Today's machine monitoring systems are highly scalable, simple to deploy, and often plug-and-play in nature.
In the article below, we explore how MachineMetrics collects and transforms data into actionable insights to drive rapid and continuous value for manufacturing operations.
Connecting Equipment
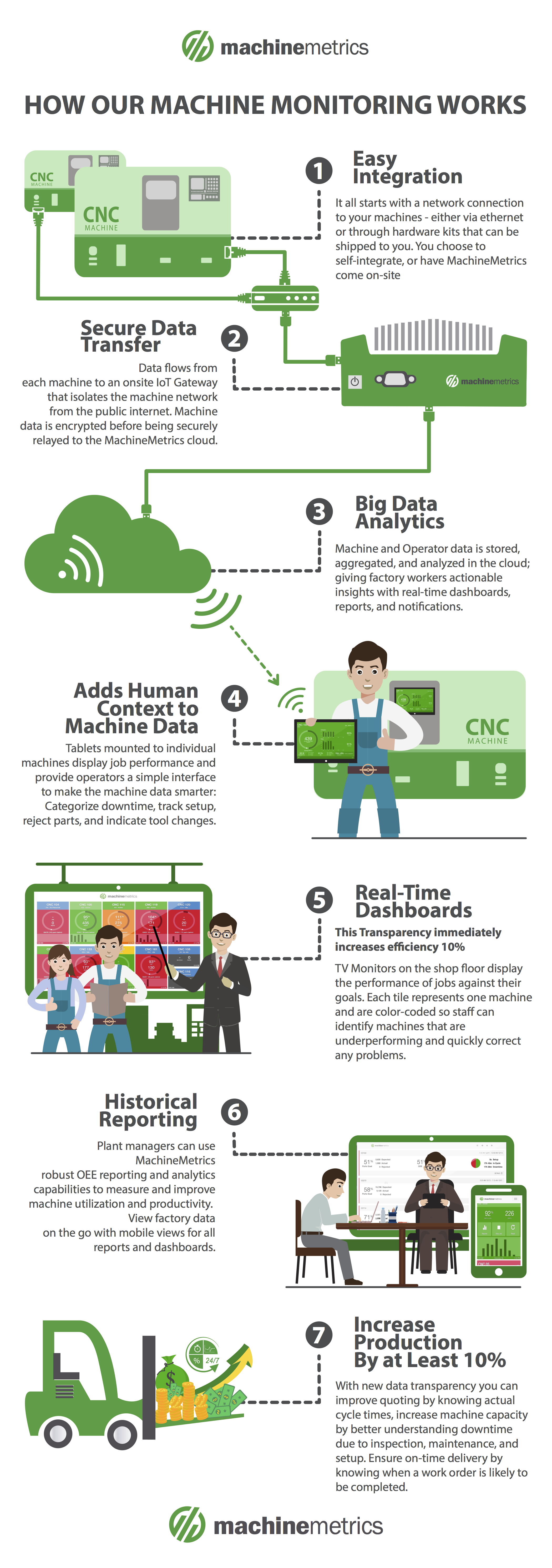
Machine monitoring begins with the capture, transformation, and contextualization of machine data at the edge. MachineMetrics supports various PLC protocols to enable connectivity across any type of equipment on the shop floor. For simple assets, or those without a standard connectivity method, sensors can also be used.
