Paradigm shifts define the world as we know it. One example is IT services and how they were managed in the earlier days of the digital transformation. Two decades ago, enterprises who intended to use digital technology to optimize business operations had to set up physical data centers, develop specialized apps and employ professionals to keep the entire architecture running. This cost hundreds of thousands of dollars and only large enterprises could follow through on a digital transformation strategy.
Then a paradigm shift occurred. Cloud computing, Software as a Service (SaaS) and open-source technology changed the entire digital transformation landscape irreversibly. Now, enterprises spend less than $2000 setting up a digital process for handling business operations and the responsibility of maintaining used solutions are left in the hands of vendors. Today, the original equipment manufacturing industry and equipment users are in the middle of an ongoing paradigm shift. This shift is Equipment as a Service (EaaS).
What is Equipment-as-a-Service?
Equipment-as-a-Service, or EaaS, is a business model that involves renting out equipment to end users and collecting periodic payments for use of the equipment.
This service-driven business model, also known as Machine-as-a-Service, provides a variety of benefits to both the EaaS provider (OEMs and Machine Builders) and the customer (manufacturers), both of which we discuss in detail below.
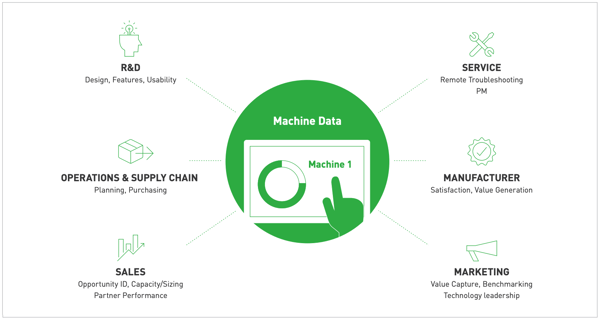
Why use an Equipment-as-a-Service Model?
In the early years, machine data, when collected, was limited to output data and was used to determine product quality, scheduling, and finance calculations. Although this ensured manufacturers could calculate the profit from production cycles, the collected data provided no insight into machine health, how to improve machine design, and machine operational capacity. This meant both OEMs and the end-users were flying blind in relation to understanding the true performance of equipment.
With industry 4.0 comes new ways to assess machines and entire operations. These new ways are powered by IIoT, IoT platforms, cloud computing, and edge computing. These interrelated technologies bring interconnectivity to shop floors and now illuminate the darkest parts of factories. Thus, creating new avenues for OEMs to provide equipment for end-users and a different system for how manufacturers obtain and use shop floor equipment.
EaaS can be defined as a paradigm shift in how manufacturers design equipment with smart manufacturing in mind with the focus on providing equipment as a service instead of a product. Within this definition, there are two types of Equipment as a Service models to take advantage of. These models include:
Model 1 – The first model involves OEMs providing equipment to enterprises through a subscription-based model. In this model, the equipment is located at the facilities of the subscribing party. The manufacturer leases the machine for a specified duration and the subscription fee will cover maintenance and repair tasks which leave software update and spare parts replacements in the hands of the OEM vendor. As payback, the OEM will own the equipment data and use it for research and development, for predictive maintenance or whatever they chose to use it for.
Model 2 – The second model involves manufacturers and OEMs outsourcing factory equipment to customers for specific durations. This means customers who do not have specific equipment that is needed for specialized applications due to equipment cost, can meet service providers and use their equipment within the equipment provider’s facilities. The payback for the service provider includes subscription payments, machine data, or in some cases, a percentage of the final sales made.
The Benefits of Equipment-as-a-Service to OEMs
Equipment manufacturers turned service providers have a lot to gain from EaaS. These benefits combine both a new way to generate revenue and a front row seat to witness how the smart factory evolves. Some of the value-added propositions of EaaS include:
- Improved Equipment Design – Connecting provided equipment to the cloud of IoT devices to IoT platforms ensures the data sets from diverse production cycles are collected, analyzed, and sent to R&D departments for use. The feedback from machines allows for data-driven improvements to machine features, capacity, and operations.
- Developing Predictive Maintenance Strategies – One of the expected gains of smart manufacturing is predictive maintenance. EaaS provides opportunities for OEMs to design equipment and integrate predictive maintenance regulations within them right out of the box. In this case, the historical data collected from prior equipment uses and failures serve as the information needed to design a predictive maintenance strategy for designed equipment.
- Revenue Growth – EaaS creates a new stream for securing revenue for OEMs and manufacturers interested in leasing equipment to clients. On the side of the OEM, leftover stock can be turned into streams of revenues by offering manufacturing SMEs with subscription plans that fit their financial capacities. While for manufacturers, equipment that remains dormant after completing a production cycle can be leased out to third-parties in need of such services.
