The Adoption of Big Data Analytics in Manufacturing
The term “big data” refers to increasingly complex, massive data stores that can’t be effectively processed using traditional methods. In manufacturing, big data can refer to information collected from a variety of sources including machine sensor data, quality assurance information, data from suppliers, production output, maintenance, financial information, and basically any other measurable process that goes into modern manufacturing.
There’s a reason manufacturers are collecting such vast swathes of data about anything and everything. Big data can be processed and refined into business insights that can fuel massive financial growth, customer retention, savings on maintenance, warehousing, and unexpected downtime, and more.
Using the power of big data and manufacturing analytics, manufacturers are more easily able to add efficiency and productivity to their businesses while knowing that the moves they make are calculated and based on accurate data. This adds not only a boost to the probability of success, but also confidence in the ideas that are implemented.
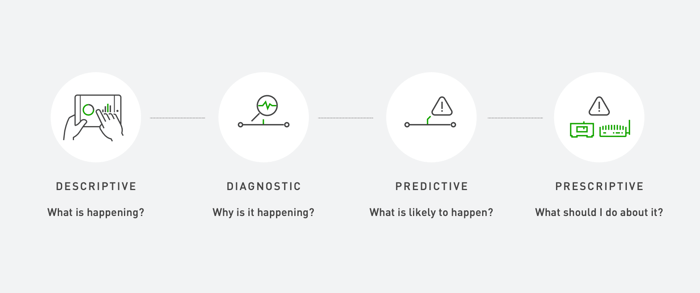
Why is the Use of Data Growing in the Manufacturing Industry?
The answer to this question is two-fold. To make increasingly complex decisions and gain deeper insights, manufacturers are relying more and more on data from a variety of sources. As more data is collected from the shop floor and transformed into usable reports, data-driven decisions can be made that were simply not possible before.
Another reason the use of data is growing in the manufacturing industry is because it’s easier to access. The barrier to entry for implementing IIoT devices and smart factory equipment is at a historical low. Manufacturers can easily and affordably measure many aspects of their business, both in terms of data capture and data warehousing and storage. For example, with MachineMetrics, manufacturers can deploy plug-and-play solutions to provide immediate visibility into shop floor performance.
Additionally, modern markets push manufacturers toward the use of big data in order to stay flexible, efficient, and relevant to their target consumers, while remaining competitive in the marketplace. Data is unlocking the next step in manufacturers’ continuous improvement journey.
Big Data Use Cases in Manufacturing
Big data has a place in nearly every aspect of running a manufacturing business. Some of the most prominent use cases for big data in manufacturing include:
Machine Utilization
When machines are underutilized, manufacturers lose time, money, and opportunity. By analyzing data about when factory machines are utilized, manufacturers can clearly see which machines serve as bottlenecks, which are being underutilized, and which are being pushed to the brink of their capacities.
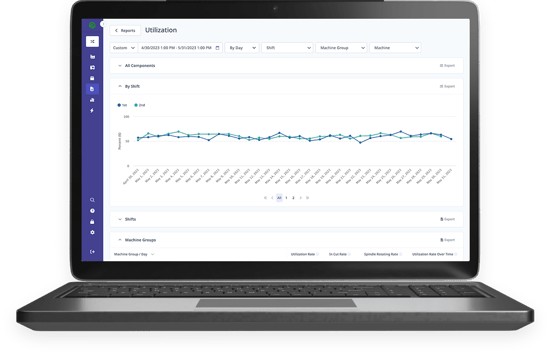
Machine Utilization Report from MachineMetrics.
Product Design
Big data can be used to gather information and inspiration about potential new products, augment understanding of how a product is actually used by customers to develop changes and improvements that better align with use expectations, as well as to determine product viability with greater ease and effectiveness.
Product Quality
Big data has been used with great success alongside machine learning to understand sentiment in customer reviews and support tickets to determine which points of failure are most frequent and frustrating for consumers. Big data can also be used for on-the-line quality control and quality assurance using technology to capture and report machine condition data.
Demand Forecasting
Big data offers manufacturers a peek into the future of what customers will want and when. By forecasting demand, manufacturers realize savings on warehouse costs, wasted supplies, and production time that could be otherwise spent elsewhere.
Customer Experience
Customers will feel more heard when their concerns are addressed. Big data offers the insight to not only address the concerns that arise but to spot and prevent future ones. Also, big data usually leads to higher quality products at lower costs and with speedier times for delivery.
