I/O Modules (Input/Output)
I/O modules are a key component of industrial networking, ensuring connectivity and control of systems, processes, and devices. Ensure data collection from peripheral devices and legacy equipment that is not compatible with desired industrial protocols.
Without Input/Output modules, organizations would be unable to exchange data between peripheral devices and their network. Learn more about the role of Input/Output modules within a connected factory environment.

Input/Output Devices: Unlock Peripheral Device Connectivity and Control
What is an I/O Module?
Input/Output Modules, or I/O Modules, manage the communication between a CPU and a network, including the transfer of data, the management of power loads, and the control of machine functions.
This enables system integrators to connect disparate devices, allowing greater control of the industrial network. I/O modules are especially helpful in instances where there exists legacy machinery, devices, and systems that are unable to natively communicate with a desired industrial protocol.
I/O modules help to extend a manufacturer's network to incorporate all manufacturing equipment, enabling greater control of the system as well as increased operational visibility. They also overcome the challenge of collecting peripheral data, which can come in various amounts, at different speeds, and in varying formats.
Some of the devices from which data can be collected using an I/O module include sensors, actuators, monitors, and valves. I/O modules can also work as accessory devices for PLCs and HMIs.
What are the Core Functions of an I/O Module?
I/O modules offer a variety of key functions within an industrial environment. Without Input/Output modules, organizations would be unable to exchange data between peripheral devices and their network. Below we outline the critical functionality of I/O modules:
- Detecting Errors: I/O modules have the ability to detect errors and report them to the CPU. One way that I/O modules detect errors is with the parity bit method.
- Processor Communication: This critical function of an I/O module involves a few components:
- Command Decoding: Receive and decode commands sent from the processor.
- Data Exchange: Exchange data between peripherals, processors, and the main memory.
- Status Reporting: Communicate the status of peripherals to the processor.
- Address Decoding: Organizes each of the peripherals connected to the I/O module by managing their unique addresses.
- Buffering Data: With data buffering, I/O modules can manage the transfer speed of data sent by the processor to peripheral devices. This compensates for the latency of peripheral devices.
- Device Communication: I/O modules can facilitate communication between connected peripheral devices.
- Control and Timing: I/O modules are designed to manage the data transactions between the internal system and peripheral devices.
What are the Different Types of I/O Communication Techniques?
There are three types of I/O communication techniques:
- Programmed I/O: In this case, the transfer of data from an I/O device to the memory will require the CPU to initiate a program. The CPU remains in a loop until the I/O device is prepared to make the data transfer.
- Interrupt Driven I/O: In this case, the CPU offers a read command to the I/O device and once the I/O device is prepared to transfer data, it sends an interrupt signal to the processor. Upon this event, the CPU then checks the status of the device and will write that information into the memory if it is ready.
- Direct Memory Access (DMA): In this communication technique, the I/O device can both send and receive data directly from the memory, bypassing the CPU altogether and enhancing the speed of memory operations.
What are the 3 Categories of Input/Output?
There are three types of I/O operations:
- Sensory Input
- Digital Input
- Analog Input
- Control Output
- Direct Digital Output
- Modulated Digital Output
- Analog Output
- Data Transfer
- Parallel
- Serial
What is the Role of I/O Modules in PLCs?
I/O modules exist within PLCs or can be added to PLCs to increase functionality, connectivity, and control of processes. They play an important role by processing communication that is sent to the PLC as well as accepting commands sent by processors. This enables them to detect errors, exchange data, buffer data, and manage data transactions between internal systems and peripheral devices.
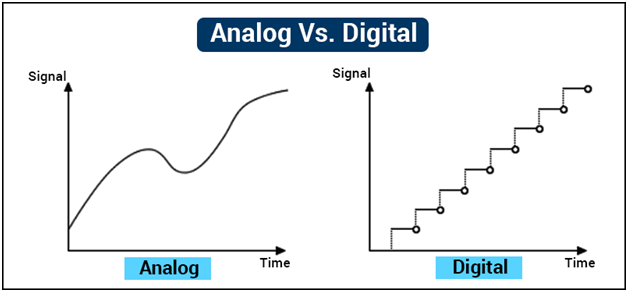
What is the Difference Between Analog and Digital I/O?
Analog and Digital I/O refer to the type of signal being transmitted between devices and systems within an I/O operation.
Analog Signals
Analog signals are continuous in both the value they represent and the time they correspond to. A good example to think of is a sound wave, which represents a continuous measurement of sounds over time. Other examples could be current or voltage.
Digital Signals
Digital signals are binary. Think “On” or “Off”, “1” or “0.” In this regard, they are discrete, rather than continuous, like analog signals. With the prevalence of digital technology, digital I/O is overtaking Analog I/O as the standard to collect data. However, analog is still in use and can be converted to digital signals as well.
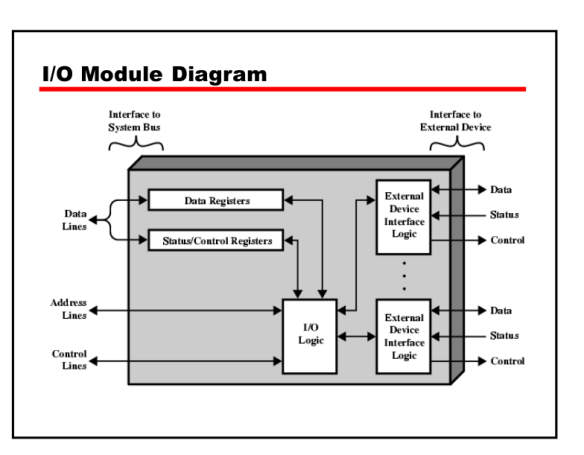
What is the Structure of an I/O Module?
How Do I Ensure Connectivity to All Equipment?
This is where a connectivity solution like MachineMetrics comes into play. MachineMetrics is an Industrial Data Platform that enables connectivity to any make and model of equipment, including both modern equipment and legacy assets.
MachineMetrics is the leading platform to collect, monitor, analyze, and drive action with manufacturing equipment data. Our platform easily captures data from your manufacturing equipment and provides a complete toolkit to drive actionable insights for frontline workers and other factory floor systems that improve the efficiency and quality of production.
Whether the equipment is compatible with widely adopted industrial protocols or not, you can easily connect and collect data across all your devices for complete operational visibility.
Want to see the platform in action? Book a Demo Today.