The Benefits of EaaS for Manufacturers
The end-user in every EaaS model is the manufacturer or the party who uses the equipment for production-related activities. In this case, the benefits of EaaS to the end-user include:
- Reduced Capital Expenditure – Purchasing manufacturing equipment is a capital intensive expenditure many manufacturers struggle with. Traditionally, SMEs tackle these higher costs by outsourcing specific components to contract manufacturers which leaves them with no control of the manufacturing process. EaaS provides an opportunity to turn CapEx to OpEX while ensuring the SME remains in charge of the production process and the quality of products manufactured.
- Increased Data Reliability – EaaS also involves providing equipment and production benchmark data to manufacturers to help optimize machine utilization and productivity. The accuracy of the benchmarked data can convince SMEs to integrate data-driven strategies that optimize productivity.
- Lower Operating Costs – In EaaS, the task of maintaining manufacturing equipment, updating software, firmware or hardware is the responsibility of the service provider. This cuts down on the operational expenditure of manufacturers and helps SMEs focus on their core responsibilities of manufacturing.
EaaS and MachineMetrics
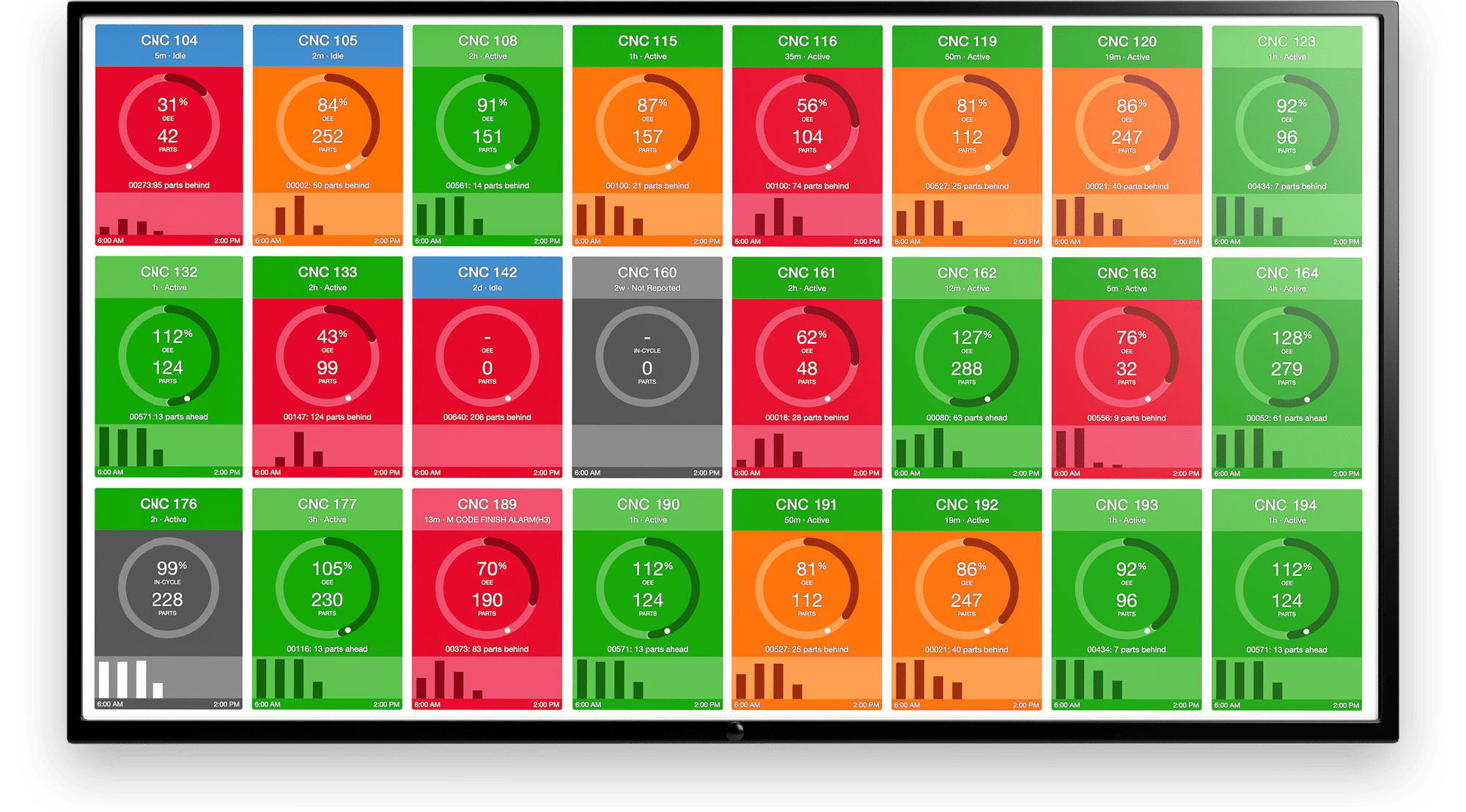
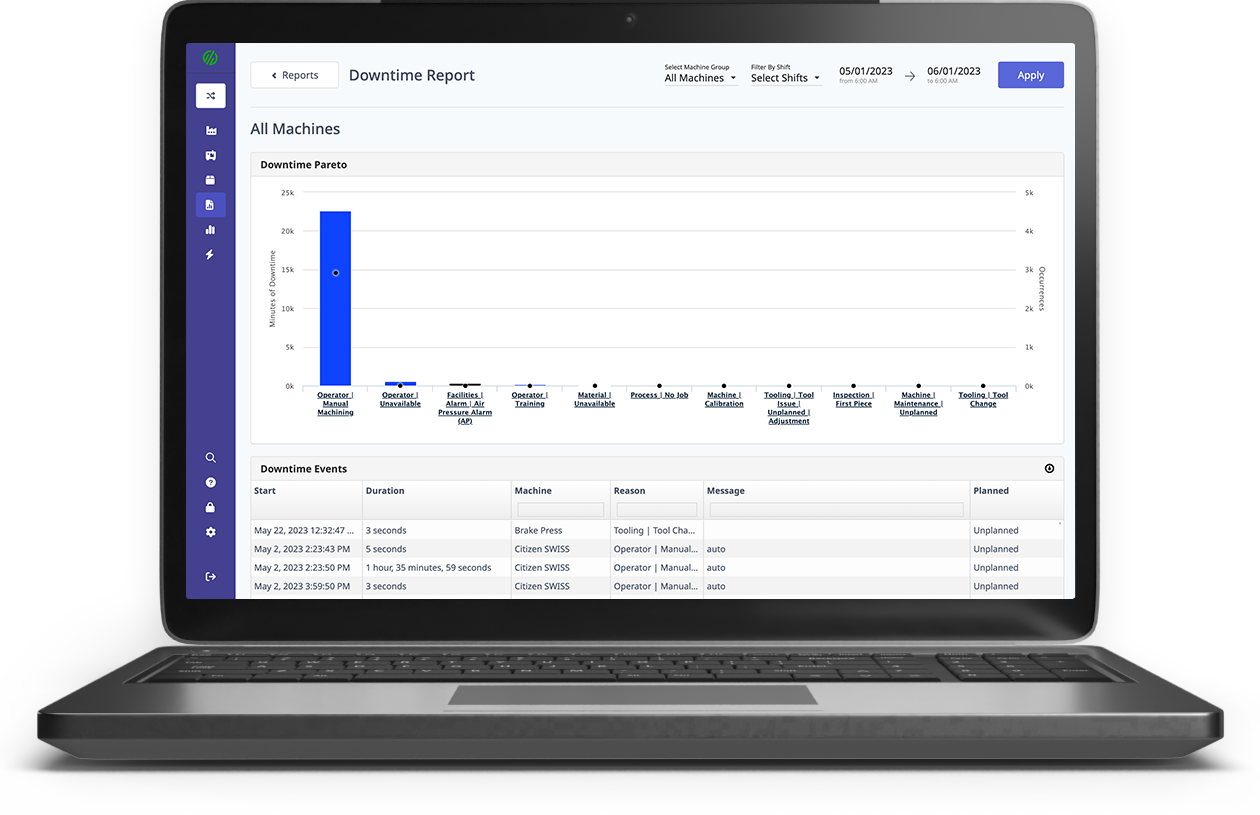
OEMs interested in EaaS will have to leverage the cloud and IoT platforms to drive data collection and processing initiatives. The MachineMetrics Platform provides a plug and play solution for collecting and aggregating machine data.
With MachineMetrics, every aspect of an equipment’s operation cycle is captured, stored, and categorized. A case study with BC Machining highlights how quick and streamlined the process of integrating equipment to the MachineMetrics platform is. In this scenario, 11 computer numerical control (CNC) machines were plugged onto the platform within a month to begin the data collection process. The capital expenditure to set up the data collection system was less than $2000.
The collected data and the corresponding analytics led to a 10% increase in productivity within the first two months. You can learn more about how the MachineMetrics Platform supports Equipment-as-a-Service initiatives for OEMs here.

.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)



.gif)






Comments