When is it risky to wait? When everyone else is moving forward. Utilizing smart manufacturing technology sooner rather than later is the smart choice. Industry Week reported that most manufacturing companies have been working on at least one smart manufacturing project since the end of last year and that "moving to smart manufacturing can help you reach and serve customers better and more profitably." They also said that many businesses are experimenting by adding sensors to their existing equipment. Why not give it a try?
What is Meant by Smart Manufacturing?
Smart manufacturing is the concept of using real-time data to deliver actionable insights that drive process improvement, process optimization, increased equipment utilization, and highly flexible responses within smart manufacturing systems.
This use of data leads to smart manufacturing plants where production equipment is integrated with data collection, analytics platforms, and other new technologies. Smart manufacturing uses a variety of technologies to make this happen. These technologies and tools include computer controls, data modeling, robotics, and edge computing.
The concept of smart manufacturing has been around for many years, but technology is now making it a reality. It’s rooted in the growing adoption of digitization in the manufacturing process. As mass-production systems grow to meet supply consumers' needs in a growing global economy, data created by the merging of cyber-physical systems is increasingly used to improve overall operations.

Manufacturing equipment is connected by sensors or devices to monitor and collect data during the manufacturing process. This data may be directly streamed to the cloud, or it may employ edge or fog computing to process it before being sent to the cloud. The data received by the cloud uses a host of emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), advanced data analysis, robust machine learning algorithms, and machine monitoring platforms. It then transforms the data into actionable insights that can be used for sharper decision-making.
The benefits of smart manufacturing extend to the entire enterprise. Insights are used to address issues within the supply chain and develop predictive maintenance programs. Smart manufacturing can even provide valuable data analytics to enhance the value of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
The arrival of smart technology in the manufacturing industry is changing how companies do business. With intelligent manufacturing, an entire manufacturing business can transform into a leaner data-driven company that reaps significant benefits and revolutionizes business processes.
How Smart Manufacturing Relates to Industry 4.0
Let’s look at the development of industrial equipment and review each successive revolution that ushered in enormous gains in productivity.
During the first industrial revolution, manufacturing moved from the hand-crafted home-based model to the factory. Innovations such as water and steam power made mass production commonplace.
The second industrial revolution saw further innovations such as improved steel making and the electrification of factories. A human could now operate a machine to produce a much greater volume of goods compared to the era of hand-crafted products.
The third industrial revolution saw the computer introduce automation and take manufacturing processes to even higher productivity levels. This enabled extensive process improvement and efficiency gains.
A collection of emerging technologies is now powering the fourth industrial revolution known as Industry 4.0. It consists of a suite of technologies such as the industrial internet, artificial intelligence, machine learning, additive manufacturing, edge computing, robotics, augmented reality, and other smart technologies.
| What is Industry 4.0? Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, or 4IR, is an all-encompassing term to refer to the way computers, data and automation are evolving and coming together to change the way work happens, and in particular, manufacturing. Read the Complete Guide. |
What is Industry 4.0? Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, or 4IR, is an all-encompassing term to refer to the way computers, data and automation are evolving and coming together to change the way work happens, and in particular, manufacturing. Read the Complete Guide.
These technologies allow manufacturing plants to leverage the vast data created at every piece of equipment to improve efficiency, enable smart services for added revenue, and deploy cyber-physical systems that increase operational efficiency and impact growth strategy.
