Key Takeaways:
- Cycle time measures the duration needed to complete one production cycle, directly impacting efficiency and output.
- Reducing cycle time can lead to higher productivity and lower production costs.
- Analyzing and optimizing cycle time is key to improving manufacturing processes and meeting production goals.
When it comes to production environments, it's always a question of how much can be produced, how quickly, and at what cost. At the end of the day, how efficient are we?
Cycle time is one of the best measures we can use to analyze the efficiency of a production process and allows managers to drill down to better understand how effective a given process, operator, machine, or job run is.
What is Cycle Time?
Cycle time is the total time a production team spends on producing a single unit.
Time measurements are the backbone of a manufacturing business. And cycle time is a crucial KPI that enables companies to schedule accurately, order materials, and set production and inventory budgets.
Cycle time varies dramatically between manufacturers due to the differences in process, the types of products being developed, and what factors they include in the measurement of a "cycle."
Users must be clear on what is included in the time calculation, and it must be stated whether the measurement is tracking a process or unit. It must also be clear if the calculation includes wait or hold times.
For example, if cycle times are calculated to reflect the time for machines to complete the entire set of operations for a single piece, it’s referred to as machine cycle time.
If the cycle time is calculated to reflect the load and unload time between operations, it’s known as effective cycle time.
Why is it Important to Measure Cycle Time?
As a critical key performance indicator, cycle time is an “all-in” number. It measures a product from its beginnings as a raw material or component through its completion as a finished good. And in between, cycle time can reveal a lot about processes and operations.
Cycle time captures all operational tasks required to complete a production unit. This time includes processing, where production equipment meets value-added tasks to produce a unit. Cycle time captures non-production time variables as well, including upstream, midstream, and downtime. Queue time related to upstream delays is also factored in.