Supply Chain Optimization
By analyzing supply chain data, manufacturers can cut costs both by finding cheaper suppliers and by bundling related products from single suppliers, boost quality, see and find solutions to logistics issues—such as snow storms and natural disasters—to continue business without missing a beat.
Benefits of Big Data In Manufacturing
Manufacturers who make effective use of big data see notable benefits to business from multiple angles. Since data can be applied in a broad manner, both use cases and benefits can be limitless, increasing in complexity and incremental value based on the "data-maturity" of the manufacturer. Some of the top benefits of big data in manufacturing that are usually the first to spur data collection and analysis include:
Competitive Advantage
Access to accurate, real-time production data allows for unprecedented business flexibility and agility that can even mesh with customer expectations. With insight into the shop floor, better decisions can be made with ease, giving manufacturers a strong advantage over less data-savvy competitors.
Innovation
Predicting trends and being able to more quickly iterate on product design leads data-driven manufacturers to innovate better. In the same vein, time and money saved on supplies and production thanks to the use cases above means that manufacturers have more resources and flexibility to commit to innovation while still seeing success.
Lower Costs
Not buying excess supplies, optimizing warehouse space, finding the most cost-effective quality suppliers available, and circumventing logistical struggles all lead to cost savings. Further, machine maintenance that keeps equipment running smoothly reduces downtime and catastrophic (and costly) equipment failure.
Improved Customer Service
The ability to analyze customer data at every stage of their journey from marketing to sales to reviews on social media means that customers are able to receive top-notch, data-driven service that addresses their real wants, needs, and concerns.
Examples of Big Data in Manufacturing