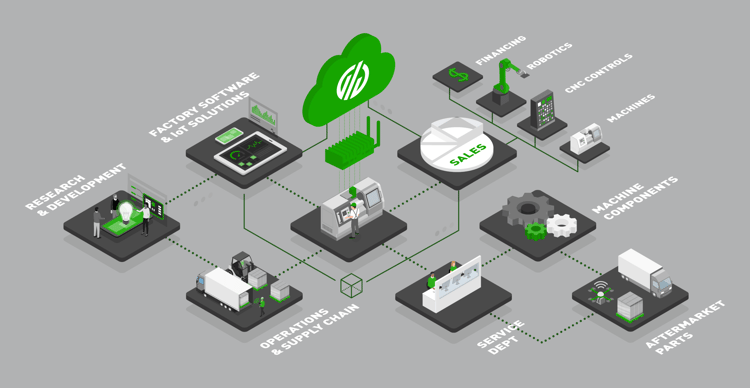
Here are some key areas where smart manufacturing relates to Industry 4.0:
Significantly Increases Operational Efficiency
By leveraging data, companies can create an end-to-end visualization of the production process. Real-time data and advanced data analytics mean that previously unnoticed trends can now be detected. This data can then be contextualized and delivered to users - from interactive HMIs at the point of operation to managers or technicians for faster, more accurate decision-making. These connected systems are then linked to ERP systems, quality software, financial software, and other functional areas. This creates an efficient and productive smart environment.
Reduces Machine Downtime
Downtime is one of the most significant wastes of resources. With Industry 4.0 technologies, companies can detect problems before they happen. Data analytics provide machine state down to the spindle level, allowing operators to make changes quickly. For unplanned stops, alerts and alarms are sent to technicians who can then stage equipment and parts for the repair during the next changeover. This big data processing means companies can develop prescriptive and predictive maintenance programs based on actual conditions while monitoring and deploying a long-term strategy to reduce downtime across all equipment.
Drives Worker Safety
Industry 4.0 technologies can help in creating the safest environment ever known in manufacturing. Robotics linked to a factory IIoT monitoring platform can perform dangerous tasks previously done by humans. Alarms and alerts also enable operators to detect failure conditions and safely stop equipment - protecting both operators and equipment from harm. In fact, 41% of manufacturers using Industry 4.0 technologies report a significant increase in worker safety. Entire factory monitoring systems for heat, humidity, gas/fume detection, and other ambient conditions can be programmed to work in conjunction with machinery to create a smart factory ecosystem with exceptional safety standards.
Takes Charge of Inventory Management and Optimization
Whether raw materials, WIP, or finished goods, inventory is always on the manufacturing manager's mind. A smart factory can use Industry 4.0 technologies for accurate scanning upon receipt, location, and picking. Sensors and devices such as RF also allow tracking of WIP so value-added steps are accurate in real-time. Industry 4.0's IIoT platforms enable deep data analysis for robust ABC analysis that helps prioritize high-profit goods during demand spikes or disruption in the supply chain. By integrating real-time data with ERP and other financial software, inventory costs can be automated.
Significantly Enhances Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management is vital for manufacturing. Smart manufacturing's use of sensors, edge computing, and the industrial internet allows many Industry 4.0 technologies to improve supply chain performance. Advanced data analysis means companies can set reliable MOQs. It also enables them to determine the need for buffer stocks and optimize buffers accordingly. Demand planning can be modeled to provide accurate forecasts, and systems have the analytical strength to allow robust "what-if" contingency planning to stay ahead of disruption.
The Potential of Smart Manufacturing
Smart manufacturing's potential is vast. Intelligent factories with attached devices can deliver data in real time and link to analytics engines using cloud-based computing. This connection makes a smart factory more responsive and flexible.
Data directs the operation's activities and tells the manufacturer what to do. This impacts the entire enterprise, not just the production department. Quality systems can use Artificial Intelligence (AI) for in-line visual inspection and precise weight and measurements per unit. Like production systems data, quality data is immediately available for better decision-making.
This same collection of sensors will give real-time visualization of machine status. Operators can respond faster in production, reduce downtime, clear jams, and report problems to technicians. When combined with AI and ML algorithms, these sensors and devices can allow predictive maintenance programs that pull machine maintenance out of the passive, reactive state and into a proactive value-added function. This helps manufacturers control cost, reduce downtime, and lengthen equipment lifespan.
Smart manufacturing can also generate new products and value-added services. The capability of monitoring a product through the end of its lifespan is a gamechanger that opens companies up to an unprecedented level of field service and helps them design better products down the road.
This potential is already proving itself through results. For companies utilizing Industry 4.0 technology to develop smart manufacturing, 88% report higher productivity, 74% report higher profitability, 43% report an increase in customer satisfaction, and 42% report an increase in machine uptime. These benefits cannot be overstated.