Cycle time also accounts for time spent on non-direct labor tasks such as inspection for quality defects and compliance. While core production tasks are essential, many non-production tasks are critical to finished goods, and the time spent on their completion is vital.
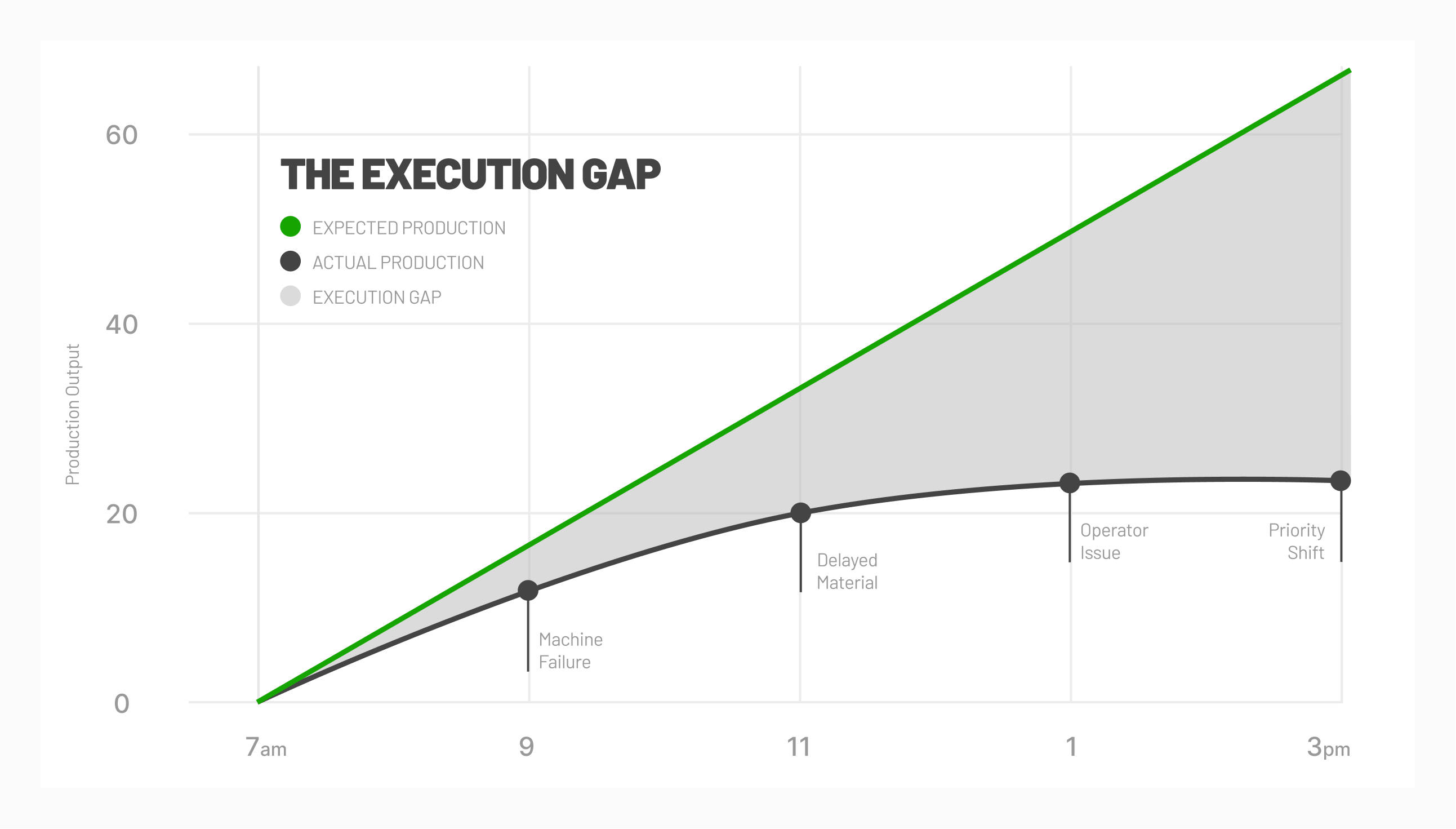
Measuring cycle time allows decision-makers to craft continuous improvement efforts for all aspects of production. The ability to break down the critical components of cycle time enables multiple process improvements to work in parallel, not just in production.
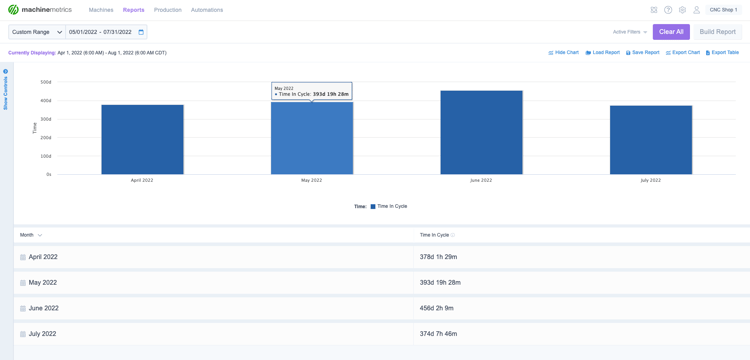
For example, if a company has 35 minutes of production, 15 minutes of inspection, and 10 minutes of waiting, three process improvement projects can take place simultaneously. Focusing only on production may shave five minutes off production time, but three projects that shave five minutes each cumulatively account for a 25% reduction in cycle time.
The key to understanding all elements of cycle time is real-time machine data. With real-time machine data analyzed in a cloud-based platform, these improvements are available as actionable insights immediately. Changes can be implemented to reduce cycle time immediately, not after the event has passed.
How Do You Calculate Cycle Time?
Cycle Time Formula
Once the elements of the measurement are determined, the calculation is relatively straightforward. In this case, computing cycle time is the total production time divided by the units produced:
Ct= Pt/Pu
- Ct = Cycle time
- Pt = Net production time
- Pu = Units produced during net production time

The Benefits of Reducing Cycle Time
Because cycle time encompasses all areas of business operations - both directly and indirectly – reducing cycle time has many benefits:
Lower Costs
As cycle time drops, efficiency and productivity rise. Processes such as inspection become faster and more efficient. Revised factory layouts reduce wait and queue time and can push through materials faster.
Cumulatively, these changes lower the cost per unit produced. Individually, labor utilization reduces due to automated processes, and the elimination of waiting time adds money to the bottom line.
Increased Capacity
Manufacturing equipment is expensive, and an optimal ROI is the goal of any company. Returning to the example above, a 25% reduction in cycle time means the company has unlocked more capacity and will be more productive.