Standard protocols supported include:
- OPC-UA
- MTConnect
- Modbus TCP
- Ethernet/IP
Custom Machine Control Connectors built include:
- FANUC FOCAS
- Heidenhain iTNC530 and iTNC640
- Citizen M700
- Mitsubishi M70/M80
- Brother Speedio
- HAAS Serial
- Matsuura CNC
- Universal Robots
Real-Time Decision-Making at the Edge
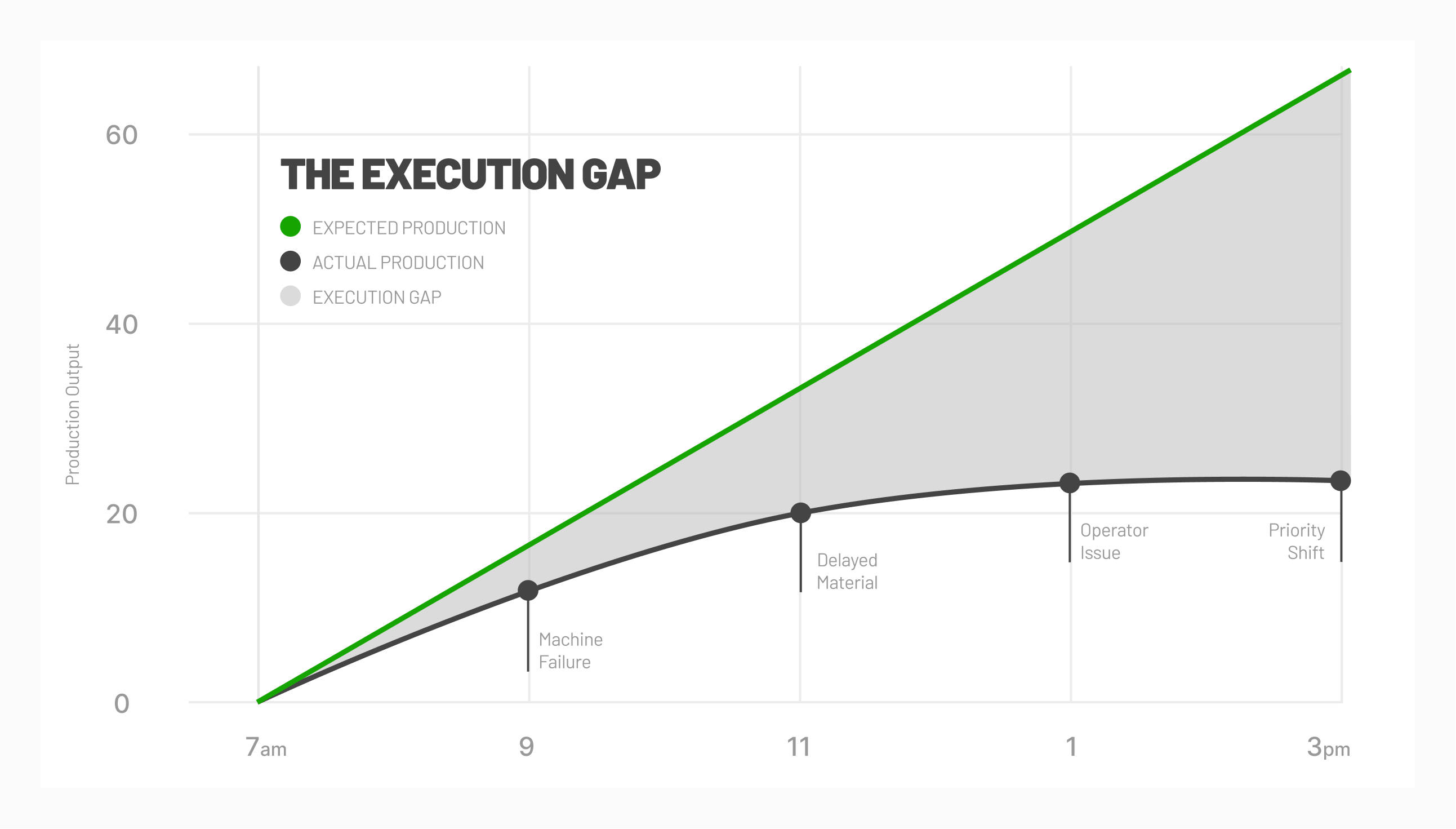
At the edge, machine monitoring propagates real-time data to make instantaneous decisions without the bandwidth costs that come with sending that data to the cloud. In this way, automation can be enabled with real-time production data, allowing manufacturers to avoid critical failures and increase equipment uptime.
The edge offers a number of benefits to manufacturers but remains only one piece of a complete infrastructure. MachineMetrics incorporates both edge and cloud as part of a hybrid structure. This structure provides real-time decision-making, while also offering a data platform that can enable deep analysis and fuel applications that deliver value across a variety of use cases.
Data Platform, Features, and Continuous Value Creation
Once data is secured and encrypted, it is sent to a database or data platform (either on-premise or in the cloud). For discrete manufacturing equipment monitoring, the solution needs to be designed for machine data, and the high volume of machine condition and sensor data associated with machine tools.
MachineMetrics also supports operational data. Operational data is information concerning the operation of the machine, such as the machine’s activity (in production, setup, maintenance), the part number being manufactured, the operator responsible for the machine, and quality data. Layering operational data on top of machine condition data unlocks the opportunity to drive vertical, rapid value-driving use cases.
Once all data is centralized in the data platform, it can then be leveraged in a number of ways for various data consumers. The first way is through automated data triggers based on machine conditions and activities. For example, a machine condition can be configured to send a notification to an operator when a machine’s override exceeds 100 for 2 minutes.
