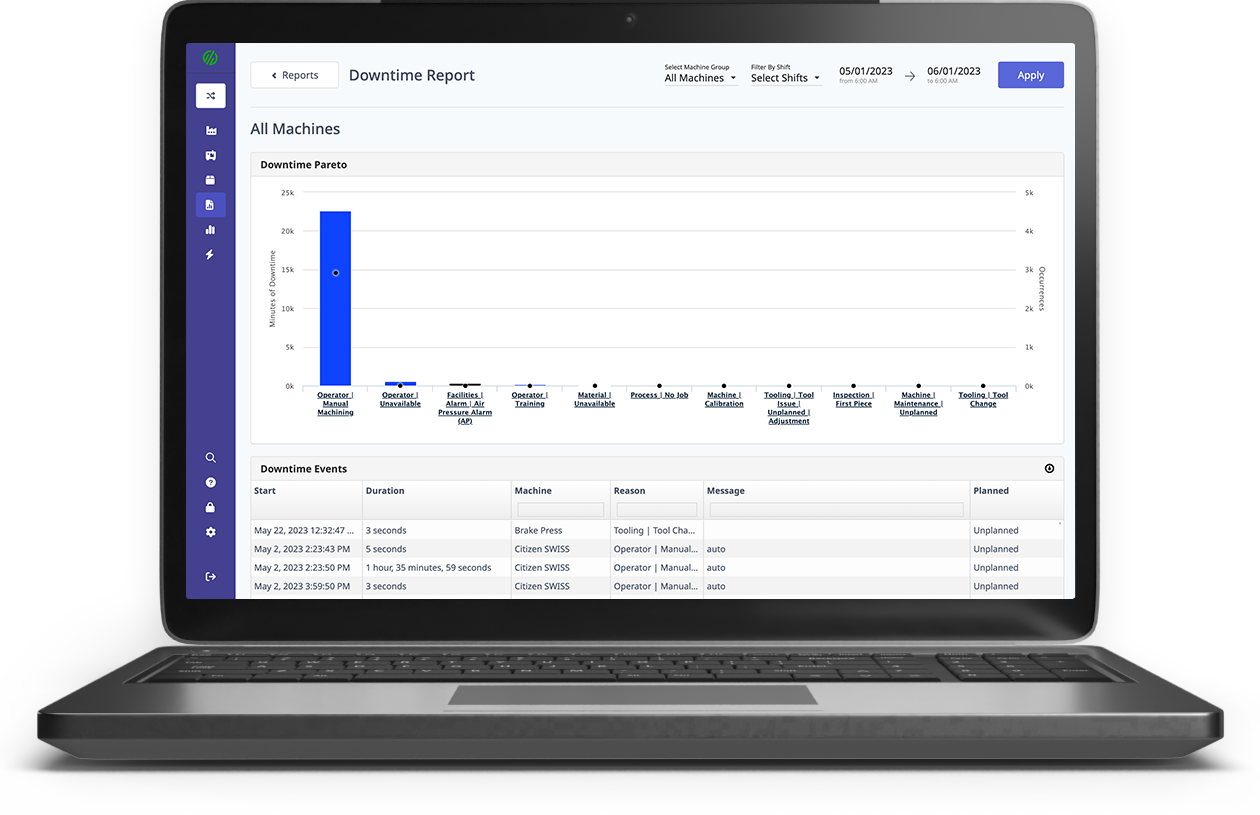
- Big Data Analytics: Having tons of data does no good unless it is processed and analyzed. This type of analysis helps digital factories make more informed decisions that are based on the numbers, allowing them to spot trends, opportunities, problems, and areas to increase efficiencies.
How Does a Digital Factory Work?
A digital factory uses advanced technology to automate manufacturing operations and all business practices within an enterprise. Using connectivity, a smart factory collects and analyzes real-time data from machine assets.
This data is used with an advanced cloud-based machine data platform for process improvement and automation, developing new maintenance strategies, and providing operators and managers with the necessary insights.