As cycle time is reduced, overall equipment effectiveness is increased. This reduction helps produce more jobs with the same resources, ensuring ROI on expensive manufacturing equipment. It also helps executives make informed Capex equipment decisions based on machine data that reduces cycle time.
Plug-and-play Machine Connectivity
Improved Service Levels
Manufacturing improvements often focus inward, but the most important effects center on outward impact. Reduced cycle time means lower lead times and faster delivery to meet customer demand.
When a company reduces lead time and delivers its product faster, new and repeat orders are more likely. Brand reputation is also enhanced. Buyers perceive the company as more responsive to demand and capable of fulfilling it.
Competitive Advantage
Reducing cycle time gives companies a competitive advantage, which comes in two forms. First, as mentioned above, reducing cycle time means that companies reduce lead times by turning around finished goods faster. This reduction can give them a market advantage as the “go-to” source.
Second, reducing cycle time allows companies to reduce lead time and innovate new products faster. With new offerings entering the market more quickly than the competition, companies realize a marketing advantage.
More Efficient Business Processes
With lower cycle time, companies can achieve more efficient business practices. This best-practices mentality leads companies to continue the improvement process across all business practices, not just those in production.
How Do You Reduce Cycle Time?
Several steps can be taken to reduce cycle time. These are best practices in most continuous improvement initiatives and are found in Lean and Six Sigma methodologies:
Begin a Process Map
A process map manually plots the workflow of a part or finished good throughout the process and at individual workstations. Often, inefficiencies, bottlenecks, waiting time, and other problems are "baked in" from legacy procedures or manual data management. Process mapping allows teams to identify and implement improvements.
Calculate Existing Cycle Times
You can't know where to go if you don't know where you are. Even if the calculation is based on manual data, a rough cycle time used as a benchmark will provide the floor upon which to build. This tendency is tied to a company's overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). In companies with manual data management, OEE is unfortunately assumed to be higher than it is.
Eliminate Waste
With a fully mapped process and an understanding of existing cycle time, improvement teams can begin to eliminate wastes that cause low cycle times. Common waste types include:
-
Quality issues where defective goods aren’t caught before completion or must be reworked to first quality
-
Excessive manual paperwork, "travelers," or other error-prone documentation
-
Non-value-added work
-
Overproduction
-
Underproduction
-
WIP staging, internal material transportation, or machine layout
Deploy Standard Work Documentation
Once problems and root causes are identified and an improvement procedure is implemented, it’s essential to keep the process from varying from the new standard and impacting the cycle count.
Standard work formalizes how tasks should be performed. It may include instructions on specific operator order of tasks, motions, communication, and other standards. This documentation must be available to anyone performing a task and should be used to train new workers. This will help keep cycle time low and prevent variance.
Audit Machine Capacity
Most manufacturers have an extensive line of finished goods or parts. They may range from simple to complex. This product mix is in play each day based on customer orders, so machine capacity should be audited in absolute terms and against product complexity.
Do you have enough capacity per machine to make a schedule if it’s heavily weighted toward a large order of the most complex and time-consuming parts? Scheduling must be flexible enough to foresee this and create production schedules that optimize the machine's capabilities against the order position.
The Drawbacks of Manual Tracking to Reduce Cycle Time
Cycle time is a valuable metric in manufacturing, and it’s critical to find a starting point to benchmark current performance and begin improvements. While these tools are important in getting started, true reduction of cycle times requires efficient data tracking, control over the process, and a high degree of organization.
Once underway, the amount of manual data management, analysis, and recording becomes overwhelming. And because these manual processes take time, they cannot be done with the frequency required to continue progress past a certain point.
Such a process is also error-prone. From simple number transposition to missing data to bias, errors can prove costly in an effort to improve cycle time. If this goes on too long, managers no longer gain the insights they need and operators feel overburdened with paperwork and forms, which may lead to higher cycle times.
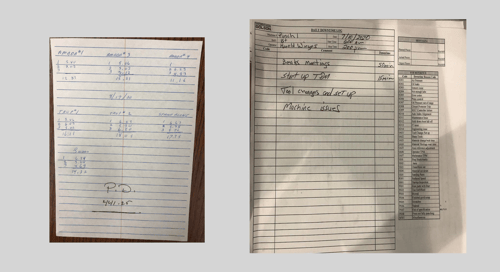 Manual data collection is an error-prone process that hinders continuous improvement initiatives.