 MachineMetrics unlocks real-time, accurate production data for instant visibility into operations, enabling smart manufacturing from the shop floor to the top floor.
MachineMetrics unlocks real-time, accurate production data for instant visibility into operations, enabling smart manufacturing from the shop floor to the top floor.
The Benefits of Smart Manufacturing
There are many benefits to a smart factory implementation:
Increased Productivity
Traditional manufacturing processes can hit a ceiling, but a smart factory increases productivity. As big data capabilities are brought to bear through advanced Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms, companies immediately realize areas for process improvement.
Real-time data insights can be put to work to increase OEE and efficiency. Optimized manufacturing processes also mean raw materials are utilized more efficiently and quality is improved. All these forces converge to raise productivity.
Lower Operational Costs
Smart factories will usually experience an immediate drop in operational costs. Data automation as part of a digital transformation helps improve manufacturing performance and enable more efficient production. This efficiency gain leads to lower labor costs, less scrap, higher throughput, and reduced inventory costs.
Greater visibility also results in reduced equipment failures. Real-time data is turned into advanced maintenance strategies centered on data-driven details of machine health and condition. This visibility extends to raw materials and the entire supply chain for end-to-end visibility across the enterprise.
Better Control Over Business Processes
Smart manufacturing utilizes advanced analytics in a comprehensive platform that includes AI-driven analysis, machine learning, digital twin technology, and more. It also integrates seamlessly with legacy software through APIs and apps so all systems have access to real-time data.
Immediate visibility enables business processes across quality, maintenance, finance, planning, and more to be optimized using the same tools and data used on the production floor.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
Traditional manufacturing processes were siloed and disconnected. Smart factories leverage data between departments to remove silos and create collaborative manufacturing systems.
One example is change management, where design specs or change orders often require a chain of approval. By automating approvals, changes are available as soon as they’re approved. This reduces confusion and lets departments run with higher confidence that what they’re producing is the correct product in the correct volume.
Higher Customer Satisfaction
Smart machines result in happy customers. Smart manufacturing facilitates this by reducing lead time, unlocking hidden capacity to meet growing demand, and producing schedules that meet or exceed quoted delivery times.
Better Maintenance Strategies
Capital equipment is one of the greatest expenses for any manufacturer. With AI-enabled machine monitoring and condition monitoring, smart factories open the door to advanced maintenance strategies.
These strategies include predictive maintenance, which uses real-time data to monitor machine health and prescribe maintenance. It also monitors machine health so repairs can be made before they become a problem, reducing breakdowns, part costs, and downtime.
Smart Manufacturing Challenges
Like all revolutions, progress to full digitization will take time. Along the way, several obstacles must be overcome. These may include:
Security
The internet alone sees tens of thousands of security breaches every day, and the industrial internet is no different. Fear over system security has long been on the mind of manufacturing managers, but today's cloud computing systems are more secure than ever. While the perception of lax security is there, the reality is that breaches are much more likely to come from user stations within a company than through a cloud hack. Learn more about security for IIoT.
Lack of Uniformity
While smart manufacturing technology is steadily increasing, the industry is still very fragmented. DIY systems abound and companies are often required to match devices from one supplier to software from another. There are also different connectivity methods, from wired to wireless to cellular. Companies often lack the in-house skillsets needed to connect, sync, and deploy a system from other vendors. MachineMetrics eliminates this problem with a turnkey suite of devices that can connect through numerous methods to ensure data isn’t only collected but also transformed and standardized to drive value.
Interoperability
Many supplier software systems aren’t fully interoperable with legacy enterprise software, leading to reluctance to deploy. Alternatively, suppliers may use the IoT software's IP strength to force manufacturers to buy additional software they don’t want or need. In contrast, the MachineMetrics platform integrates through API with existing enterprise software to enhance its capabilities, not obsolete it.
Job Loss in Manufacturing and IT
With a high level of autonomous or semi-autonomous machines, many workers may fear losing their manufacturing jobs. This fear is also true of IT professionals who fear being overwhelmed with deploying a radical new system only to be let go and replaced by a robot.