Legacy systems are also linked in this journey. This process includes using APIs and other tools to connect legacy software in a two-way, real-time data exchange. The data generated by connected machines are available for use by the software.
Devices are used to retrofit analog equipment and machines so that data from any generation of equipment and any OEM are included. This comprehensive connection of machine assets, enterprise software, and other critical systems means that the entire company and all its processes are operating under a single version of the truth.
AI-driven analytics and advanced machine learning algorithms create complete visibility over the production process and supply chain and deliver the opportunity to automate and improve production performance.
How Digital Factories are Disrupting Manufacturing
Digital factories position advanced analytics at the edge, connecting physical assets to digital resources. This enables automation and process improvement on a scale that’s impossible using manual data collection and analysis.
Digital factories are also extending the power of machine data platforms to other enterprise software like supply chain management. This extension is especially useful for supply chain management, where complete visibility in production processes is also achieved across the supply chain.
Because everyone can access the same data in a smart factory, all business practices focus on manufacturing products with the lowest cost, highest quality, and least waste. Results are seen immediately, and advanced sales and marketing insights are available for new and existing products.
These improvements and savings drive the re-examination of other business processes. For example, IIoT technology significantly increases efficiency, productivity, and equipment utilization, and many companies can re-evaluate their Capex strategy and modify their cost models because of the unlocked capacity.
What are the Benefits of a Digital Factory?
One of the most obvious benefits is a major boost to efficiency. By removing inefficient human decision-making processes that are slow, biased, or incorrect, a smart factory can produce more with less.
Digital manufacturing opens up opportunities for more, new, higher-paying jobs that many people find more engaging and fulfilling. These higher-paying jobs also attract young, new talent to the field with new insights and concepts to better the facility.
A smart factory is also a breeding grounds for innovation. The agility realized with real-time analytics mean there is more room to experiment, be creative, find solutions to new problems within the market, and test ideas at scale without spending unnecessary resources.
Digital factories even see an uptick in customer satisfaction, because costs can go down, shipping times can go down, all the while quality and consistency go up.
How to Implement a Digital Factory
Here are several ways to start your digital transformation and implement a digital factory operating model:
Connect
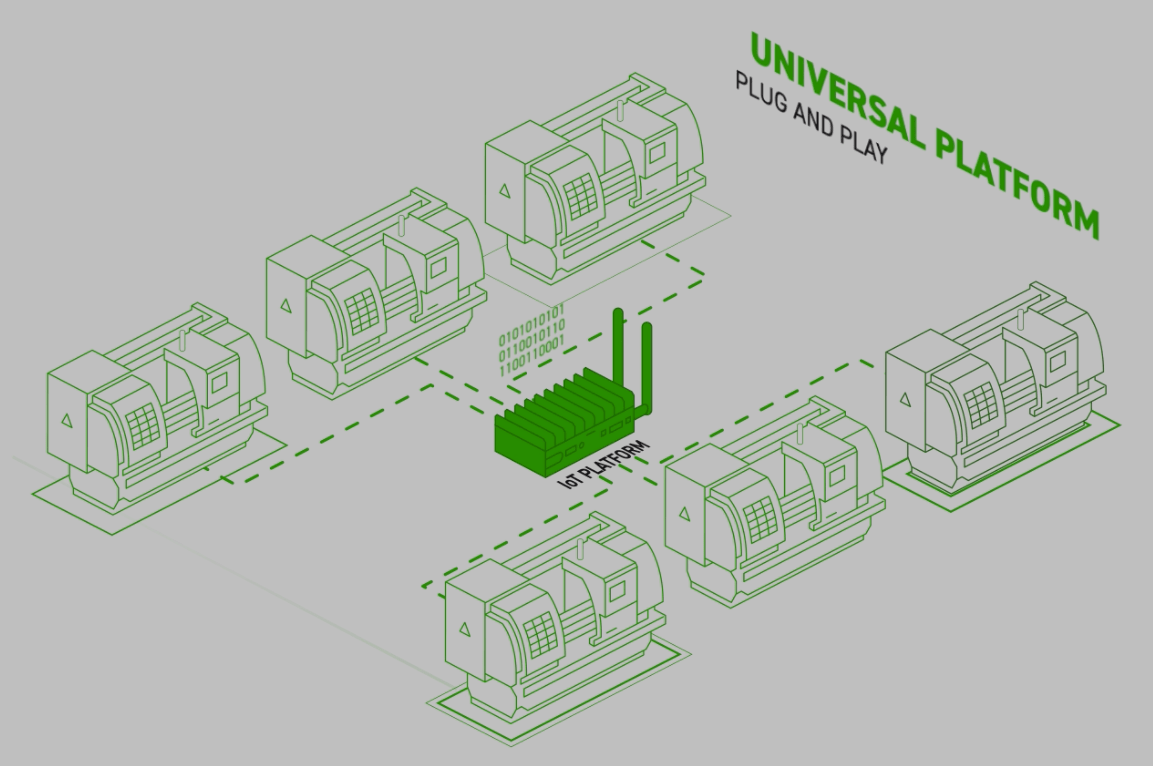
The first step is to connect machine assets. Machine data platforms using IIoT technology allow companies to connect machines from different OEMs and across different generations of the same OEM, including digital and legacy analog equipment.