Manual data collection is an error-prone process that hinders continuous improvement initiatives.
Automating Data Collection to Reduce Cycle Times
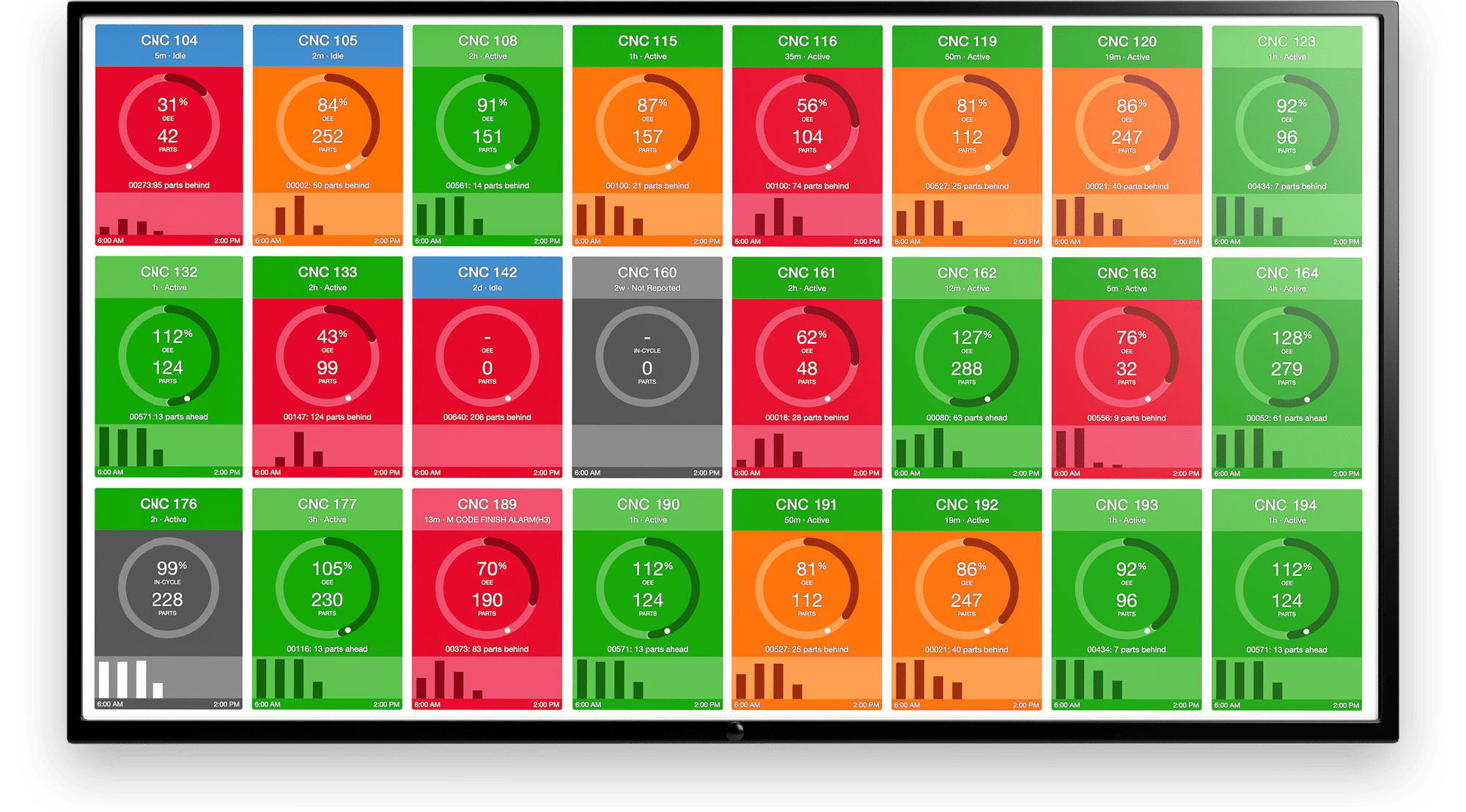
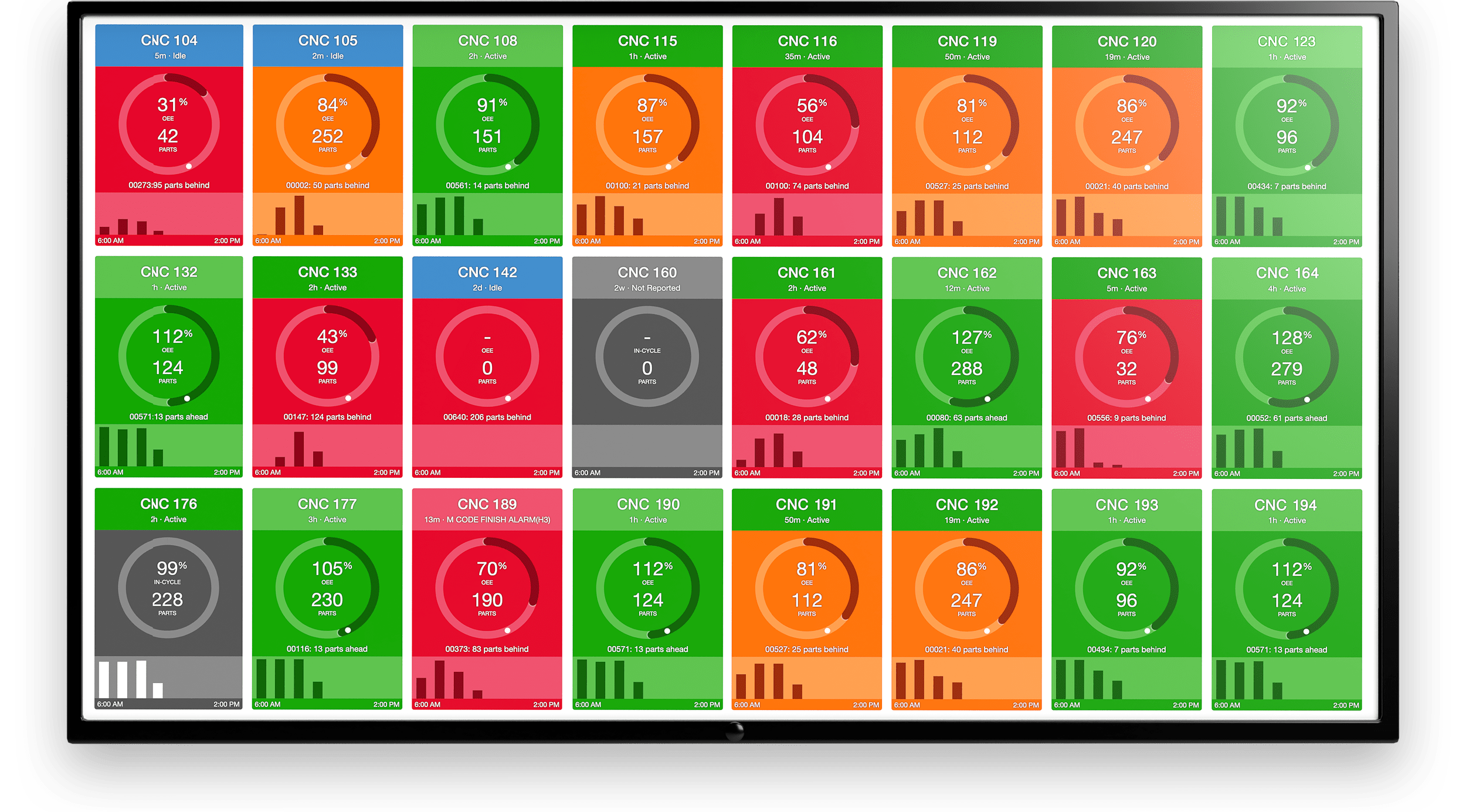
MachineMetrics Machine Data Platform puts your data to work inside a powerful data-driven analytics engine that connects to equipment across the factory floor.
Data is collected to monitor and report exact task times, reasons for downtime, and other critical factors needed to reduce cycle time. By using real-time data from the source, tracking cycle time is automated and manual recording becomes unnecessary. Actionable insights are generated to let you see the results of improvements and dive deeper to achieve continuous improvement.