The Application of IIoT with MachineMetrics
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) offers an enormous opportunity to achieve smart manufacturing powered by Industry 4.0 technologies. MachineMetrics offers out-of-the-box functionality to make this a reality. Our platform also enables advanced analytics, machine learning, and the connection of devices across a factory (including new OEM and legacy analog manufacturing equipment).
MachineMetrics understands that smart manufacturing doesn’t need to be cost-prohibitive or ad hoc. By utilizing the best-in-class platform, companies can realize the benefits of smart manufacturing and capture unprecedented cost savings, higher productivity, better quality, improved processes, and a competitive edge in their smart manufacturing environment.
Accurate Data Drives Smart Manufacturing
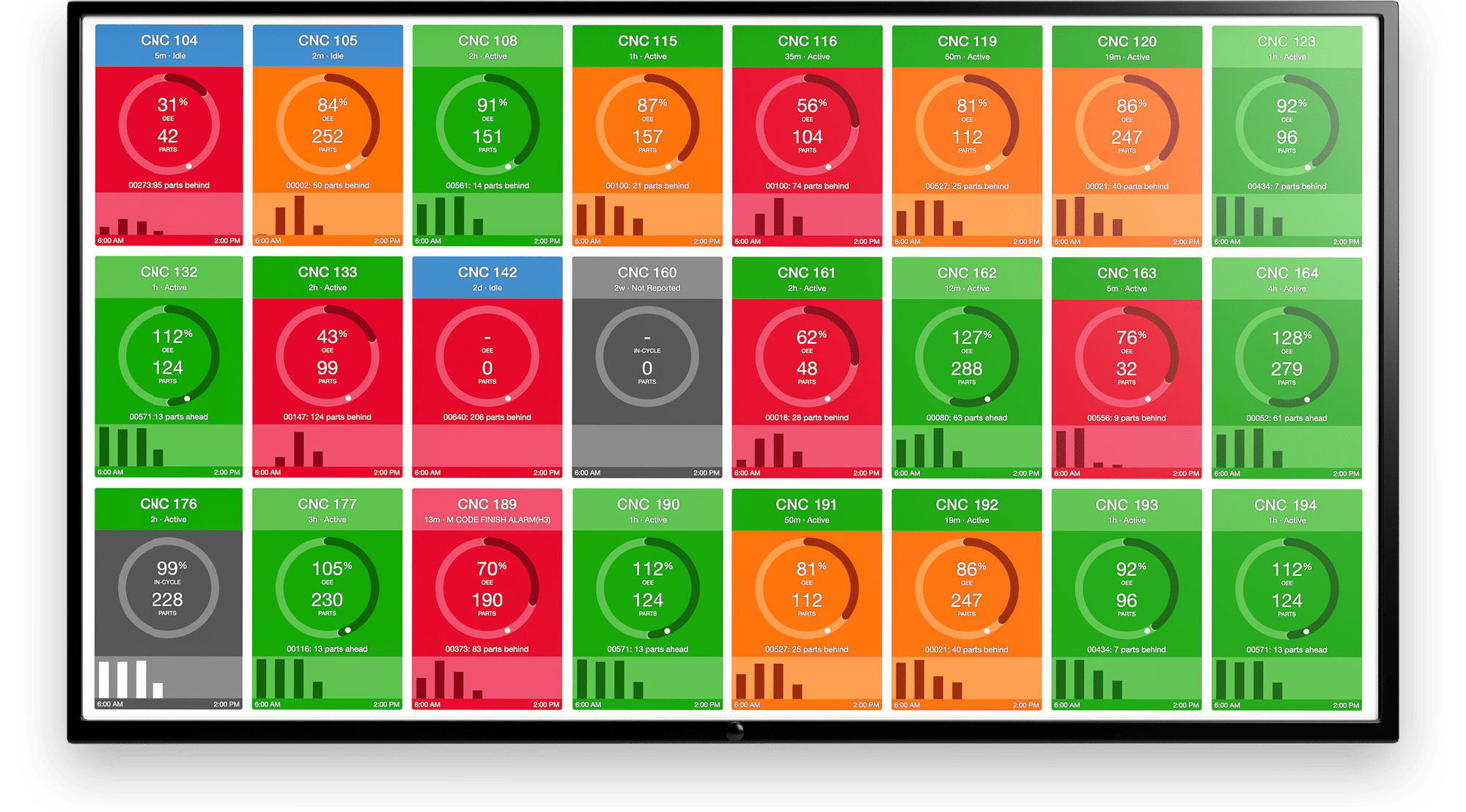
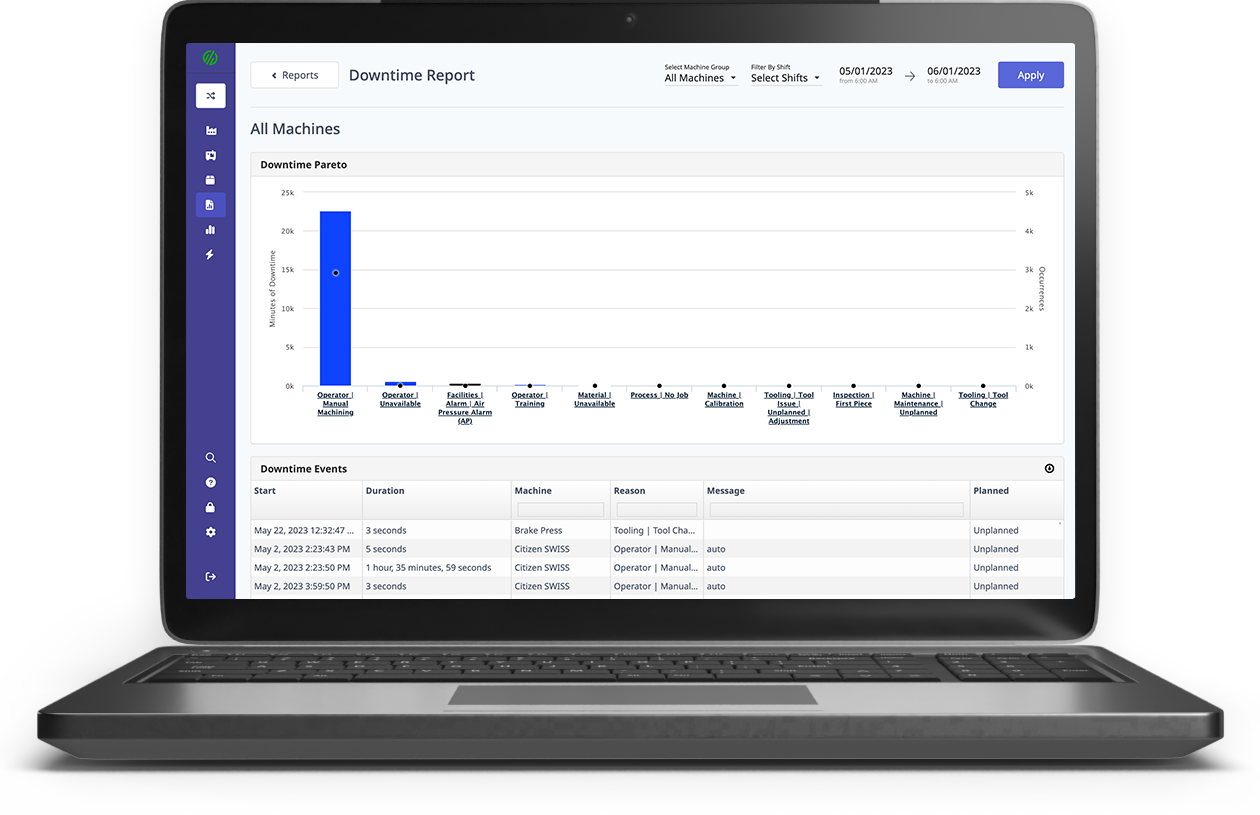
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



.gif)






Comments