One of our customers, BC Machining, utilizes data to understand when their machining tools are going to break. Via our High Frequency Data Adapter, BC Machining is able to extract high frequency data straight from the control of the machine. After building an algorithm, we are able to predict and prevent machine tool failures by monitoring certain thresholds.
This advanced big data use case has been able to eliminate nearly 100% of scrap parts. Furthermore, it has saved operator time, as BC Machining no longer needs to sort the scrap part, allowing both them and the machines to be focused on producing good parts and generating revenue for the company. The result has been $72,000 in annual savings per machine.
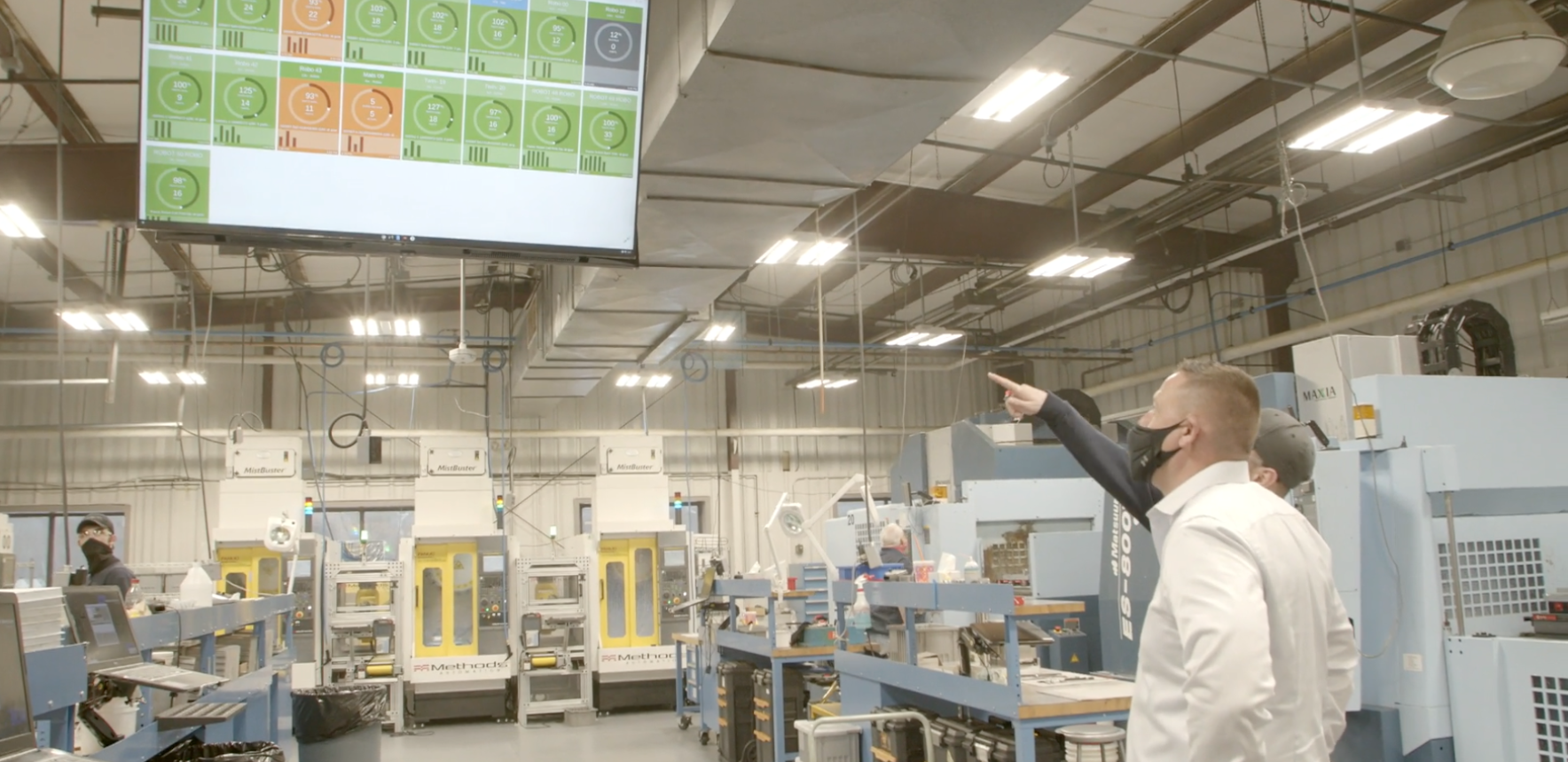
Other manufacturers use big data to keep factory floor workers on track through the use of visible stats that update in real-time. With this, workers are able to understand where they stand in relation to production goals, as well as react quickly to any problems on the shop floor, such as a downtime event.
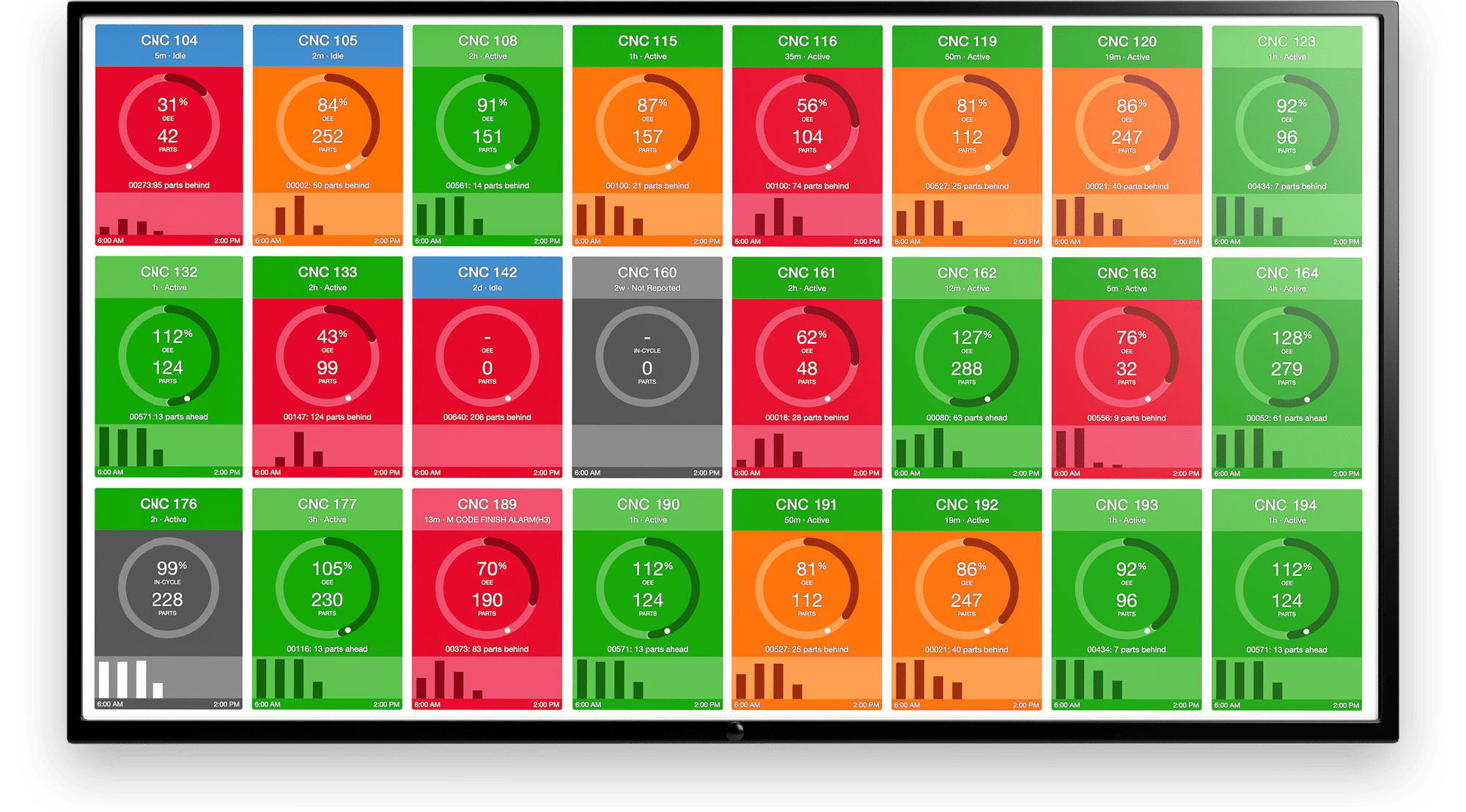
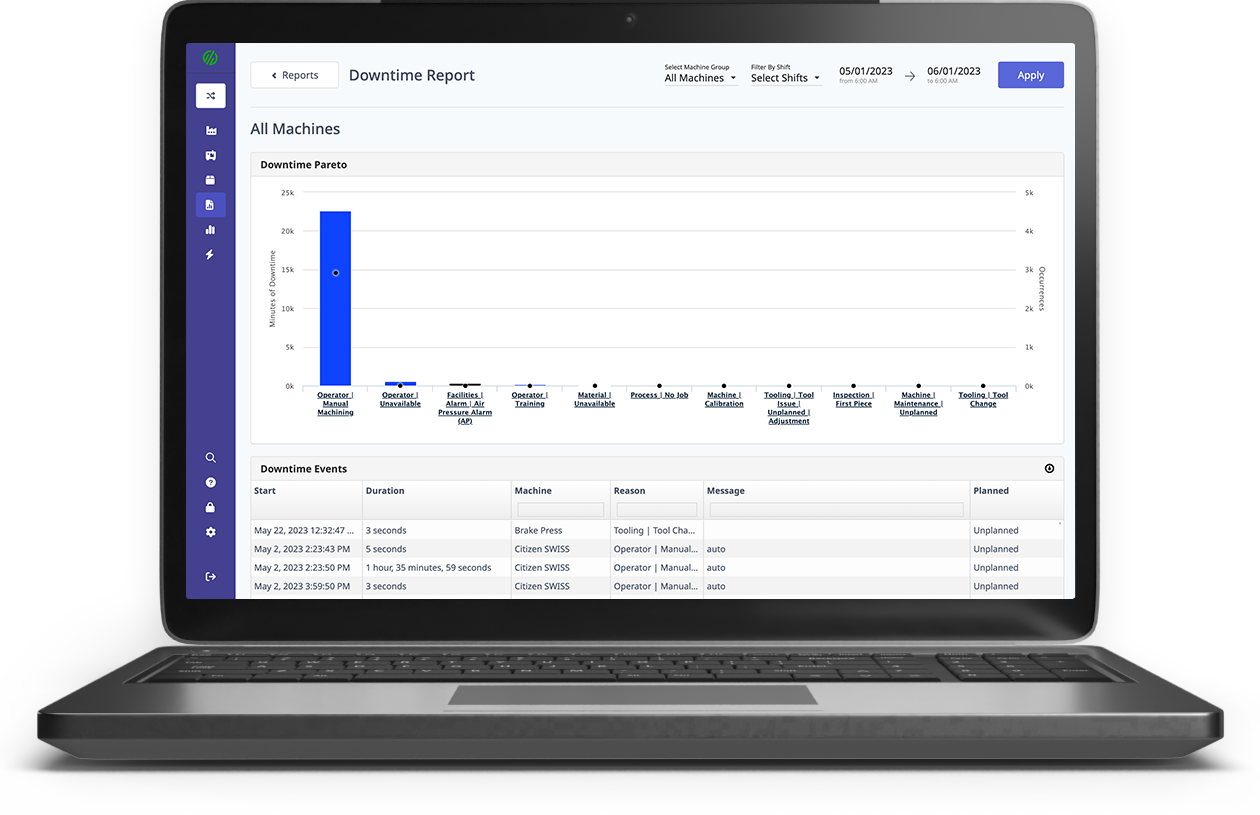
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)








Comments