MachineMetrics also delivers prescriptive and predictive insights to address waste. Because assets and machine components like spindles and sensors are connected at the point of production, quality issues can be addressed as or before they happen.
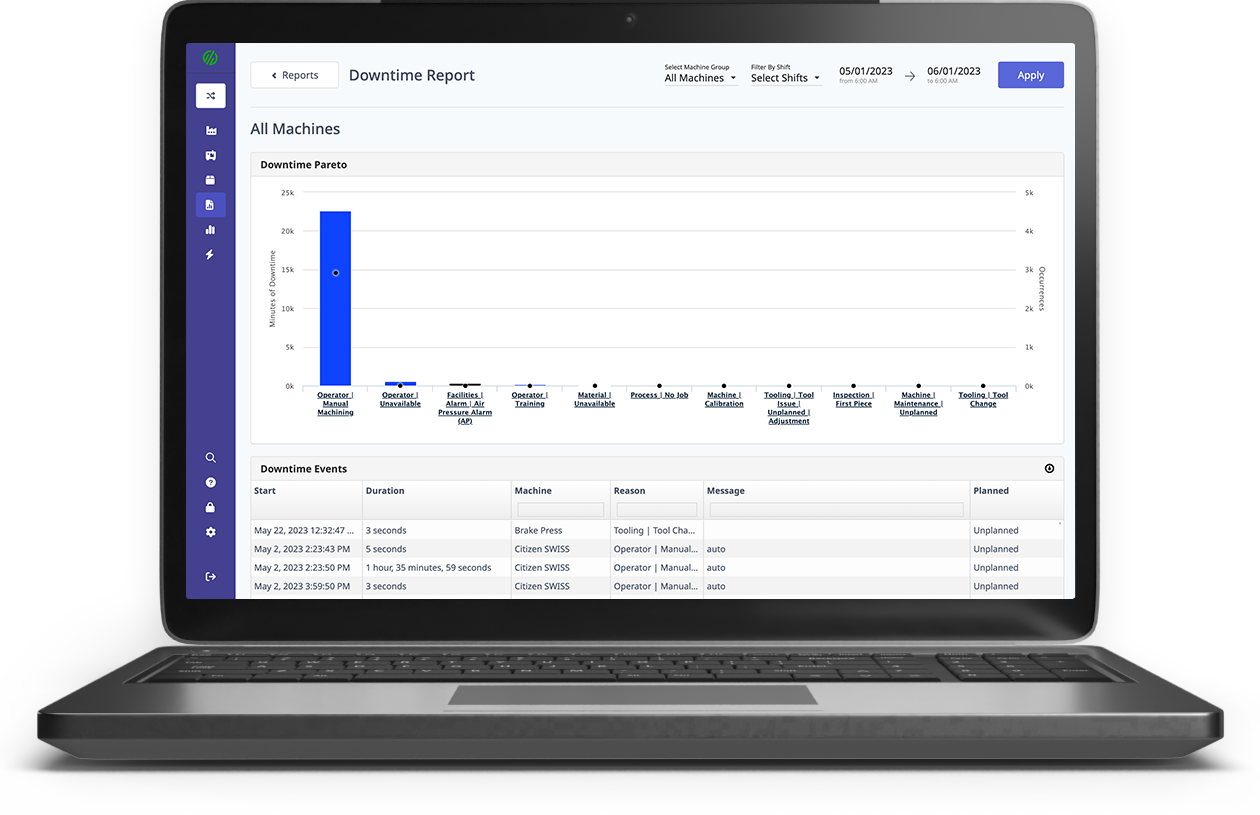
These insights based on actual cycle times also uncover trends that help you identify areas where you can make further changes, such as WIP staging, machine layout, transportation bottlenecks, and more.
MachineMetrics helps manufacturers achieve a more accurate "paperless" production environment. And once improvements are implemented, robust, configurable workflows mean that standard work is digital and at the fingertips of anyone who needs it - in much higher quality.
If you are interested in reducing cycle time to unlock capacity and improve efficiency, we may be able to help. Book some time with our team to learn the impact of a production monitoring platform on your operation.
Reduce Cycle Times Using Machine Data
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)


.gif)






Comments