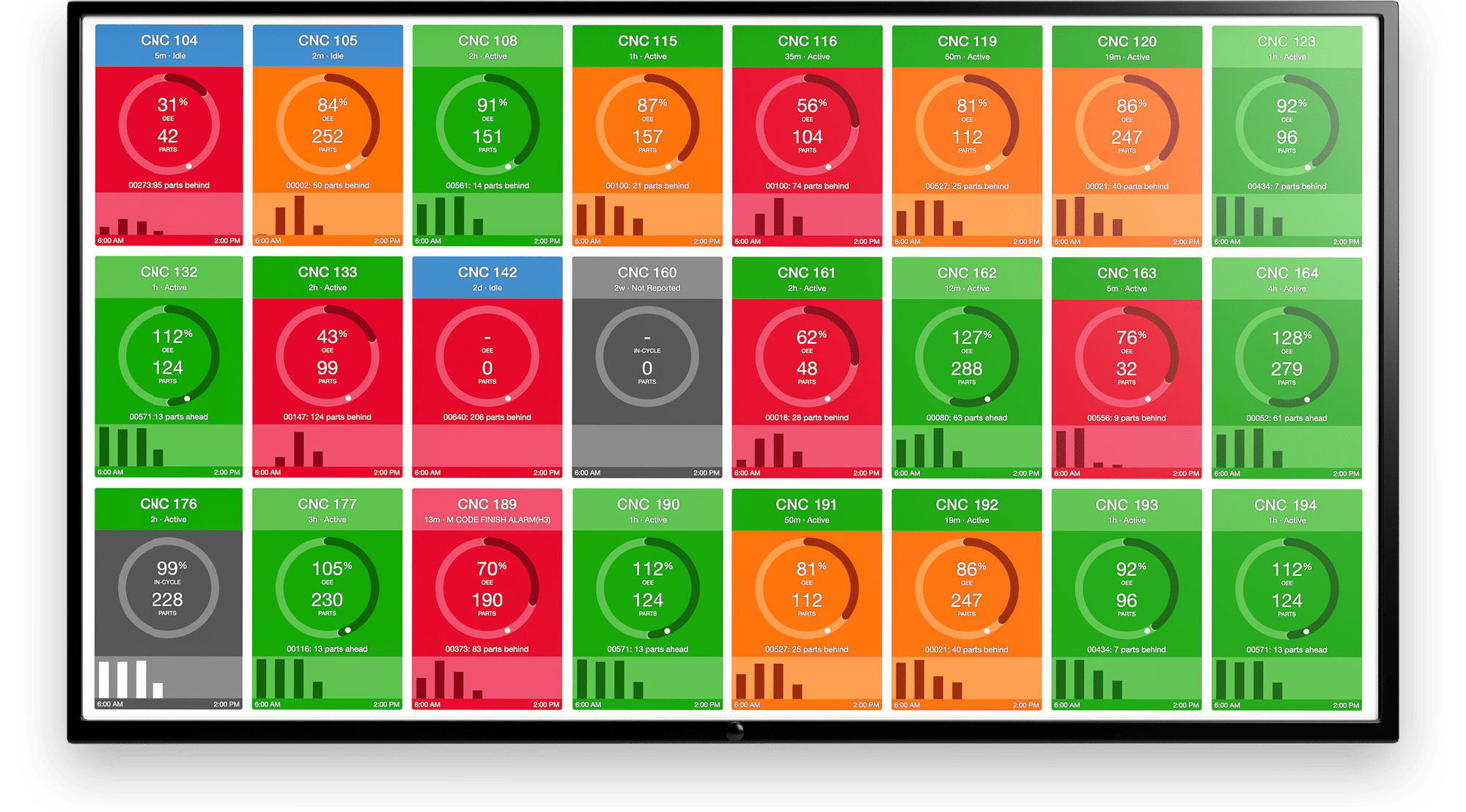
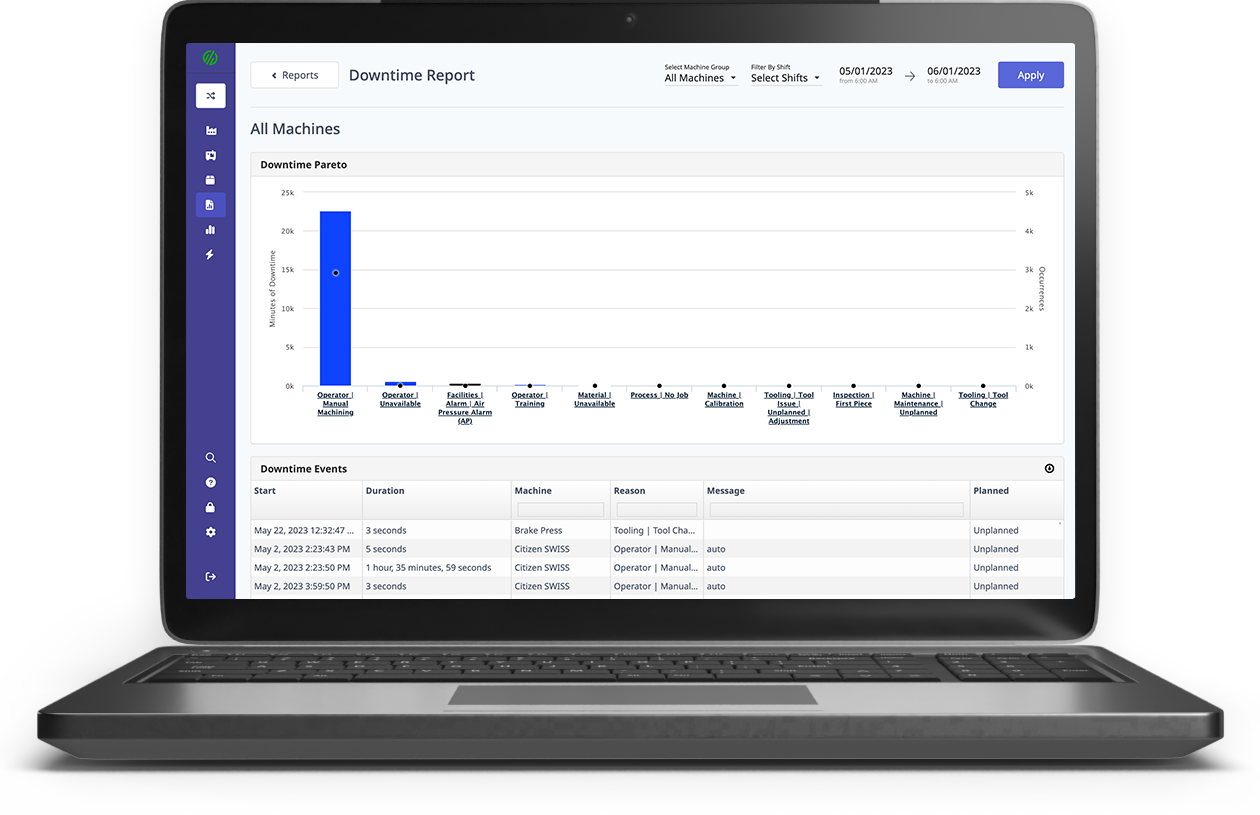
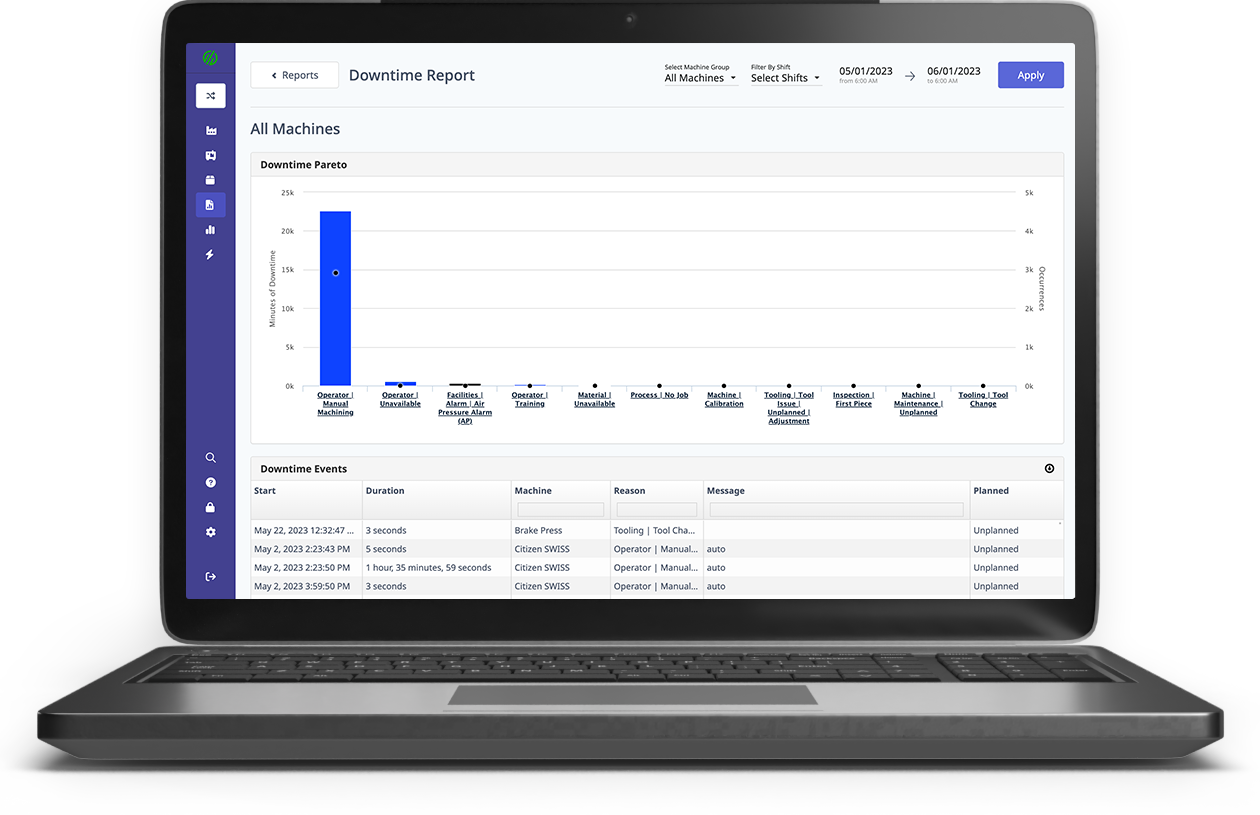
Users can also take advantage of a robust ecosystem of pre-built features that come out of the box in platforms like MachineMetrics and can be immediately visualized for quick decision-making by individuals. More standard features include real-time dashboards, job/quality performance reporting, and bottleneck analytics to give workers the insights needed to make proactive decisions.
Some systems, such as MachineMetrics, may also include operator features where operators can add input to enhance