Assess Current Manufacturing
Companies must thoroughly assess where they stand and the pace at which they plan to achieve a digital factory. Will the changes be incremental or "all in"? How will “buy-in” be achieved?
These questions must be answered, and current performance must be benchmarked to understand where a company is and how to get where it wants to go.
Choose the Right Solution Provider
Many companies begin a digital journey to a smart factory with ad hoc solutions. But this can cause interoperability issues between some devices, platforms, and edge devices.
A comprehensive, AI-driven machine data platform like MachineMetrics offers a turnkey opportunity to proceed. It includes platform analytics, edge devices, and strong customer support across the entire system.
Create a Digital Factory Culture
As digital factory teams move forward and the impact of real-time machine data becomes apparent, creating a digital culture is more manageable. In a digital culture, communication and collaboration are based on data-driven insights. Process improvement becomes easier to accomplish and can be identified by any employee with access to data.
Challenges and Solutions in the Implementation of Digital Factories
Here are a few of the challenges of implementing a digital factory and how you can overcome them:
IT Skills
Many small and medium-sized businesses lack advanced IT skillsets on, adding to the cost of implementation. So, select a trusted solution provider with a track record of customer service. Providers like MachineMetrics offer a system with an intuitive installation that can be up and running in minutes.
Lack of Planning
It’s easy to start a digital transformation to a smart factory without fully understanding what it means and what you want it to do. The solution is to engage early and deep dive into processes to understand where you are and what solution providers best match your organization.
Executives May Fear the Cost
Many solutions are expensive. But with the proper planning and selection, the right solution provider will deliver a system far exceeding ROI expectations. A pilot program can quickly make believers out of skeptical executives.
Digital Factory Software
MachineMetrics supports digital factory initiatives at every level of implementation. From our high-speed data connectors that collect machine data directly from the source at 1kHz (1000x faster than the 1hZ available on most industrial sensors) to our data standardization software that ensures the information you collect plays nice together and can get you results immediately.
Our cloud and edge computing capabilities support both deep analytics and long-term storage on the cloud as well as near-instant, real-time analysis to fuel fast decision making on the edge.
Our customizable dashboards offer multiple views into your data and everyone can access the information they need when they need it in a simple-to-understand, color-coded format. For shop floor workers, we offer tablets directly at the machinery so they can overlay human context with the data we collect. All of this plus industrial-level security has our customers seeing ROI in as little as five days.
Reach out to our team to learn more about MachineMetrics, or book a demo today.

.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)







Comments