the value of the data and communicate with their teammates in real-time. These use cases may include categorizing downtime, tracking setups as they occur, rejecting off-quality pieces, and annotating tool changes.
Of course, if your monitoring platform is cloud-based, the data, reports, visualizations, etc. can be accessed anywhere, anytime as long as an individual has access to an internet-enabled device.
The value of an interoperable system like MachineMetrics is that the machine data can be extended to support use cases across the enterprise. This accurate production data can optimize processes across maintenance, quality, scheduling, finance, HR, and more. In this regard, machine monitoring can go far beyond the simple monitoring of utilization and downtime.
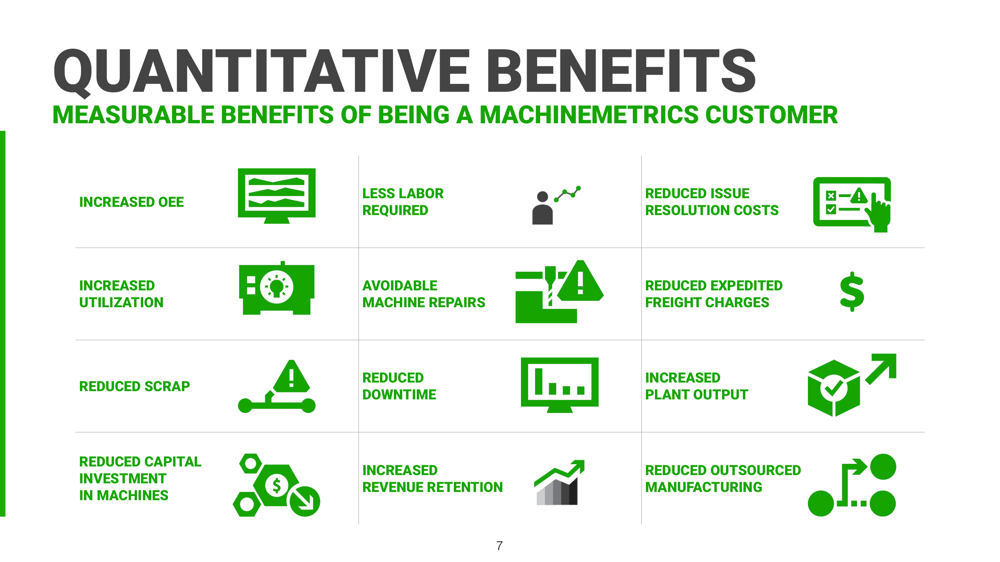
Quantitative Benefits
With limitless use cases for leveraging machine data, here are just a few of the top benefits manufacturers experience when deploying a machine monitoring solution. For a full review of the top use cases and value driven from machine monitoring, read the Top Use Cases eBook.
Want to See the Platform in Action?
Download the Infographic
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)









Comments